
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is limited to 2.5 milliwatts, giving it a very short range of up to 10 metres (33 ft). It employs UHF radio waves in the ISM bands, from 2.402 GHz to 2.48 GHz. It is mainly used as an alternative to wired connections to exchange files between nearby portable devices and connect cell phones and music players with wireless headphones.

A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network for interconnecting electronic devices within an individual person's workspace. A PAN provides data transmission among devices such as computers, smartphones, tablets and personal digital assistants. PANs can be used for communication among the personal devices themselves, or for connecting to a higher level network and the Internet where one master device takes up the role as gateway.

A wearable computer, also known as a body-borne computer, is a computing device worn on the body. The definition of 'wearable computer' may be narrow or broad, extending to smartphones or even ordinary wristwatches.

Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports to provide visitors.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information (telecommunication) between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, such as light and magnetic or electric fields, or the use of sound.

Handsfree is an adjective describing equipment that can be used without the use of hands or, in a wider sense, equipment which needs only limited use of hands, or for which the controls are positioned so that the hand can occupy themselves with another task without needing to hunt far afield for the controls.

Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 centimetres (1.6 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be used for the bootstrapping of capable wireless connections. Like other proximity card technologies, NFC is based on inductive coupling between two electromagnetic coils present on a NFC-enabled device such as a smartphone. NFC communicating in one or both directions uses a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band, compliant with the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 848 kbit/s.
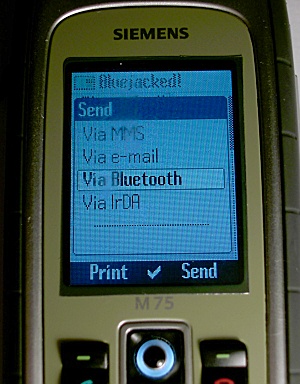
Bluejacking is the sending of unsolicited messages over Bluetooth to Bluetooth-enabled devices such as mobile phones, PDAs or laptop computers, sending a vCard which typically contains a message in the name field to another Bluetooth-enabled device via the OBEX protocol.

Mobile computing is human–computer interaction in which a computer is expected to be transported during normal usage and allow for transmission of data, which can include voice and video transmissions. Mobile computing involves mobile communication, mobile hardware, and mobile software. Communication issues include ad hoc networks and infrastructure networks as well as communication properties, protocols, data formats, and concrete technologies. Hardware includes mobile devices or device components. Mobile software deals with the characteristics and requirements of mobile applications.

A mobile device, also referred to as a digital assistant, is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physical keyboard. Many mobile devices can connect to the Internet and connect with other devices, such as car entertainment systems or headsets, via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, or near-field communication. Integrated cameras, the ability to place and receive voice and video telephone calls, video games, and Global Positioning System (GPS) capabilities are common. Power is typically provided by a lithium-ion battery. Mobile devices may run mobile operating systems that allow third-party applications to be installed and run.
Bluesnarfing is the unauthorized access of information from a wireless device through a Bluetooth connection, often between phones, desktops, laptops, and PDAs. This allows access to calendars, contact lists, emails and text messages, and on some phones, users can copy pictures and private videos. Both Bluesnarfing and Bluejacking exploit others' Bluetooth connections without their knowledge. While Bluejacking is essentially harmless as it only transmits data to the target device, Bluesnarfing is the theft of information from the target device.
Mobile malware is malicious software that targets mobile phones or wireless-enabled Personal digital assistants (PDA), by causing the collapse of the system and loss or leakage of confidential information. As wireless phones and PDA networks have become more and more common and have grown in complexity, it has become increasingly difficult to ensure their safety and security against electronic attacks in the form of viruses or other malware.
Proximity marketing is the localized wireless distribution of advertising content associated with a particular place. Transmissions can be received by individuals in that location who wish to receive them and have the necessary equipment to do so.

The Palm Treo 700p is a cell phone with advanced capabilities, commonly referred to as a smartphone. Unlike the slightly earlier Treo 700w, this model is based on Palm OS. This is the first Palm OS-based Treo model to feature high-speed cellular network support, and is also the first Treo model to support Bluetooth 1.2.

A headset is a combination of headphone and microphone. Headsets connect over a telephone or to a computer, allowing the user to speak and listen while keeping both hands free. They are commonly used in customer service and technical support centers, where employees can converse with customers while typing information into a computer. They are also common among computer gamers and let them talk with each other and hear others while using their keyboards and mice to play the game.
Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless personal area network technology designed and marketed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group aimed at novel applications in the healthcare, fitness, beacons, security, and home entertainment industries. Compared to Classic Bluetooth, Bluetooth Low Energy is intended to provide considerably reduced power consumption and cost while maintaining a similar communication range.
Mobile security, or mobile device security, is the protection of smartphones, tablets, and laptops from threats associated with wireless computing. It has become increasingly important in mobile computing. The security of personal and business information now stored on smartphones is of particular concern.
Bluetooth beacons are hardware transmitters — a class of Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) devices that broadcast their identifier to nearby portable electronic devices. The technology enables smartphones, tablets and other devices to perform actions when in close proximity to a beacon.
A microphone blocker is a phone microphone connector used to trick feature phones that have a physical microphone switch to disconnect the microphone. Microphone blockers won't operate on smartphones or laptops because the microphone is controlled with software rather than a physical switch.











