Related Research Articles

Najd is the central region of Saudi Arabia, in which about a third of the country's modern population resides. It is the home of the House of Saud, from which it pursued unification with Hejaz since the time of the Emirate of Diriyah.
Kahlan was one of the main tribal confederations of Saba' in Ancient Yemen. They are descended from Kahlan bin Saba bin Yishjab bin Yarub bin Qahtan.

The Ghassanids, also called the Jafnids, were an Arab tribe which founded a kingdom which was in place from the third century to the seventh century in the area of the Levant and northern Arabia. They emigrated from South Arabia in the early third century to the Levant. Some merged with Hellenized Christian communities, converting to Christianity in the first few centuries, while others may have already been Christians before emigrating north to escape religious persecution.

The Himyarite Kingdom was a polity in the southern highlands of Yemen, as well as the name of the region which it claimed. Until 110 BCE, it was integrated into the Qatabanian kingdom, afterwards being recognized as an independent kingdom. According to classical sources, their capital was the ancient city of Zafar, relatively near the modern-day city of Sana'a. Himyarite power eventually shifted to Sana'a as the population increased in the fifth century. After the establishment of their kingdom, it was ruled by kings from dhū-Raydān tribe. The kingdom was named Raydān.

The tribe of Shammar is a tribal Arab Qahtanite confederation, descended from the Tayy, which migrated into the northern Arabian Peninsula from Yemen in the second century. It is the largest branch of the Tayy, and one of the largest and most influential Arab tribes. The historical and traditional seat of the tribe's leadership is in the city of Ḥaʼil in what was the Emirate of Jabal Shammar in what is now Saudi Arabia. In its "golden age", around 1850, the Shammar ruled much of central and northern Arabia from Riyadh to the frontiers of Syria and the vast area of Upper Mesopotamia.
The Azd, or Al-Azd, is an ancient Arabian tribe. The lands of Azd occupied an area west of Bisha and Al Bahah in what is today Saudi Arabia.

The Banū Khuzāʿa is the name of an Azdite, Qaḥṭānite tribe, which is one of the main ancestral tribes of Arabia. They ruled Mecca for 400 years before the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and many members of the tribe now live in and around that city. Others are also present in significant numbers in other countries, mainly Iraq, Palestine, and Jordan, but also can be found across the Middle East.
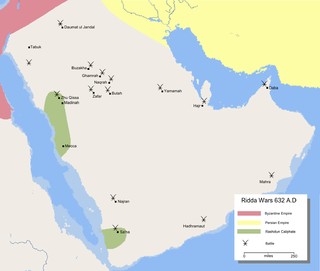
The Ridda Wars were a series of military campaigns launched by the first caliph Abu Bakr against rebellious Arabian tribes. They began shortly after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in 632 and concluded the next year, with all battles won by the Rashidun Caliphate.
Asad ibn Abd al-Uzza was a grandson of Qusai ibn Kilab and the matrilineal great-great-grandfather of the prophet of Islam Muhammad.

Zahran, also known as Banū ʿZahrān ibn Kaʿab, is one of the oldest Arabian tribes in the Arabian Peninsula. It is regarded as one of the largest tribes in Al Bahah Province, also known as 'the Garden of Hejaz' and 'the region of 1001 towers' due to its natural beauty and numerous traditional stone towers dotted throughout the region.

The Tayy, also known as Ṭayyi, Tayyaye, or Taiyaye, are a large and ancient Arab tribe, among whose descendants today are the tribes of Bani Sakher and Shammar. The nisba (patronymic) of Tayy is aṭ-Ṭāʾī (ٱلطَّائِي). In the second century CE, they migrated to the northern Arabian ranges of the Shammar and Salma Mountains, which then collectively became known as the Jabal Tayy, and later Jabal Shammar. The latter continues to be the traditional homeland of the tribe until the present day. They later established relations with the Sasanian and Byzantine empires.

The Tanûkhids, Tanukh, or Banū Tanūkh were a confederation of Arab tribes, sometimes characterized as Saracens. They first rose to prominence in northern Arabia and southern Syria in the 2nd century CE. Both Lakhmid and Tanukhid inscriptions have been found at Umm el-Jimal in Jordan and Namara in Syria. The ancient Tanukh tribal confederation was largely taken over by several branches of the large Azd and Quda'a tribes. Their main base during the time of their most famous ruler, Queen Mavia, was in Aleppo. During the 8th and 9th centuries, the Tanukhid strongholds were the cities of Qinnasrin and Maarat al-Numan.

The Banu Shahr is a tribe from the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula. It belongs to the ancient tribe al-Azd that has many clans linked to it. As far as ancestry goes, Banu Shahr, Bani Amr, Bal-Ahmar, Bal-Asmar, Bal-Qarn, Shumran, and some others all belong to "al-Azd".

The House of Busaid, also known as the House of Al Said, is the current ruling royal family of Oman, and former ruling house of the Omani Empire (1744–1856), Sultanate of Muscat and Oman (1856–1970) and the Sultanate of Zanzibar (1856–1964). It was founded by Ahmad bin Said Al Busaidi in 1744 and is currently headed by Haitham bin Tariq Al Said.
The Expedition of Ali ibn Abi Talib, against the Banu Tai tribe, took place in August 630 AD, 9AH, second month, of the Islamic Calendar. to destroy the statue (idol) of the pagan deity al-Fuls (al-Qullus).
Bariq is a tribe from Bareq in south-west Saudi Arabia. It belongs to the ancient Al-Azd tribe which has many clans linked to it. As far as ancestry goes, Aws, Khazraj, Ghassān and Banu Khuza'a, and others all belong to Al-Azd. They were one of the tribes of Arabia during Muhammad's era.
Arfajah ibn Harthama al-Bariqi was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was a member of the Azd branch of the Bariq clan that inhabited Southwestern Arabia.

Mu'aqqir or Amr Ibn Aws b. Himar al-Bariqi , a knight and the leader of the Bariq tribe which was in Bariq Of Azd Yemen and was famous for its glory, He is considered one of the greatest writers of Arabic poetry in pre-Islamic (Jahiliyyah) times.
Al-Ali is a group of Arab clans who are not necessarily from a common ancestor but were once rulers of their own Arab state in Southern Persia and are still influential in Iraq and the United Arab Emirates as they are the ruling family in Umm al-Quwain. Many of whom are from an Arab tribe, a branch of Bani Malik from Central Arabia. Bani Malik are named after the renowned army leader, Malik Al-Ashtar Al-Nakha'i, and are a branch of Azd Mecca. Azd Mecca are one of four branches of Azd, a major pre-Islamic tribes, a branch of Kahlan which was one of the branches of Qahtan the other being Himyar. Most of Al-Ali tribe migrated by the end of the 16th century from what is now Saudi Arabia to different neighboring countries. Members of Al-Ali tribe live in Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, Iraq and Jordan.

Khawlan is an ancient Yemeni tribe that archeologists view as one of the old tribes of Yemen that were contemporary to the kingdoms of Saba and Ma'in. There are two tribes in Yemen with the name Khawlan which are, Khawlan Al-Tiyal/Al-Aaliyah in Ma'rib, Sana'a, and Al-Bayda governorates, and they are currently a part of the Bakil tribal confederation. Khawlan Al-Tiyal means as it is situated on the highest point in Yemen.
References
- ↑ Abu-Bakr Muhammad ibn-al-Hasan ibn-Durayd al-Azdi, A.H. 223–321 / A.D. 838–933
- ↑ Reformer on the Throne: Sultan Qaboos Bin Said Al Said. Plekhanov, Sergei. 2004