
Scandinavia is a subregion of Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. Scandinavia most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer to the Scandinavian Peninsula. In English usage, Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Nordic countries. Iceland and the Faroe Islands are sometimes included in Scandinavia for their ethnolinguistic relations with Sweden, Norway and Denmark. While Finland differs from other Nordic countries in this respect, some authors call it Scandinavian due to its economic and cultural similarities.

The history of Sweden can be traced back to the melting of the Northern Polar Ice Caps. From as early as 12000 BC, humans have inhabited this area. Throughout the Stone Age, between 8000 BC and 6000 BC, early inhabitants used stone-crafting methods to make tools and weapons for hunting, gathering and fishing as means of survival. Written sources about Sweden before AD 1000 are rare and short, usually written by outsiders. It is usually accepted that Swedish recorded history, in contrast with pre-history, starts around the late 10th century, when sources are common enough that they can be contrasted with each other.

Norrbotten County is the northernmost county or län of Sweden. It is also the largest county by land area, almost a quarter of Sweden's total area. It shares borders with Västerbotten County to the southwest, the Gulf of Bothnia to the southeast, the counties of Nordland and Troms in Norway to the northwest, and Lapland Province in Finland to the northeast.
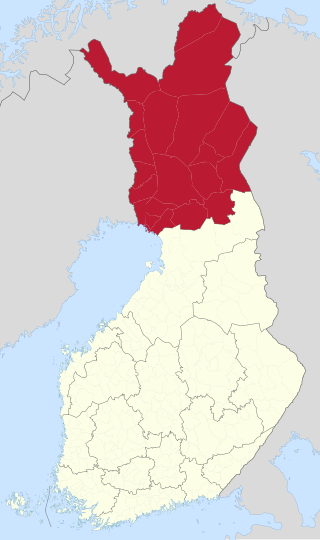
Lapland is the largest and northernmost region of Finland. The 21 municipalities in the region cooperate in a Regional Council. Lapland borders the region of North Ostrobothnia in the south. It also borders the Gulf of Bothnia, Norrbotten County in Sweden, Finnmark County and Troms County in Norway, and Murmansk Oblast and the Republic of Karelia in Russia. Topography varies from vast mires and forests of the South to fells in the North. The Arctic Circle crosses Lapland, so polar phenomena such as the midnight sun and polar night can be viewed in Lapland.

Norrbotten, known in English as North Bothnia, is a Swedish province (landskap) in northernmost Sweden. It borders south to Västerbotten, west to Swedish Lapland, and east to Finland.

Kemi is a town and municipality of Finland. It is located very near the city of Tornio and the Swedish border. The distance to Oulu is 105 kilometres (65 mi) to the south and to Rovaniemi is 117 kilometres (73 mi) to the northeast. It was founded in 1869 by a decree of the Emperor Alexander II of Russia because of its proximity to a deepwater port.

Tornio is a city and municipality in Lapland, Finland. The city forms a cross-border twin city together with Haparanda on the Swedish side. The municipality covers an area of 1,348.83 square kilometres (520.79 sq mi), of which 161.59 km2 (62.39 sq mi) is water. The population density is 17.68 inhabitants per square kilometre (45.8/sq mi), with a total population of 21,018.
Kvenland, known as Cwenland, Qwenland, Kænland, and similar terms in medieval sources, is an ancient name for an area in Fennoscandia and Scandinavia. Kvenland, in that or nearly that spelling, is known from an Old English account written in the 9th century, which used information provided by Norwegian adventurer and traveler Ohthere, and from Nordic sources, primarily Icelandic. A possible additional source was written in the modern-day area of Norway. All known Nordic sources date from the 12th and 13th centuries. Other possible references to Kvenland by other names and spellings are also discussed here.

Kvens are a Balto-Finnic ethnic minority in Norway. They are descended from Finnish peasants and fishermen who emigrated from the northern parts of Finland and Sweden to Northern Norway in the 18th and 19th centuries. In 1996, Kvens were granted minority status in Norway, and in 2005 the Kven language was recognized as a minority language in Norway.
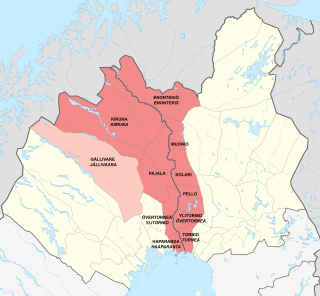
Meänmaa, or sometimes Torne Valley or Torne River Valley lies at the border of Sweden and Finland. It is named after the Torne River flowing through the valley and into the Gulf of Bothnia. Geographically the townships and municipalities that make up the area are Haparanda, Övertorneå, Pajala and Kiruna in Sweden, and Tornio, Ylitornio, Pello, Kolari, Muonio and Enontekiö in Finland. Culturally the highland Swedish municipality Gällivare is sometimes also considered part of Meänmaa due to the large share of Meänkieli-speaking population in it. Torne Valley should not be confused with Torne Valley Sub-region.

The Sámi people are a Native people of northern Europe inhabiting Sápmi, which today encompasses northern parts of Sweden, Norway, Finland, and the Kola Peninsula of Russia. The traditional Sámi lifestyle, dominated by hunting, fishing and trading, was preserved until the Late Middle Ages, when the modern structures of the Nordic countries were established.

Tornedalians are an ethnic group native to the Meänmaa region of northern Sweden and Finland. Tornedalians are a recognized national minority in Sweden. Tornedalians generally divide themselves into three distinct groups: Tornedalians, Lantalaiset, and Kvens.
The Treaty of Novgorod was signed on 3 June 1326 in Novgorod and marked the end of decades of the Norwegian-Novgorodian border skirmishes in the far-northern region of Finnmark. The terms were an armistice for 10 years. A few years earlier in 1323, the Republic of Novgorod had settled its conflict with Sweden in the Treaty of Nöteborg.
The Swedish–Novgorodian Wars were a series of conflicts in the 12th and 13th centuries between the Novgorod Republic and medieval Sweden over control of the Gulf of Finland, an area vital to the Hanseatic League and part of the trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks. The Swedish attacks against Orthodox Russians had religious overtones, but before the 14th century there is no knowledge of official crusade bulls issued by the pope.
Matti Kurki was a legendary Finnish chieftain of the birkarls. If he was a real person, he is thought to have lived in the late 13th century, at that time when king Magnus the Barnlock ruled the Kingdom of Sweden.

The Bothnian Bay or Bay of Bothnia is the northernmost part of the Gulf of Bothnia, which is in turn the northern part of the Baltic Sea. The land holding the bay is still rising after the weight of ice-age glaciers has been removed, and within 2,000 years the bay will be a large freshwater lake since its link to the south Kvarken is mostly less than 20 metres (66 ft) deep. The bay today is fed by several large rivers, and is relatively unaffected by tides, so has low salinity. It freezes over each year for up to six months. Compared to other parts of the Baltic, it has little plant or animal life.
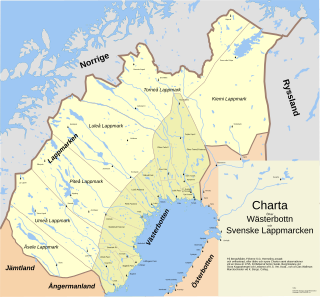
Lappmarken was an earlier Swedish name for the northern part of the old Kingdom of Sweden inhabited by the Sami people. In addition to the present-day Swedish Lapland, it also covered Västerbotten, Jämtland and Härjedalen, as well as the Finnish Lapland. As a name, it is related to Finnmark, an old Norwegian name for the Sami area. "Finn" and "Lapp" are mutually exchangeable old names for the Sami people, although the latter is sometimes deemed offensive.

The expedition to Lapland, the northernmost region in Sweden, by Carl Linnaeus between May and October 1732 was an important part of his scientific career.

The forest Sami are Sami people who lived in the woods and who, unlike the reindeer-herding Sami people, did not move up into the fells during the summer season. Historically, there have been forest Sami in Sweden in the area ranging from northern Ångermanland to the far north. In the early 1600s the term granlapp was also used to refer to the Sami people who paid taxes only to Sweden, compared to the semi-nomadic fell Sami, who, since they worked in the fells that straddled the Swedish-Norwegian border, had to pay taxes to both countries. When Ernst Manker studied the life of the forest Sami in the early 20th century, nearly all of their habitations had been abandoned. Only one forest Sami village remained, in Malå in Västerbotten, an area known as Stenundslandet in Anundsjö. There is a modern-day group who consider themselves forest Sami in Finland, but they are not part of the Sami parliament, for example.















