Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, chemistry, and genetics. It differs from biological computing, a subfield of computer engineering which uses bioengineering to build computers.

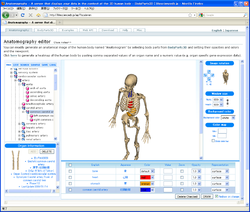
Anthropometry refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various attempts to correlate physical with racial and psychological traits. Anthropometry involves the systematic measurement of the physical properties of the human body, primarily dimensional descriptors of body size and shape. Since commonly used methods and approaches in analysing living standards were not helpful enough, the anthropometric history became very useful for historians in answering questions that interested them.
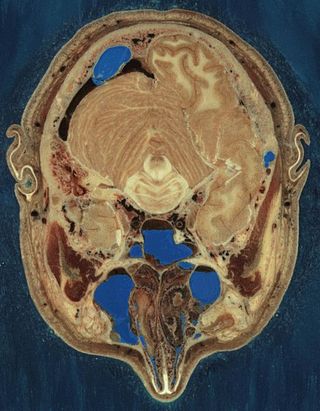
The Visible Human Project is an effort to create a detailed data set of cross-sectional photographs of the human body, in order to facilitate anatomy visualization applications. It is used as a tool for the progression of medical findings, in which these findings link anatomy to its audiences. A male and a female cadaver were cut into thin slices, which were then photographed and digitized. The project is run by the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM) under the direction of Michael J. Ackerman. Planning began in 1986; the data set of the male was completed in November 1994 and the one of the female in November 1995. The project can be viewed today at the NLM in Bethesda, Maryland. There are currently efforts to repeat this project with higher resolution images but only with parts of the body instead of a cadaver.
Poser is a 3D computer graphics program distributed by Bondware. Poser is optimized for the 3D modeling of human figures. By enabling beginners to produce basic animations and digital images, along with the extensive availability of third-party digital 3D models, it has attained much popularity.

Yoshito Okubo is a Japanese professional footballer who most recently played as a forward for Cerezo Osaka. He played for the Japan national team scoring 6 goals in 60 appearances

Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine its size, shape, firmness, or location.

Tarō Asō is a Japanese politician serving as the Vice President of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) since 2021. Asō previously served as Prime Minister of Japan from 2008 to 2009 and as Deputy Prime Minister of Japan and Minister of Finance from 2012 to 2021. He was the longest-serving Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Finance in Japanese history, having previously served as Minister for Foreign Affairs from 2005 to 2007 and as Minister for Internal Affairs and Communications from 2003 to 2005. He leads the Shikōkai faction within the LDP.
Zygote Media Group is a company specializing in 3D human anatomy content and technology. Established in 1994, the company initially focused on creating anatomically accurate 3D human models for the entertainment industry. Over time, Zygote Media Group has transitioned its specialization to the enhanced visualization of human anatomy and life sciences.

Ikuno-ku (生野区) is one of 24 wards of Osaka, Japan. The Tsuruhashi (鶴橋) area of Ikuno-ku is well known for the large number of Koreans, particularly Korean Japanese citizens living there, as well as for its large number of yakiniku restaurants. Many families from Korea have lived in the Tsuruhashi district for three generations or more. Ikuno-ku is located in the southeastern part of Osaka City and is adjacent to Higashiosaka City in the east, Higashinari-ku of Osaka City in the north, Tennoji-ku in the west, and Abeno-ku, Higashisumiyoshi-ku and Hirano-ku in the south.

The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with respect to the main body of the organism. In medical disciplines, all references to a location on or in the body are made based upon the standard anatomical position.
The Foundational Model of Anatomy Ontology (FMA) is a reference ontology for the domain of human anatomy. It is a symbolic representation of the canonical, phenotypic structure of an organism; a spatial-structural ontology of anatomical entities and relations which form the physical organization of an organism at all salient levels of granularity.

The Monster Kid is a shōnen manga and anime series by Fujiko Fujio named after its protagonist. The first series was broadcast on TBS from April 21, 1968 to March 23, 1969. The second series was broadcast on TV Asahi from September 2, 1980 to September 28, 1982. A live-action series was broadcast on Nippon Television and Yomiuri Television from April 17 to June 12, 2010. The 94-episode 1982 iteration was aired around the world, marketed as The Monster Kid, which was the official English title.

MakeHuman is a free and open source 3D computer graphics middleware designed for the prototyping of photorealistic humanoids. It is developed by a community of programmers, artists, and academics interested in 3D character modeling.
Victoria is an articulated 3D female figure developed and sold by Daz 3D. There have been several "generations" of the figure, all bearing the same name.

Kyō Kara Ore Wa!! is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Hiroyuki Nishimori. The manga was initially published in Shogakukan's shōnen manga magazine Shōnen Sunday Zōkan, running monthly from September 1988 to August 1990. The series was then transferred to Weekly Shōnen Sunday and serialized from September 1990 to November 1997. Its chapters were collected in 38 tankōbon volumes. A four-chapter manga sequel, titled Kyō Kara Ore wa!!: Yūsha Sagawa to Ano Futari-hen, was serialized in Shōnen Sunday S from November 2018 to February 2019 and collected in a single tankōbon volume.
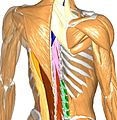
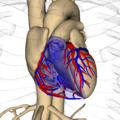
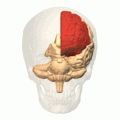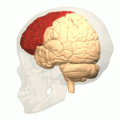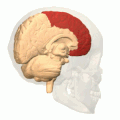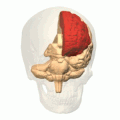
ZygoteBody, formerly Google Body, is a web application by Zygote Media Group that renders manipulable 3D anatomical models of the human body. Several layers, from muscle tissues down to blood vessels, can be removed or made transparent to allow better study of individual body parts. Most of the body parts are labelled and are searchable.

Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a specific-technology or application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in art, printed media, simulators, videos and video games. These images are either static or dynamic. CGI both refers to 2D computer graphics and 3D computer graphics with the purpose of designing characters, virtual worlds, or scenes and special effects. The application of CGI for creating/improving animations is called computer animation, or CGI animation.
Computational human phantoms are models of the human body used in computerized analysis. Since the 1960s, the radiological science community has developed and applied these models for ionizing radiation dosimetry studies. These models have become increasingly accurate with respect to the internal structure of the human body.

Speed Power Gunbike is an action video game for the PlayStation, released exclusively in Japan on April 23, 1998 from publisher Sony Music Entertainment Japan. It is the first game developed by Inti Creates, a group of designers with similar goals and interests who had recently broken off from Capcom. The game was heavily inspired by science fiction anime of the 1980s.

The GigaMesh Software Framework is a free and open-source software for display, editing and visualization of 3D-data typically acquired with structured light or structure from motion.