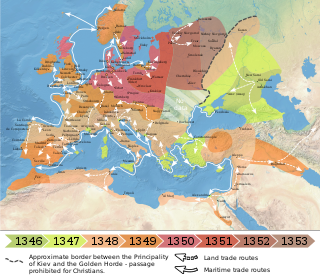
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as 50 million people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. The disease is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis and spread by fleas and through the air. One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and distributed name service that provides a naming system for computers, services, and other resources in the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the associated entities. Most prominently, it translates readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols. The Domain Name System has been an essential component of the functionality of the Internet since 1985.
The terms foobar, foo, bar, baz, and others are used as metasyntactic variables and placeholder names in computer programming or computer-related documentation. They have been used to name entities such as variables, functions, and commands whose exact identity is unimportant and serve only to demonstrate a concept. The style guide for Google developer documentation recommends against using them as example project names because they are unclear and can cause confusion.

Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name, or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name. In the ICZN, the system is also called binominal nomenclature, "binomi'N'al" with an "N" before the "al", which is not a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system".
A pseudonym or alias is a fictitious name that a person assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true name (orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individual's own. Many pseudonym holders use them because they wish to remain anonymous, but anonymity is difficult to achieve and often fraught with legal issues.
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather, or an earlier male ancestor. It is the male equivalent of a matronymic.

The Stanley Cup is the championship trophy awarded annually to the National Hockey League (NHL) playoff champion. It is the oldest existing trophy to be awarded to a professional sports franchise in North America, and the International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF) considers it to be one of the "most important championships available to the sport". The trophy was commissioned in 1892 as the Dominion Hockey Challenge Cup and is named after Lord Stanley of Preston, the Governor General of Canada, who donated it as an award to Canada's top-ranking amateur ice hockey club. The entire Stanley family supported the sport, the sons and daughters all playing and promoting the game. The first Cup was awarded in 1893 to the Montreal Hockey Club, and winners from 1893 to 1914 were determined by challenge games and league play. Professional teams first became eligible to challenge for the Stanley Cup in 1906. In 1915, the National Hockey Association (NHA) and the Pacific Coast Hockey Association (PCHA), the two main professional ice hockey organizations, reached an agreement in which their respective champions would face each other annually for the Stanley Cup. It was established as the de facto championship trophy of the NHL in 1926 and then the de jure NHL championship prize in 1947.

A surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person.

A given name is the part of a personal name that identifies a person, potentially with a middle name as well, and differentiates that person from the other members of a group who have a common surname. The term given name refers to a name usually bestowed at or close to the time of birth, usually by the parents of the newborn. A Christian name is the first name which is given at baptism, in Christian custom.
A demonym or gentilic is a word that identifies a group of people in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place. Demonyms are used to designate all people of a particular place, regardless of ethnic, linguistic, religious or other cultural differences that may exist within the population of that place. Examples of demonyms include Cochabambino, for someone from the city of Cochabamba; French for a person from France; and Swahili, for a person of the Swahili coast.

A digital object identifier (DOI) is a persistent identifier or handle used to uniquely identify various objects, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). DOIs are an implementation of the Handle System; they also fit within the URI system. They are widely used to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports, data sets, and official publications.

Vissarion Grigoryevich Belinsky was a Russian literary critic of Westernizing tendency. Belinsky played one of the key roles in the career of poet and publisher Nikolay Nekrasov and his popular magazine Sovremennik. He was the most influential of the Westernizers, especially among the younger generation. He worked primarily as a literary critic, because that area was less heavily censored than political pamphlets. He agreed with Slavophiles that society had precedence over individualism, but he insisted the society had to allow the expression of individual ideas and rights. He strongly opposed Slavophiles on the role of Orthodoxy, which he considered a retrograde force. He emphasized reason and knowledge, and attacked autocracy and theocracy.
Ipatovo kurgan refers to kurgan 2 of the Ipatovo Barrow Cemetery 3, a cemetery of kurgan burial mounds, located near the town of Ipatovo in Stavropol Krai, Russia, some 120 kilometers (75 mi) northeast of Stavropol.

The Maykop culture, c. 3700 BC–3000 BC, is a major Bronze Age archaeological culture in the western Caucasus region.
A birth name is the name given to a person upon birth. The term may be applied to the surname, the given name, or the entire name. Where births are required to be officially registered, the entire name entered onto a birth certificate or birth register may by that fact alone become the person's legal name.

Corrado Invernizzi is an Italian actor.
A uniform resource locator (URL), colloquially known as an address on the Web, is a reference to a resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably. URLs occur most commonly to reference web pages (HTTP/HTTPS) but are also used for file transfer (FTP), email (mailto), database access (JDBC), and many other applications.
Sigurd Fasting was a Norwegian philologist specializing in Russian studies.










