
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) may be more useful when comparing living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the per capita GDP and the same is called Mean Standard of Living.

Per capita income (PCI) or average income measures the average income earned per person in a given area in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a measurement of prices in different countries that uses the prices of specific goods to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currencies. In many cases, PPP produces an inflation rate that is equal to the price of the basket of goods at one location divided by the price of the basket of goods at a different location. The PPP inflation and exchange rate may differ from the market exchange rate because of poverty, tariffs, and other transaction costs.
The world economy or the global economy is the economy of all humans of the world, referring to the global economic system which includes all economic activities which are conducted both within and between nations, including production, consumption, economic management, work in general, exchange of financial values and trade of goods and services. In some contexts, the two terms are distinct "international" or "global economy" being measured separately and distinguished from national economies while the "world economy" is simply an aggregate of the separate countries' measurements. Beyond the minimum standard concerning value in production, use and exchange, the definitions, representations, models and valuations of the world economy vary widely. It is inseparable from the geography and ecology of planet Earth.
Real gross domestic product is a macroeconomic measure of the value of economic output adjusted for price changes. This adjustment transforms the money-value measure, nominal GDP, into an index for quantity of total output. Although GDP is total output, it is primarily useful because it closely approximates the total spending: the sum of consumer spending, investment made by industry, excess of exports over imports, and government spending. Due to inflation, GDP increases and does not actually reflect the true growth in an economy. That is why the GDP must be divided by the inflation rate to get the growth of the real GDP. Different organizations use different types of 'Real GDP' measures, for example, the UNCTAD uses 2005 Constant prices and exchange rates while the FRED uses 2009 constant prices and exchange rates, and recently the World Bank switched from 2005 to 2010 constant prices and exchange rates.
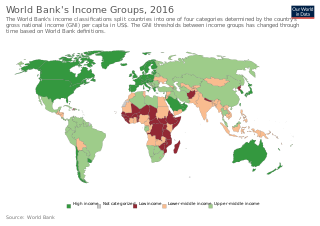
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents, minus income earned in the domestic economy by nonresidents. Comparing GNI to GDP shows the degree to which a nation's GDP represents domestic or international activity. GNI has gradually replaced GNP in international statistics. While being conceptually identical, it is calculated differently. GNI is the basis of calculation of the largest part of contributions to the budget of the European Union. In February 2017, Ireland's GDP became so distorted from the base erosion and profit shifting ("BEPS") tax planning tools of U.S. multinationals, that the Central Bank of Ireland replaced Irish GDP with a new metric, Irish Modified GNI*. In 2017, Irish GDP was 162% of Irish Modified GNI*.
An emerging market is a market that has some characteristics of a developed market, but does not fully meet its standards. This includes markets that may become developed markets in the future or were in the past. The term "frontier market" is used for developing countries with smaller, riskier, or more illiquid capital markets than "emerging". As of 2006, the economies of China and India are considered to be the largest emerging markets. According to The Economist, many people find the term outdated, but no new term has gained traction. Emerging market hedge fund capital reached a record new level in the first quarter of 2011 of $121 billion. The nine largest emerging and developing economies by either nominal or PPP-adjusted GDP are 4 of the 5 BRICS countries along with Indonesia, South Korea, Mexico, Saudi Arabia and Turkey.

A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a nation with a gross national income per capita of US$12,696 or more in 2020, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" and "developed country", the technical definitions of these terms differ. The term "first world" commonly refers to countries that aligned themselves with the U.S. and NATO during the Cold War. Several institutions, such as the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) or International Monetary Fund (IMF), take factors other than high per capita income into account when classifying countries as "developed" or "advanced economies". According to the United Nations, for example, some high-income countries may also be developing countries. The GCC countries, for example, are classified as developing high-income countries. Thus, a high-income country may be classified as either developed or developing. Although the Vatican City is a sovereign state, it is not classified by the World Bank under this definition.
India's per capita net national income or NNI was around 135 thousand rupees in 2020. The per-capita income is a crude indicator of the prosperity of a country. In contrast, the gross national income at constant prices stood at over 128 trillion rupees. The same year, GNI growth rate at constant prices was around 6.6 percent. While GNI and NNI are both indicators for a country's economic performance and welfare, the GNI is related to the GDP or the gross domestic product plus the net receipts from abroad, including wages and salaries, property income, net taxes and subsidies receivable from abroad. On the other hand, the NNI of a country is equal to its GNI net of depreciation.

This article includes a list of China's historical gross domestic product (GDP) values, the market value of all final goods and services produced by a nation in a given year. The GDP dollar estimates presented here are either calculated at market or government official exchange rates (nominal), or derived from purchasing power parity (PPP) calculations. This article also includes historical GDP growth.




