
The euro is the official currency of 19 of the 27 member states of the European Union. This group of states is known as the eurozone or euro area and includes about 343 million citizens as of 2019. The euro, which is divided into 100 cents, is the second-largest and second-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market after the United States dollar.

The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central bank of the Eurozone, a monetary union of 19 EU member states which employ the euro. Established by the Treaty of Amsterdam, the ECB is one of the world's most important central banks and serves as one of seven institutions of the European Union, being enshrined in the Treaty on European Union (TEU). The bank's capital stock is owned by all 27 central banks of each EU member state. The current President of the ECB is Christine Lagarde. Headquartered in Frankfurt, Germany, the bank formerly occupied the Eurotower prior to the construction of its new seat.

Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, also known as Hellas, is a country located in Southeast Europe. Its population is approximately 10.7 million as of 2018; Athens is its largest and capital city, followed by Thessaloniki.

The economy of Greece is the 51st largest in the world with a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of $209.853 billion per annum. In terms of purchasing power parity, Greece is the world's 53rd largest economy, at $336.486 billion per annum. As of 2019, Greece is the sixteenth-largest economy in the 27-member European Union. According to IMF figures for 2019, Greece's GDP per capita was $19,570 at nominal value and $31,572 at purchasing power parity.

The European Investment Bank (EIB) is a publicly owned international financial institution whose shareholders are the EU member states. It was established in 1958 under the Treaty of Rome as a "policy-driven bank" using financing operations to further EU policy goals such as European integration and social cohesion. It should not be confused with the European Central Bank, which is based in Frankfurt (Germany) or with the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) which is based in London.
An investment bank is a financial services company or corporate division that engages in advisory-based financial transactions on behalf of individuals, corporations, and governments. Traditionally associated with corporate finance, such a bank might assist in raising financial capital by underwriting or acting as the client's agent in the issuance of securities. An investment bank may also assist companies involved in mergers and acquisitions (M&A) and provide ancillary services such as market making, trading of derivatives and equity securities, and FICC services. Most investment banks maintain prime brokerage and asset management departments in conjunction with their investment research businesses. As an industry, it is broken up into the Bulge Bracket, Middle Market, and boutique market.

The eurozone, officially called the euro area, is a monetary union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender. The monetary authority of the eurozone is the Eurosystem. Eight members of the European Union continue to use their own national currencies, although most of them will be obliged to adopt the euro in the future.
Alpha Bank is the second largest Greek bank by total assets, and the largest by market capitalization of €2.13 billion. It has a subsidiary and branch in London, England and subsidiaries in Albania, Cyprus and Romania. Founded in 1879, it has been controlled by the Costopoulos family since its inception. Currently Ioannis Costopoulos, grandson of original founder John F. Costopoulos, and nephew of Stavros Costopoulos, foreign minister in the government of Georgios Papandreou, is the honorary chairman. On 16 January 2015 Alpha Bank requested Emergency Liquidity Assistance (ELA) from the Bank of Greece.

Piraeus Bank, is a Greek multinational financial services company with its headquarters in Athens, Greece. Piraeus Bank's stocks are listed on the Athens Stock Exchange (ATHEX) since January 1918.

The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the second largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States, and the third one in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, after China and the United States. The European Union's GDP was estimated to be $18.8 trillion (nominal) in 2018, representing about 22% of the global economy.

Dexia N.V./S.A., also referred to as the Dexia Group, was a Franco-Belgian financial institution active in public finance, providing retail and commercial banking services to individuals and SMEs, asset management, and insurance; with headquarters in Saint-Josse-ten-Noode, Brussels. The company had about 35,200 members of staff and a core shareholders' equity of €19.2 billion, as of 31 December 2010, and provided governments and local public finance operators with banking and other financial services. Asset Management and Services provided asset management, investor and insurance services, in particular to clients of the two other business lines.
Capital controls are residency-based measures such as transaction taxes, other limits, or outright prohibitions that a nation's government can use to regulate flows from capital markets into and out of the country's capital account. These measures may be economy-wide, sector-specific, or industry specific. They may apply to all flows, or may differentiate by type or duration of the flow.

Bank of Cyprus is a Cypriot financial services company established in 1899 and headquartered in Strovolos.
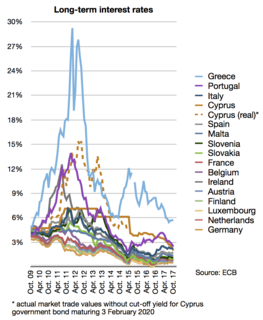
The European debt crisis is a multi-year debt crisis that has been taking place in the European Union since the end of 2009. Several eurozone member states were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bail out over-indebted banks under their national supervision without the assistance of third parties like other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF).

The Greek government-debt crisis was the sovereign debt crisis faced by Greece in the aftermath of the financial crisis of 2007–08. Widely known in the country as The Crisis, it reached the populace as a series of sudden reforms and austerity measures that led to impoverishment and loss of income and property, as well as a small-scale humanitarian crisis. In all, the Greek economy suffered the longest recession of any advanced capitalist economy to date, overtaking the US Great Depression. As a result, the Greek political system has been upended, social exclusion increased, and hundreds of thousands of well-educated Greeks have left the country.

The European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) is a special purpose vehicle financed by members of the eurozone to address the European sovereign-debt crisis. It was agreed by the Council of the European Union on 9 May 2010, with the objective of preserving financial stability in Europe by providing financial assistance to eurozone states in economic difficulty. The Facility's headquarters are in Luxembourg City, as are those of the European Stability Mechanism. Treasury management services and administrative support are provided to the Facility by the European Investment Bank through a service level contract. Since the establishment of the European Stability Mechanism, the activities of the EFSF are carried out by the ESM.
The European Stability Mechanism (ESM) is an intergovernmental organization located in Luxembourg City, which operates under public international law for all eurozone Member States having ratified a special ESM intergovernmental treaty. It was established on 27 September 2012 as a permanent firewall for the eurozone, to safeguard and provide instant access to financial assistance programmes for member states of the eurozone in financial difficulty, with a maximum lending capacity of €500 billion.
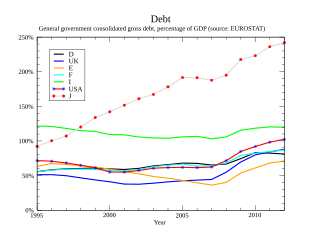
Debt crisis is a situation in which a government loses the ability of paying back its governmental debt. When the expenditures of a government are more than its tax revenues for a prolonged period, the government may enter into a debt crisis. Various forms of governments finance their expenditures primarily by raising money through taxation. When tax revenues are insufficient, the government can make up the difference by issuing debt.

The European debt crisis is an ongoing financial crisis that has made it difficult or impossible for some countries in the euro area to repay or re-finance their government debt without the assistance of third parties.
FCA Bank, a joint venture between Fiat Chrysler Automobiles Italy S.p.A. and Crédit Agricole Consumer Finance S.A is a bank dedicated to motorists, which mainly operates in the automotive financing sector and cooperates with prestigious automotive brands as well as motorhome and caravan manufacturer Erwin Hymer Group.















