Related Research Articles

The Mandelbrot set is a two-dimensional set with a relatively simple definition that exhibits great complexity, especially as it is magnified. It is popular for its aesthetic appeal and fractal structures. The set is defined in the complex plane as the complex numbers for which the function does not diverge to infinity when iterated starting at , i.e., for which the sequence , , etc., remains bounded in absolute value.

Oscar Zariski was a Russian-born American mathematician and one of the most influential algebraic geometers of the 20th century.

Eugenio Calabi was an Italian-born American mathematician and the Thomas A. Scott Professor of Mathematics at the University of Pennsylvania, specializing in differential geometry, partial differential equations and their applications.

Pierre Joseph Louis Fatou was a French mathematician and astronomer. He is known for major contributions to several branches of analysis. The Fatou lemma and the Fatou set are named after him.
Complex dynamics, or holomorphic dynamics, is the study of dynamical systems obtained by iterating a complex analytic mapping. This article focuses on the case of algebraic dynamics, where a polynomial or rational function is iterated. In geometric terms, that amounts to iterating a mapping from some algebraic variety to itself. The related theory of arithmetic dynamics studies iteration over the rational numbers or the p-adic numbers instead of the complex numbers.

Adrien Douady was a French mathematician born in La Tronche, Isère. He was the son of Daniel Douady and Guilhen Douady.
An external ray is a curve that runs from infinity toward a Julia or Mandelbrot set. Although this curve is only rarely a half-line (ray) it is called a ray because it is an image of a ray.
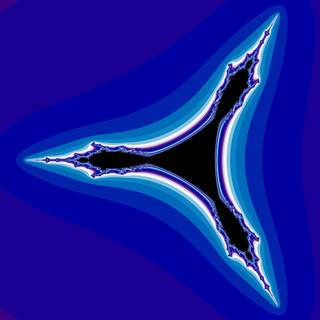
In mathematics, the tricorn, sometimes called the Mandelbar set, is a fractal defined in a similar way to the Mandelbrot set, but using the mapping instead of used for the Mandelbrot set. It was introduced by W. D. Crowe, R. Hasson, P. J. Rippon, and P. E. D. Strain-Clark. John Milnor found tricorn-like sets as a prototypical configuration in the parameter space of real cubic polynomials, and in various other families of rational maps.
The filled-in Julia set of a polynomial is a Julia set and its interior, non-escaping set.
A complex quadratic polynomial is a quadratic polynomial whose coefficients and variable are complex numbers.
Arithmetic dynamics is a field that amalgamates two areas of mathematics, dynamical systems and number theory. Part of the inspiration comes from complex dynamics, the study of the iteration of self-maps of the complex plane or other complex algebraic varieties. Arithmetic dynamics is the study of the number-theoretic properties of integer, rational, p-adic, or algebraic points under repeated application of a polynomial or rational function. A fundamental goal is to describe arithmetic properties in terms of underlying geometric structures.
The mathematical disciplines of combinatorics and dynamical systems interact in a number of ways. The ergodic theory of dynamical systems has recently been used to prove combinatorial theorems about number theory which has given rise to the field of arithmetic combinatorics. Also dynamical systems theory is heavily involved in the relatively recent field of combinatorics on words. Also combinatorial aspects of dynamical systems are studied. Dynamical systems can be defined on combinatorial objects; see for example graph dynamical system.
The Danish Mathematical Society is a society of Danish mathematicians founded in 1873 at the University of Copenhagen, a year after the French Mathematical Society. According to the society website, it has "the purpose of acting for the benefit of mathematics in research and education."
Hans Vilhem Rådström (1919–1970) was a Swedish mathematician who worked on complex analysis, continuous groups, convex sets, set-valued analysis, and game theory. From 1952, he was lektor at Stockholm University, and from 1969, he was Professor of Applied Mathematics at Linköping University.
Böttcher's equation, named after Lucjan Böttcher, is the functional equation

Tamar Debora Ziegler is an Israeli mathematician known for her work in ergodic theory, combinatorics and number theory. She holds the Henry and Manya Noskwith Chair of Mathematics at the Einstein Institute of Mathematics at the Hebrew University.

Nessim Sibony was a French mathematician, specializing in the theory of several complex variables and complex dynamics in higher dimension. Since 1981, he was professor at the University of Paris-Sud in Orsay.
Leifur Ásgeirsson was the first Icelandic mathematician to gain major international recognition.
Anna Maria Zdunik is a Polish mathematician. She specializes in dynamical systems, and is a professor at the University of Warsaw.
The Icelandic Mathematical Society is the umbrella organization for mathematicians in Iceland. As of 2017, the Society has nearly 300 members. It is based in Reykjavik and hosts several conferences related to mathematics.
References
- 1 2 3 Hjorth, Poul G. (June 2012), "Interview with Bodil Branner", Newsletter of the European Mathematical Society , 84, archived from the original on 2015-02-17, retrieved 2015-02-17
- ↑ Munkholm, Hans Jørgen (February 5, 2002), Bodil Branner og Dansk Matematisk Forening (in Danish), retrieved 2015-02-16.
- ↑ Hjorth, Poul G.; Petersen, Carsten Lunde (2006), Dynamics on the Riemann sphere: A Bodil Branner Festschrift, Including papers from the Symposium on Holomorphic Dynamics held in Holbæk, June 2003, Zürich: European Mathematical Society (EMS), doi:10.4171/011, ISBN 3-03719-011-6, MR 2348951 .
- ↑ List of Fellows of the American Mathematical Society, retrieved 2015-02-16.