
Case Black, also known as the Fifth Enemy Offensive in Yugoslav historiography and often identified with its final phase, the Battle of the Sutjeska was a joint attack by the Axis taking place from 15 May to 16 June 1943, which aimed to destroy the main Yugoslav Partisan force, near the Sutjeska river in south-eastern Bosnia. The failure of the offensive marked a turning point for Yugoslavia during World War II. It was also the last major German-Italian joint operation against the partisans.

The 12th Army was a World War II field army of the Wehrmacht.

The 1st Mountain Division was an elite formation of the German Wehrmacht during World War II, and is remembered for its involvement in multiple large-scale war crimes. It was created on 9 April 1938 in Garmisch Partenkirchen from the Mountain Brigade which was itself formed on 1 June 1935. The division consisted mainly of Bavarians and some Austrians.

Gebirgsjäger are the light infantry part of the alpine or mountain troops (Gebirgstruppe) of Germany, Austria and Switzerland. The word Jäger is a characteristic term used for light infantry in German speaking countries.

Operation Rösselsprung was a combined airborne and ground assault by the German XV Mountain Corps and collaborationist forces on the Supreme Headquarters of the Yugoslav Partisans in the Bosnian town of Drvar in the Independent State of Croatia during World War II. It was launched 25 May 1944, with the goal of capturing or killing Partisan leader Marshal Josip Broz Tito and destroying the headquarters, support facilities and co-located Allied military missions. It is associated with the Seventh Enemy Offensive in Yugoslav history, forming part of the Seven Enemy Offensives historiographical framework. The airborne assault itself is also known as the Raid on Drvar.
The IX Waffen Mountain Corps of the SS (Croatian) (German: IX. Waffen-Gebirgskorps der SS (Kroatisches)), later simply IX SS Mountain Corps, was a Waffen-SS corps during World War II. Originally set up to control Croatian and Albanian SS divisions, it also commanded a variety of other German and Hungarian units of the Waffen-SS. It saw action on the Eastern Front between July 1944 and January 1945 when it was virtually destroyed during the Siege of Budapest.

The 7th SS Volunteer Mountain Division "Prinz Eugen", initially named the SS-Volunteer Division Prinz Eugen, was a mountain infantry division of the Waffen-SS, an armed branch of the German Nazi Party that served alongside but was never formally part of the Wehrmacht during World War II. At the post-war Nuremberg trials, the Waffen-SS was declared to be a criminal organisation due to its major involvement in war crimes and crimes against humanity. From 1942 to 1945, the division fought a counter-insurgency campaign against communist-led Yugoslav Partisan resistance forces in occupied Yugoslavia. It was formed in 1941 from both Reich Germans and Volksdeutsche – ethnic German volunteers and conscripts from the Banat, Independent State of Croatia, Hungary and Romania. The division surrendered on 11 May 1945 to Yugoslav Partisan forces.

World War II in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia began on 6 April 1941, when the country was invaded and swiftly conquered by Axis forces and partitioned among Germany, Italy, Hungary, Bulgaria and their client regimes. Shortly after Germany attacked the USSR on 22 June 1941, the communist-led republican Yugoslav Partisans, on orders from Moscow, launched a guerrilla liberation war fighting against the Axis forces and their locally established puppet regimes, including the Axis-allied Independent State of Croatia (NDH) and the Government of National Salvation in the German-occupied territory of Serbia. This was dubbed the National Liberation War and Socialist Revolution in post-war Yugoslav communist historiography. Simultaneously, a multi-side civil war was waged between the Yugoslav communist Partisans, the Serbian royalist Chetniks, the Axis-allied Croatian Ustaše and Home Guard, Serbian Volunteer Corps and State Guard, Slovene Home Guard, as well as Nazi-allied Russian Protective Corps troops.

The XV SS Cossack Cavalry Corps was a World War II cavalry corps of the Waffen-SS, the armed wing of the German Nazi Party, primarily recruited from Cossacks.

The 1st Cossack Cavalry Division was a Russian Cossack division of the German Army that served during World War II. It was created on the Eastern Front mostly with Don Cossacks already serving in the Wehrmacht, those who escaped from the advancing Red Army and Soviet POWs. In 1944, the division was transferred to the Waffen SS, becoming part of the XV SS Cossack Cavalry Corps, established in February 1945. At the end of the war, the unit ceased to exist.
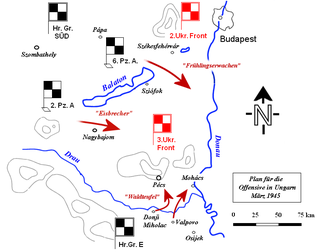
The Battle of the Transdanubian Hills was a defensive operation of the Bulgarian First Army during Bulgaria's participation in World War II against German Wehrmacht forces, who were trying to capture the north bank of the Drava river as part of Operation Spring Awakening.

The Belgrade offensive or the Belgrade strategic offensive operation was a military operation during World War II in Yugoslavia in which Belgrade was liberated from the German Wehrmacht through the joint efforts of the Soviet Red Army, Yugoslav Partisans, and the Bulgarian Army. Soviet forces and local militias launched separate but loosely cooperative operations that undermined German control of Belgrade and ultimately forced a retreat. Martial planning was coordinated evenly among command leaders, and the operation was largely enabled through tactical cooperation between Josip Broz Tito and Joseph Stalin that began in September 1944. These martial provisions allowed Bulgarian forces to engage in operations throughout Yugoslav territory, which furthered tactical success while increasing diplomatic friction.
Army Group F was a strategic command formation of the Wehrmacht during the Second World War. The commander of Army Group F served also as the Oberbefehlshaber Südost.

114th Jäger Division was a light infantry division of the German Army in World War II. It was formed in April 1943, following the reorganization and redesignation of the 714th Infantry Division. The 714th Division had been formed in May 1941, and transferred to Yugoslavia to conduct anti-partisan and Internal security operations. It was involved in Operation Delphin which was an anti-partisan operation in Croatia that took place between 15 November and 1 December 1943. The objective of the mission was to destroy the Partisan elements on the Dalmatian islands off central Dalmatia.

117th Jäger Division was a German infantry division of World War II. The division was formed in April 1943 by the reorganization and redesignation of the 717th Infantry Division. The 717th Division had been formed in April 1941. It was transferred to Yugoslavia in May 1941, to conduct anti-Četnik and anti partisan and Internal security operations.

The 118th Jäger Division was a light infantry division of the German Army in World War II. It was formed in April 1943, by the redesignation of the 718th Infantry Division which had itself been formed in April 1941. It was transferred to Yugoslavia in May 1941, to conduct anti partisan and Internal security operations. It took part in the Battle of the Sutjeska in June 1943, and fought partisans in Bosnia before being sent to the Dalmatian coast to guard against Allied landings in the summer of 1944.

The 369th (Croatian) Infantry Division was a legionary division of the German Army (Wehrmacht) during World War II.

The 373rd (Croatian) Infantry Division was a division of the German Army during World War II. It was formed in June 1943 using a brigade from the Home Guard of the Independent State of Croatia with the addition of a German cadre. The division was commanded by Germans down to battalion and even company level in nearly all cases, and was commonly referred to as a "legionnaire division". Originally formed with the intention of service on the Eastern Front, it was used instead for anti-Partisan operations in the territory of the NDH until the end of the war. It fought mainly in the western areas of the NDH, and was involved in the attempt to kill or capture the leader of the Partisans, Josip Broz Tito, in May 1944. Severely depleted by desertion, the division withdrew towards the Reich border in the early months of 1945, eventually surrendering to the Partisans on 10 May 1945 near Brežice in modern-day Slovenia.

The Free Arabian Legion was the collective name of several Nazi German units formed from Arab volunteers from the Middle East, notably Iraq, and North Africa during World War II.
XXXXIX Mountain Corps was a mountain warfare corps of the German Army during World War II.


















