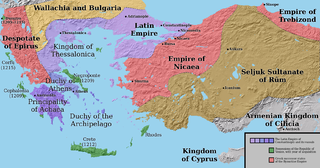
The Principality of Achaea or Principality of Morea was one of the three vassal states of the Latin Empire, which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom of Thessalonica, along with the Duchy of Athens, until Thessalonica was captured by Theodore, the despot of Epirus, in 1224. After this, Achaea became for a while the dominant power in Greece.

William of Villehardouin was the fourth prince of Achaea in Frankish Greece, from 1246 to 1278. The younger son of Prince Geoffrey I, he held the Barony of Kalamata in fief during the reign of his elder brother Geoffrey II. William ruled Achaea as regent for his brother during Geoffrey's military campaigns against the Greeks of Nicaea, who were the principal enemies of his overlord, the Latin Emperor of Constantinople Baldwin II. William succeeded his childless brother in the summer of 1246. Conflicts between Nicaea and Epirus enabled him to complete the conquest of the Morea in about three years. He captured Monemvasia and built three new fortresses, forcing two previously autonomous tribes, the Tzakones and Melingoi, into submission. He participated in the unsuccessful Egyptian crusade of Louis IX of France, who rewarded him with the right to issue currency in the style of French royal coins.

Louis of Burgundy was a member of the Capetian House of Burgundy who ruled the Principality of Achaea and claimed the defunct Kingdom of Thessalonica.

Glarentza, also known as or Clarenia, Clarence, or Chiarenza, was a medieval town located near the site of modern Kyllini in Elis, at the westernmost point of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece. Founded in the mid-13th century by William II of Villehardouin, the town served as the main port and mint of the Frankish Principality of Achaea, being located next to the Principality's capital, Andravida. Commerce with Italy brought great prosperity, but the town began to decline in the early 15th century as the Principality itself declined. In 1428, Glarentza was ceded to the Byzantine Despotate of the Morea, and served as its co-capital, being the residence of one of the Palaiologos despots, until the Ottoman conquest in 1460. Under Ottoman rule, Glarentza declined rapidly as the commercial links with Italy were broken, and by the 16th century was abandoned and falling into ruin. Little remains of the town today: traces of the city wall, of a church and a few other buildings, as well as the silted-up harbour.

John of Saint Omer was baron of a third of Akova and marshal of the Principality of Achaea.

The Barony of Vostitsa was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the northern coast of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, centred on the town of Vostitsa.

The Barony of Patras was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the northwestern coast of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, centred on the town of Patras. It was among the twelve original baronies of the Principality of Achaea, but passed into the hands of the Latin Archbishop of Patras at about the middle of the 13th century. From 1337 on, Patras was an ecclesiastical domain de facto independent of the Principality, although the archbishops still recognized its suzerainty for their secular fiefs. The archbishops maintained close relations with the Republic of Venice, which governed the barony in 1408–1413 and 1418. The barony survived until the Byzantine reconquest in 1429–30.

The Barony of Passavant or Passava was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the mountains between the Mani peninsula and the plain of Laconia, in the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, centred on the fortress of Passavant or Passava. It was among the twelve original baronies of the Principality of Achaea, but was conquered by the Byzantines in the early 1260s.

The Barony of Geraki was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located on the western slopes of Mount Parnon in Laconia, of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, and centred on the castle of Geraki. After the fall of Geraki to the Byzantines, the ruling family, the Nivelets, retained their baronial title and were compensated with new lands in Messenia, as the Barony of Nivelet.

The Barony of Karytaina or of Skorta was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, centred on the town of Karytaina in the mountainous region known as Skorta.

The Barony of Arcadia was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located on the western coast of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, and centred on the town of Arcadia, ancient and modern Kyparissia.

The Barony of Chalandritsa was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the northern Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, and centred on the town of Chalandritsa south of Patras.
Geoffrey of Briel, in older literature Geoffrey of Bruyères, was a French knight and the third lord of the Barony of Karytaina in the Principality of Achaea, in Frankish Greece. He led a colourful and turbulent life, narrated in detail in the Chronicle of the Morea. Accounted the finest knight in the Principality, he fought in the wars against the Byzantine Greeks, was captured in the Battle of Pelagonia in 1259, and was sent back to Achaea bearing the Byzantine terms in 1261. Geoffrey was twice deprived of his barony, once for rebelling against his uncle, the Prince of Achaea William II of Villehardouin, and then for abandoning the Principality without leave in order to spend time with a mistress, the wife of one of his feudatories, in Italy. He was pardoned both times, but henceforth held his title as a gift of the Prince. He died childless in 1275, and the Barony of Karytaina was split up.
The Treaty of Sapienza was concluded in June 1209 between the Republic of Venice and the newly established Principality of Achaea, under Prince Geoffrey I of Villehardouin, concerning the partition of the Peloponnese (Morea) peninsula, conquered following the Fourth Crusade. By its terms, Venice, which had been accorded most of the Peloponnese in the Partitio Romaniae, recognized Villehardouin in possession of the entire peninsula except for the two forts of Modon and Coron, which came under Venetian control, and secured commercial and tax privileges in the Principality. The text of the treaty is also a valuable primary source for the early history of the Principality of Achaea.
Margaret of Villehardouin was the daughter of William II of Villehardouin, Prince of Achaea, and his third wife Anna Komnene Doukaina.
Nicholas le Maure was a French knight of the Principality of Achaea, lord of Saint-Sauveur, who served as the Principality's bailli on behalf of the Angevins of Naples between 1314 and 1315/6.

The Battle of Picotin was fought on 22 February 1316 between the Catalan forces of the infante Ferdinand of Majorca, claimant to the Principality of Achaea, and the forces loyal to Princess Matilda of Hainaut, comprising native levies from the barons loyal to the Princess as well as Burgundian knights. The battle ended in a crushing victory for Ferdinand, but he was later engaged and killed by the troops of Matilda's husband, Louis of Burgundy, at the Battle of Manolada.
Margaret of Nully also known as Margaret of Passavant, was the hereditary Lady of Passavant, Akova and Mitopoli in the Principality of Achaea, in Frankish Greece.
John of Nully was a French knight from Nully became the first Baron of Passavant in the Principality of Achaea. The date of his death is unknown.

The Battle of Saint George took place on 9 September 1320 between the Latin Principality of Achaea and the forces of the Byzantine governor of Mystras, at the fortress of Saint George in Skorta in Arcadia. As a result of the battle, Arcadia, the heartland of the Morea, came firmly under Byzantine control.







