Related Research Articles

An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.

Electronic paper, also known as electronic ink (e-ink) or intelligent paper, is a display device that mimics the appearance of ordinary ink on paper. Unlike conventional flat panel displays that emit light, an electronic paper display reflects ambient light, like paper. This may make them more comfortable to read, and provide a wider viewing angle than most light-emitting displays. The contrast ratio in electronic displays available as of 2008 approaches newspaper, and newly (2008) developed displays are slightly better. An ideal e-paper display can be read in direct sunlight without the image appearing to fade.

The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and science.

A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations.

Madras Institute of Technology (MIT) is an engineering institute located in Chromepet, Chennai, India. It is one of the four autonomous constituent colleges of Anna University. It was established in 1949 by Chinnaswami Rajam as the first self-financing engineering institute in the country and later merged with Anna University. The institute was among the first educational institutions in India to offer new areas of specialization, such as aeronautical engineering, automobile engineering, electronics engineering and instrumentation technology. Madras Institute of Technology (MIT) was the first self-financing institute opened in India.

Qualcomm is an American multinational corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, and incorporated in Delaware. It creates semiconductors, software, and services related to wireless technology. It owns patents critical to the 5G, 4G, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA and WCDMA mobile communications standards.

William Daniel "Danny" Hillis is an American inventor, entrepreneur, and computer scientist, who pioneered parallel computers and their use in artificial intelligence. He founded Thinking Machines Corporation, a parallel supercomputer manufacturer, and subsequently was Vice President of Research and Disney Fellow at Walt Disney Imagineering.

E Ink is a brand of electronic paper (e-paper) display technology commercialized by the E Ink Corporation, which was co-founded in 1997 by MIT undergraduates JD Albert and Barrett Comiskey, MIT Media Lab professor Joseph Jacobson, Jerome Rubin and Russ Wilcox.
Joseph Jacobson, is a tenured professor and head of the Molecular Machines group at the Center for Bits and Atoms at the MIT Media Lab, and is one of the inventors of microencapsulated electrophoretic display commonly used in electronic devices such as e-readers. He is the founder of several companies including E Ink Corporation, Gen9, Inc., and Kovio, is on the scientific board of several more companies.

A flexible display or rollable display is an electronic visual display which is flexible in nature, as opposed to the traditional flat screen displays used in most electronic devices. In recent years there has been a growing interest from numerous consumer electronics manufacturers to apply this display technology in e-readers, mobile phones and other consumer electronics. Such screens can be rolled up like a scroll without the image or text being distorted. Technologies involved in building a rollable display include electronic ink, Gyricon, Organic LCD, and OLED.
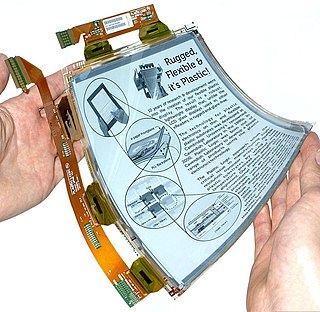
Plastic Logic Germany develops and manufactures electrophoretic displays (EPD), based on organic thin-film transistor (OTFT) technology, in Dresden, Germany.

Stephen Anthony Benton was the E. Rudge ('48) and Nancy Allen Professor of Media & Sciences, and the Director for Center for Advanced Visual Studies (CAVS) at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He was the inventor of the rainbow hologram and a pioneer in medical imaging and fine arts holography. Benton held 14 patents in optical physics and photography, and taught media arts and sciences at MIT.

Pen computing refers to any computer user-interface using a pen or stylus and tablet, over input devices such as a keyboard or a mouse.

Electronic textiles or e-textiles are fabrics that enable electronic components such as batteries, lights, sensors, and microcontrollers to be embedded in them. They are not to be confused with smart textiles, which are fabrics that have been developed with new technologies that provide added value. Many smart clothing, wearable technology, and wearable computing projects involve the use of e-textiles.
Digital newspaper technology is the technology used to create or distribute a digital newspaper.

An ebook, also known as an e-book or eBook, is a book publication made available in digital form, consisting of text, images, or both, readable on the flat-panel display of computers or other electronic devices. Although sometimes defined as "an electronic version of a printed book", some e-books exist without a printed equivalent. E-books can be read on dedicated e-reader devices, but also on any computer device that features a controllable viewing screen, including desktop computers, laptops, tablets and smartphones.
Kovio, Inc. was a privately held Silicon Valley technology company headquartered in San Jose, California that manufactured electronic devices based on a proprietary printed silicon electronics platform. Products included Near Field Communication (NFC) tags for use in mobile marketing, authentication, and advertising as well as electronic article surveillance (EAS) labels for anti-shoplifting applications. On January 21, 2014 Thin Film Electronics ASA acquired Kovio technology, intellectual property and production equipment.
JD Albert is an American engineer, inventor, and educator. Albert is one of the inventors of microencapsulated electrophoretic display commonly used in electronic devices such as e-readers.

Tactile is a real-time text-to-braille translation device currently under development at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was conceived by a team of undergraduate students, competing as "Team 100% Enthusiasm", during a 15-hour MIT "hackathon". The device is slid over printed text and a camera captures images of the words and sends them to a microcontroller. The information moves the pins up and down, translating the text into Braille. Once on the market it is hoped to be much cheaper than existing devices.

Migo is a technology company that "provides affordable data services for emerging markets". Its content delivery network distributes digital products and services to mass market consumers at the local corner store through Migo Download Stations (MDS).
References
- ↑ Primozic, Ursa (2016-05-27). "Interview with Barrett Comiskey, father of electronic ink: "Our objective was to give life to the surfaces around us"". Visionect. Retrieved 2021-12-22.
- ↑ "Barrett Comiskey". ContentAsia Summit. Retrieved 2021-12-23.
- 1 2 "Migo". www.migo.tv. Archived from the original on 2015-12-10. Retrieved 2015-12-08.
- 1 2 "Interview with Barrett Comiskey, father of electronic ink: "Our objective was to give life to the surfaces around us"". Interview with Barrett Comiskey, father of electronic ink: “Our objective was to give life to the surfaces around us” | The paper | Visionect. 27 May 2016. Retrieved 2016-05-31.
- ↑ "E Ink Holdings Inc. (8069.TWO) Stock Price, News, Quote & History - Yahoo Finance". finance.yahoo.com.
- ↑ "How Electronic Ink Was Invented - Science Friday". Science Friday. Retrieved 2016-05-31.
- ↑ Klein, Alec. "A New Printing Technology Sets Off a High-Stakes Race". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660 . Retrieved 2015-12-08.
- 1 2 Jones, Chris (2008-09-23). "The New American". Esquire. Retrieved 2015-12-08.
- ↑ McCrum, Robert (15 January 2006). "E-read all about it". The Observer. Retrieved 2015-12-08.
- ↑ Comiskey, Barrett; Albert, J. D.; Yoshizawa, Hidekazu; Jacobson, Joseph (1998-07-16). "An electrophoretic ink for all-printed reflective electronic displays". Nature. 394 (6690): 253–255. Bibcode:1998Natur.394..253C. doi:10.1038/28349. ISSN 0028-0836. S2CID 204998708.
- ↑ "Patent Database: "Comiskey, Barrett" U.S. Patent Collection". patft.uspto.gov. Retrieved 2015-12-08.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "The World Economic Forum Designates Technology Pioneers for 2002: Barrett Comiskey, Co-Founder of E Ink Corporation, Selected". www.thefreelibrary.com. Retrieved 2015-12-08.
- ↑ Journal, Erin WhiteStaff Reporter of The Wall Street (2005-05-24). "Going With Their Gut: MBA Graduates Take Entrepreneurial Plunge". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660 . Retrieved 2021-12-23.
- ↑ Jones, Chris (2008-09-23). "The New American". Esquire. Retrieved 2021-12-23.
- ↑ "Strategic Insights Inc. and Nicobar Group Team Up in Strategic Partnership Agreement, Allowing Customers to Expand their Reach into China, the U.S. and Canada". www.businesswire.com. 2018-01-29. Retrieved 2022-01-13.
- ↑ "Migo - A New Window to the World". Migo. Retrieved 2022-01-13.
- 1 2 "Migo provides affordable data services for emerging markets". DIGITIMES. Retrieved 2022-01-13.
- ↑ Kynge, James; Ruehl, Mercedes (2020-08-19). "Do US sanctions spell 'death' of Huawei?". Financial Times. Retrieved 2021-12-22.
- ↑ "IBC announces Innovation Awards shortlist". IBC. Archived from the original on 2021-07-29. Retrieved 2022-01-13.
- ↑ "Barrett Comiskey, LinkedIn". www.linkedin.com. Retrieved 2015-12-08.