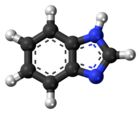
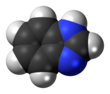
Phenothiazine, abbreviated PTZ, is an organic compound that has the formula S(C6H4)2NH and is related to the thiazine-class of heterocyclic compounds. Derivatives of phenothiazine are highly bioactive and have widespread use and rich history.

The cumene process is an industrial process for synthesizing phenol and acetone from benzene and propylene. The term stems from cumene, the intermediate material during the process. It was invented by R. Ūdris and P. Sergeyev in 1942 (USSR), and independently by Heinrich Hock in 1944.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces of one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens. Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.

Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non-adjacent nitrogen atoms in meta-substitution.
Thiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a 5-membered heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. The term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1).

Catechol, also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4(OH)2. It is the ortho isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances. Small amounts of catechol occur in fruits and vegetables.
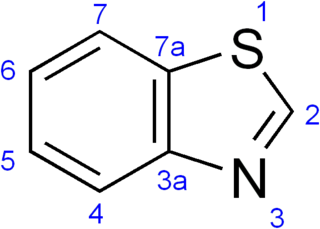
Benzothiazole is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C
7H
5NS. It is colorless, slightly viscous liquid. Although the parent compound, benzothiazole is not widely used, many of its derivatives are found in commercial products or in nature. Firefly luciferin can be considered a derivative of benzothiazole.

Tiabendazole, also known as thiabendazole or TBZ and the trade names Mintezol, Tresaderm, and Arbotect, is a preservative, an antifungal agent, and an antiparasitic agent.
Thiazolidine is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula (CH2)3(NH)S. It is a 5-membered saturated ring with a thioether group and an amine group in the 1 and 3 positions. It is a sulfur analog of oxazolidine. Thiazolidine is a colorless liquid. Although the parent thiazolidine is only of academic interest, some derivatives, i.e., the thiazolidines, are important, such as the antibiotic penicillin.

Benzoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure, and an odor similar to pyridine. Although benzoxazole itself is of little practical value, many derivatives of benzoxazoles are commercially important.

o-Phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. OPD is a white compound although samples appear darker owing to oxidation by air. It is isomeric with m-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine.

Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.

Imidazolidine is a heterocyclic compound (CH2)2(NH)2CH2. The parent imidazolidine is lightly studied, but related compounds substituted on one or both nitrogen centers are more common. Generally, they are colorless, polar, basic compounds. Imidazolidines are cyclic 5-membered examples of the general class of aminals.

Divinylbenzene (DVB) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H4(CH=CH2)2 and structure H2C=CH−C6H4−HC=CH2. It is related to styrene by the addition of a second vinyl group. It is a colorless liquid manufactured by the thermal dehydrogenation of isomeric diethylbenzenes. Under synthesis conditions, o-divinylbenzene converts to naphthalene and thus is not a component of the usual mixtures of DVB.

2,6-Xylidine is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(CH3)2NH2. It is one of several isomeric xylidines. It is a colorless viscous liquid. Commercially significant derivatives are the anesthetics lidocaine, bupivacaine, mepivacaine, and etidocaine.

2,4,6-Trimethylaniline is an organic compound with formula (CH3)3C6H2NH2. It is an aromatic amine that is of commercial interest as a precursor to dyes. It is prepared by selective nitration of mesitylene, avoiding oxidation of the methyl groups, followed by reduction of the resulting nitro group to the aniline.

1-Methylimidazole or N-methylimidazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula CH3C3H3N2. It is a colourless liquid that is used as a specialty solvent, a base, and as a precursor to some ionic liquids. It is a fundamental nitrogen heterocycle and as such mimics for various nucleoside bases as well as histidine and histamine.
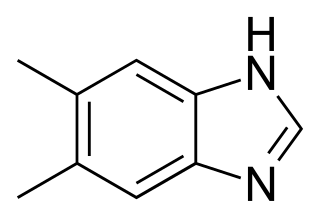
5,6-Dimethylbenzimidazole is a natural benzimidazole derivative. It is a component of vitamin B12 where it serves as a ligand for the cobalt atom.
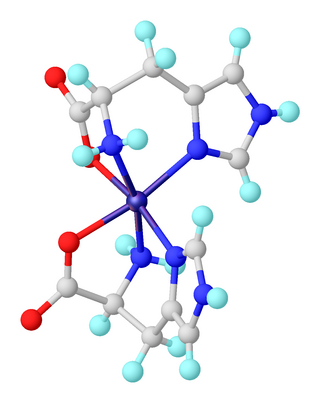
A transition metal imidazole complex is a coordination complex that has one or more imidazole ligands. Complexes of imidazole itself are of little practical importance. In contrast, imidazole derivatives, especially histidine, are pervasive ligands in biology where they bind metal cofactors.