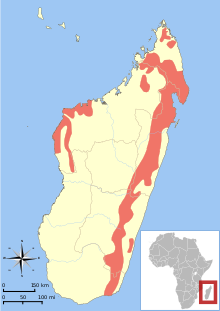
The Indriidae are a family of strepsirrhine primates. They are medium- to large-sized lemurs, with only four teeth in the toothcomb instead of the usual six. Indriids, like all lemurs, live exclusively on the island of Madagascar.

Daubentonia is the sole genus of the Daubentoniidae, a family of lemuroid primate native to much of Madagascar.

The indri, also called the babakoto, is one of the largest living lemurs, with a head-body length of about 64–72 cm and a weight of between 6 and 9.5 kg. It has a black and white coat and maintains an upright posture when climbing or clinging. It is monogamous and lives in small family groups, moving through the canopy, and is herbivorous, feeding mainly on leaves but also seeds, fruits, and flowers. The groups are quite vocal, communicating with other groups by singing, roaring and other vocalisations. Besides humans, it is the only mammal found that can use rhythm.

Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini is a suborder of primates that includes the lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Africa, and the lorises from India and southeast Asia. Collectively they are referred to as strepsirrhines. Also belonging to the suborder are the extinct adapiform primates which thrived during the Eocene in Europe, North America, and Asia, but disappeared from most of the Northern Hemisphere as the climate cooled. Adapiforms are sometimes referred to as being "lemur-like", although the diversity of both lemurs and adapiforms does not support this comparison.

Lemurs are wet-nosed primates of the superfamily Lemuroidea, divided into 8 families and consisting of 15 genera and around 100 existing species. They are endemic to the island of Madagascar. Most existing lemurs are small, have a pointed snout, large eyes, and a long tail. They chiefly live in trees and are active at night.

The ring-tailed lemur is a medium- to larger-sized strepsirrhine (wet-nosed) primate and the most internationally recognized lemur species, owing to its long, black-and-white, ringed tail. It belongs to Lemuridae, one of five lemur families, and is the only member of the Lemur genus. Like all lemurs, it is endemic to the island of Madagascar, where it is endangered. Known locally in Malagasy as maky or hira, it ranges from gallery forests to spiny scrub in the southern regions of the island. It is omnivorous, as well as the most adapted to living terrestrially of the extant lemurs.

The gray mouse lemur, grey mouse lemur or lesser mouse lemur is a small lemur, a type of strepsirrhine primate, found only on the island of Madagascar. Weighing 58 to 67 grams, it is the largest of the mouse lemurs, a group that includes the smallest primates in the world. The species is named for its mouse-like size and coloration and is known locally as tsidy, koitsiky, titilivaha, pondiky, and vakiandry. The gray mouse lemur and all other mouse lemurs are considered cryptic species, as they are nearly indistinguishable from each other by appearance. For this reason, the gray mouse lemur was considered the only mouse lemur species for decades until more recent studies began to distinguish between the species.

Chiromyiformes is an infraorder of strepsirrhine primates that includes the aye-aye from Madagascar and its extinct relatives.

The ruffed lemurs of the genus Varecia are strepsirrhine primates and are the largest extant lemurs within the family Lemuridae. Like all living lemurs, they are found only on the island of Madagascar. Formerly considered to be a monotypic genus, two species are now recognized: the black-and-white ruffed lemur, with its three subspecies, and the red ruffed lemur.

The giant mouse lemurs are members of the strepsirrhine primate genus Mirza. Two species have been formally described; the northern giant mouse lemur and Coquerel's giant mouse lemur. Like all other lemurs, they are native to Madagascar, where they are found in the western dry deciduous forests and further to the north in the Sambirano Valley and Sahamalaza Peninsula. First described in 1867 as a single species, they were grouped with mouse lemurs and dwarf lemurs. In 1870, British zoologist John Edward Gray assigned them to their own genus, Mirza. The classification was not widely accepted until the 1990s, which followed the revival of the genus by American paleoanthropologist Ian Tattersall in 1982. In 2005, the northern population was declared a new species, and in 2010, the World Wide Fund for Nature announced that a southwestern population might also be a new species.

Ankarana Special Reserve is a protected area in northern Madagascar created in 1956. It is a small, partially vegetated plateau composed of 150-million-year-old middle Jurassic limestone. With an average annual rainfall of about 2,000 millimetres (79 in), the underlying rocks have been eroded to produce caves and feed subterranean rivers—a karst topography. The rugged relief and the dense vegetation have helped protect the region from human intrusion.

Coquerel's sifaka is a diurnal, medium-sized lemur of the sifaka genus Propithecus. It is native to northwest Madagascar. Coquerel's sifaka was once considered to be a subspecies of Verreaux's sifaka, but was eventually granted full species level, and is listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List due to habitat loss and hunting. In popular culture, it is known for being the species of the title character in the children's TV show Zoboomafoo. The species was named after French entomologist Charles Coquerel.

Fork-marked lemurs or fork-crowned lemurs are strepsirrhine primates; the four species comprise the genus Phaner. Like all lemurs, they are native to Madagascar, where they are found only in the west, north, and east sides of the island. They are named for the two black stripes which run up from the eyes, converge on the top of the head, and run down the back as a single black stripe. They were originally placed in the genus Lemur in 1839, later moved between the genera Cheirogaleus and Microcebus, and given their own genus in 1870 by John Edward Gray. Only one species was recognized, until three subspecies described in 1991 were promoted to species status in 2001. New species may yet be identified, particularly in northeast Madagascar.

The collared brown lemur, also known as the red-collared brown lemur or red-collared lemur, is a medium-sized strepsirrhine primate and one of twelve species of brown lemur in the family Lemuridae. It is only found in south-eastern Madagascar. Like most species of lemur, it is arboreal, moving quadrupedally and occasionally leaping from tree to tree. Like other brown lemurs, this species is cathemeral, lives in social groups, primarily eats fruit, exhibits sexual dichromatism, and does not demonstrate female dominance. The species is listed as Endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and is threatened primarily by habitat loss.

Lemurs, primates belonging to the suborder Strepsirrhini which branched off from other primates less than 63 million years ago, evolved on the island of Madagascar, for at least 40 million years. They share some traits with the most basal primates, and thus are often confused as being ancestral to modern monkeys, apes, and humans. Instead, they merely resemble ancestral primates.

Subfossil lemurs are lemurs from Madagascar that are represented by recent (subfossil) remains dating from nearly 26,000 years ago to approximately 560 years ago. They include both extant and extinct species, although the term more frequently refers to the extinct giant lemurs. The diversity of subfossil lemur communities was greater than that of present-day lemur communities, ranging to as high as 20 or more species per location, compared with 10 to 12 species today. Extinct species are estimated to have ranged in size from slightly over 10 kg (22 lb) to roughly 160 kg (350 lb). Even the subfossil remains of living species are larger and more robust than the skeletal remains of modern specimens. The subfossil sites found around most of the island demonstrate that most giant lemurs had wide distributions and that ranges of living species have contracted significantly since the arrival of humans.

Milne-Edwards's sifaka, or Milne-Edwards's simpona, is a large arboreal, diurnal lemur endemic to the eastern coastal rainforest of Madagascar. Milne-Edwards's sifaka is characterized by a black body with a light-colored "saddle" on the lower part of its back. It is closely related to the diademed sifaka, and was until recently considered a subspecies of it. Like all sifakas, it is a primate in the family Indriidae.

Lemurs were first classified in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus, and the taxonomy remains controversial today, with approximately 70 to 100 species and subspecies recognized, depending on how the term "species" is defined. Having undergone their own independent evolution on Madagascar, lemurs have diversified to fill many ecological niches normally filled by other types of mammals. They include the smallest primates in the world, and once included some of the largest. Since the arrival of humans approximately 2,000 years ago, lemurs have become restricted to 10% of the island, or approximately 60,000 square kilometers (23,000 sq mi), and many face extinction. Concerns over lemur conservation have affected lemur taxonomy, since distinct species receive increased conservation attention compared to subspecies.
Plesiopithecus is an extinct genus of early strepsirrhine primate from the late Eocene.