
In biochemistry, a kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. This transesterification produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group. These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis.
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades.
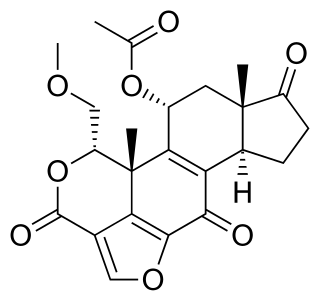
Wortmannin, a steroid metabolite of the fungi Penicillium funiculosum, Talaromyces wortmannii, is a non-specific, covalent inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). It has an in vitro inhibitory concentration (IC50) of around 5 nM, making it a more potent inhibitor than LY294002, another commonly used PI3K inhibitor. It displays a similar potency in vitro for the class I, II, and III PI3K members although it can also inhibit other PI3K-related enzymes such as mTOR, DNA-PKcs, some phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) at high concentrations Wortmannin has also been reported to inhibit members of the polo-like kinase family with IC50 in the same range as for PI3K. The half-life of wortmannin in tissue culture is about 10 minutes due to the presence of the highly reactive C20 carbon that is also responsible for its ability to covalently inactivate PI3K. Wortmannin is a commonly used cell biology reagent that has been used previously in research to inhibit DNA repair, receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell proliferation.

Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as Akt, is the collective name of a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that play key roles in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription, and cell migration.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer.

Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform also known as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta isoform or p110δ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3CD gene.
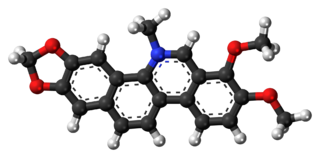
Chelerythrine is a benzophenanthridine alkaloid present in the plant Chelidonium majus. It is a potent, selective, and cell-permeable protein kinase C inhibitor in vitro. And an efficacious antagonist of G-protein-coupled CB1 receptors. This molecule also exhibits anticancer qualities and it has served as a base for many potential novel drugs against cancer. Structurally, this molecule has two distinct conformations, one being a positively charged iminium form, and the other being an uncharged form, a pseudo-base.

Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase is a kinase enzyme which acts to inactivate the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase by phosphorylating it using ATP.
The PHLPP isoforms are a pair of protein phosphatases, PHLPP1 and PHLPP2, that are important regulators of Akt serine-threonine kinases and conventional/novel protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms. PHLPP may act as a tumor suppressor in several types of cancer due to its ability to block growth factor-induced signaling in cancer cells.

Protein kinase C, zeta (PKCζ), also known as PRKCZ, is a protein in humans that is encoded by the PRKCZ gene. The PRKCZ gene encodes at least two alternative transcripts, the full-length PKCζ and an N-terminal truncated form PKMζ. PKMζ is thought to be responsible for maintaining long-term memories in the brain. The importance of PKCζ in the creation and maintenance of long-term potentiation was first described by Todd Sacktor and his colleagues at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center in 1993.

Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1 (S6K1), also known as p70S6 kinase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPS6KB1 gene. It is a serine/threonine kinase that acts downstream of PIP3 and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 in the PI3 kinase pathway. As the name suggests, its target substrate is the S6 ribosomal protein. Phosphorylation of S6 induces protein synthesis at the ribosome.

Protein kinase C iota type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCI gene.

Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 (PDK2) also known as pyruvate dehydrogenase lipoamide kinase isozyme 2, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDK2 gene. PDK2 is an isozyme of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 is an enzyme that in humans and Strongylocentrotus purpuratus is encoded by the PKN2 gene.

PIKfyve, a FYVE finger-containing phosphoinositide kinase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIKFYVE gene.
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K and Akt.

In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the PDPK1 gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas.

BIM-1 and the related compounds BIM-2, BIM-3, and BIM-8 are bisindolylmaleimide-based protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors. These inhibitors also inhibit PDK1 explaining the higher inhibitory potential of LY33331 compared to the other BIM compounds a bisindolylmaleimide inhibitor toward PDK1.
c-Met inhibitors are a class of small molecules that inhibit the enzymatic activity of the c-Met tyrosine kinase, the receptor of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF). These inhibitors may have therapeutic application in the treatment of various types of cancers.
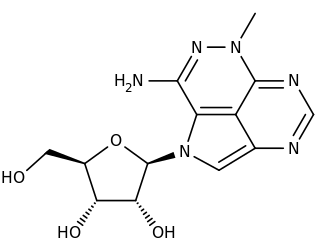
Triciribine is a cancer drug which was first synthesized in the 1970s and studied clinically in the 1980s and 1990s without success. Following the discovery in the early 2000s that the drug would be effective against tumours with hyperactivated Akt, it is now again under consideration in a variety of cancers. As PTX-200, the drug is currently in two early stage clinical trials in breast cancer and ovarian cancer being conducted by the small molecule drug development company Prescient Therapeutics.














