Related Research Articles

The French Colonial Empire comprised the overseas colonies, protectorates and mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French colonial empire," that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French colonial empire," which began with the conquest of Algiers in 1830. At its apex between the two world wars, the second French colonial empire was the second-largest colonial empire in the world behind the British Empire.

British Cameroon or the British Cameroons was a British mandate territory in British West Africa, formed of the Northern Cameroons and Southern Cameroons. Today, the Northern Cameroons forms parts of the Borno, Adamawa and Taraba states of Nigeria, while the Southern Cameroons forms part of the Northwest and Southwest regions of Cameroon.

The Scramble for Africa is a term widely used by historians to describe the invasion, annexation, division, and colonization of most of Africa by seven Western European powers during an era known as "New Imperialism". The 10 percent of Africa that was under formal European control in 1870 increased to almost 90 percent by 1914, with only Liberia and Ethiopia remaining independent.
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on independence movements in the colonies and the collapse of global colonial empires. Other scholars extend the meaning to include economic, cultural and psychological aspects of the colonial experience.

Frederick John Dealtry Lugard, 1st Baron Lugard, known as Sir Frederick Lugard between 1901 and 1928, was a British soldier, mercenary, explorer of Africa and a colonial administrator. He was Governor of Hong Kong (1907–1912), the last Governor of Southern Nigeria Protectorate (1912–1914), the first High Commissioner (1900–1906) and last Governor (1912–1914) of Northern Nigeria Protectorate and the first Governor-General of Nigeria (1914–1919).

Kamerun was an African colony of the German Empire from 1884 to 1920 in the region of today's Republic of Cameroon. Kamerun also included northern parts of Gabon and the Congo with western parts of the Central African Republic, southwestern parts of Chad and far northeastern parts of Nigeria.

The decolonisation of Africa is a process that largely took place from mid-1950s to 1975 during the Cold War, with radical government changes on the continent as colonial governments made the transition to independent states. The process was often marred with violence, political turmoil, widespread unrest, and organised revolts in both northern and sub-Saharan countries including the Mau Mau rebellion in British Kenya, the Algerian War in French Algeria, the Congo Crisis in the Belgian Congo, the Angolan War of Independence in Portuguese Angola, the Zanzibar Revolution in the Sultanate of Zanzibar, and the Nigerian Civil War in the secessionist state of Biafra.

Indirect rule was a system of governance used by the British and others to control parts of their colonial empires, particularly in Africa and Asia, which was done through pre-existing indigenous power structures. Indirect rule was used by various colonial rulers: the French in Algeria and Tunisia, the Dutch in the East Indies, the Portuguese in Angola and Mozambique and the Belgians in Rwanda and Burundi. These dependencies were often called "protectorates" or "trucial states". By this system, the day-to-day government and administration of areas both small and large were left in the hands of traditional rulers, who gained prestige and the stability and protection afforded by the Pax Britannica, at the cost of losing control of their external affairs, and often of taxation, communications, and other matters, usually with a small number of European "advisors" effectively overseeing the government of large numbers of people spread over extensive areas.

African nationalism is an umbrella term which refers to a group of political ideologies in sub-Saharan Africa, which are based on the idea of national self-determination and the creation of nation states. The ideology emerged under European colonial rule during the 19th and 20th centuries and was loosely inspired by nationalist ideas from Europe. Originally, African nationalism was based on demands for self-determination and played an important role in forcing the process of decolonisation of Africa. However, the term refers to a broad range of different ideological and political movements and should not be confused with Pan-Africanism which may seek the federation of several or all nation states in Africa.
The Economic history of Nigeria falls into three periods. They are the: pre-colonial, the colonial and the post-colonial or independence periods. The pre-colonial period covers the longest the part of Nigerian history. The colonial period covers a period of 60 years,1900-1960 while the independence period dates from October 1, 1960.

European colonialism and colonization was the policy or practice of acquiring full or partial political control over other societies and territories, founding a colony, occupying it with settlers, and exploiting it economically. For example, colonial policies, such as the type of rule implemented, the nature of investments, and identity of the colonizers, are cited as impacting postcolonial states. Examination of the state-building process, economic development, and cultural norms and mores shows the direct and indirect consequences of colonialism on the postcolonial states.

Education in Nigeria is overseen by the Federal Ministry of Education. The local authorities take responsibility for implementing state-controlled policy regarding public education and state schools. The education system is divided into Kindergarten, Primary education, Secondary education, and Tertiary education. Nigeria's federal government has been dominated by instability since declaring independence from Britain, and as a result, a unified set of education policies is yet to be successfully implemented. Regional differences in quality, curriculum, and funding characterize the education system in Nigeria. Currently, Nigeria possesses the largest population of out-of-school learning youths in the world. The educational systems in Nigeria are divided into two the public where the student only pays for PTA while the private where students pay school fees and some other fees like sports, exam fees, computer fees etc. and they are costly
Africa's fifty-six sovereign states range widely in their history and structure, and their laws are variously defined by customary law, religious law, common law, Western civil law, other legal traditions, and combinations thereof.

Colonial Nigeria was ruled by the British Empire from the mid-nineteenth century until 1960 when Nigeria achieved independence. British influence in the region began with the prohibition of slave trade to British subjects in 1807. Britain annexed Lagos in 1861 and established the Oil River Protectorate in 1884. British influence in the Niger area increased gradually over the 19th century, but Britain did not effectively occupy the area until 1885. Other European powers acknowledged Britain's dominance over the area in the 1885 Berlin Conference.

The historiography of the British Empire refers to the studies, sources, critical methods and interpretations used by scholars to develop a history of the British Empire. Historians and their ideas are the main focus here; specific lands and historical dates and episodes are covered in the article on the British Empire. Scholars have long studied the Empire, looking at the causes for its formation, its relations to the French and other empires, and the kinds of people who became imperialists or anti-imperialists, together with their mindsets. The history of the breakdown of the Empire has attracted scholars of the histories of the United States, the British Raj, and the African colonies. John Darwin (2013) identifies four imperial goals: colonising, civilising, converting, and commerce.
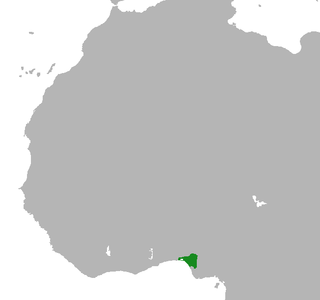
The Kingdom of Benin, also known as the Edo Kingdom or the Benin Empire, was a kingdom within what is now southern Nigeria. It has no historical relation to the modern republic of Benin, which was known as Dahomey from the 17th century until 1975. The Kingdom of Benin's capital was Edo, now known as Benin City in Edo State, Nigeria. The Benin Kingdom was "one of the oldest and most developed states in the coastal hinterland of West Africa". It grew out of the previous Edo Kingdom of Igodomigodo around the 11th century AD, and lasted until it was annexed by the British Empire in 1897.

Second colonial occupation is a term coined by the historians Anthony Low and John Lonsdale to describe the phase of British colonial rule in Sub-Saharan Africa beginning in the aftermath of World War II. It was characterised by "a great intensification of government activity" and new focus on economic development.
Philip Aigbona Igbafe was a Nigerian historian, professor and former public administrator noted for his work on the history of the Edo people of the precolonial Kingdom of Benin. Igbafe belongs to the Ibadan History School and his major works examine the motives for colonialism and highlights the political, social and economic consequences of British rule for the African kingdom.
Abosede George is an associate professor of history and Africana studies at Barnard College. Her academic focus are in the areas of African history, childhood and youth studies, social reform in Africa, urban history, girl studies, women's studies, and migration studies. She is the incumbent President of the Nigerian Studies Association, an affiliate organization of the African Studies Association.
Ayodeji Oladimeji Olukoju is a Nigerian University distinguished professor of history at the University of Lagos, Nigeria. He was a two-term vice chancellor of Caleb University, Imota between 2010 and 2016. Olukoju's research interests are in the area of maritime, transport, economic, social, corporate and urban history of Nigeria.
References
- ↑ Kachim, Joseph Udimal (2018). "The Second Colonial Occupation: Development Planning, Agriculture, and the Legacies of British Rule in Nigeria, by Bekeh Utietiang Ukelina". African Historical Review. 50 (1–2): 192–195. doi:10.1080/17532523.2018.1507287.
- ↑ Schler, Lynn (2019). "Bekeh Utietiang Ukelina. The Second Colonial Occupation: Development Planning, Agriculture, and the Legacies of British Rule in Nigeria". The American Historical Review. 124 (1): 385–386. doi:10.1093/ahr/rhy529.
- ↑ Mitcham, John C. (2019). "Reviewed Work: The Second Colonial Occupation: Development Planning, Agriculture, and the Legacies of British Rule in Nigeria by Bekeh Utietiang Ukelina". Agricultural History. 93 (2): 369–371. doi:10.3098/ah.2019.093.2.369.