
The economy of Uzbekistan was formerly associated with a Soviet-style command economy, with a slow transformation to a market economy. However, in recent years and since the election of President Shavkat Mirziyoyev, Uzbekistan has seen rapid economic and social reform, aimed at boosting growth and transforming Uzbekistan into a true, modern market economy. International Financial Institutions, including EBRD, Asian Development Bank and the World Bank are actively engaging in supporting Uzbekistan's successful reform process and have rapidly increased their presence in the country.
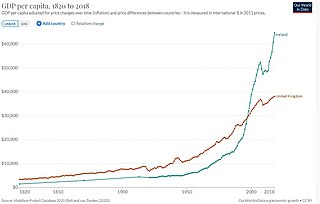
The "Celtic Tiger" is a term referring to the economy of Ireland from the mid-1990s to the late 2000s, a period of rapid real economic growth fuelled by foreign direct investment. The boom was dampened by a subsequent property bubble which resulted in a severe economic downturn.

The Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) is a department of His Majesty's Government in the United Kingdom responsible for environmental protection, food production and standards, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in the entire United Kingdom. Concordats set out agreed frameworks for co operation, between it and the Scottish Government, Welsh Government and Northern Ireland Executive, which have devolved responsibilities for these matters in their respective nations.
Bord na Móna is a semi-state company in Ireland, created in 1946 by the Turf Development Act 1946. The company began developing the peatlands of Ireland with the aim to provide economic benefit for Irish Midland communities and achieve security of energy supply for the recently formed Irish Republic. The development of peatlands involved the mechanised harvesting of peat, which took place primarily in the Midlands of Ireland.
International Consumer Research & Testing (ICRT) is a global consortium of more than 40 consumer organisations dedicated to carrying out joint research and testing in the consumer interest.

St. James's Gate Brewery is a brewery founded in 1759 in Dublin, Ireland, by Arthur Guinness. The company is now a part of Diageo, a company formed from the merger of Guinness and Grand Metropolitan in 1997. The main product of the brewery is Draught Guinness.

Ardrahan Farmhouse Cheese creates two varieties of cheese. They originate from Ardrahan Farmhouse, Kanturk, County Cork in Ireland. The two varieties are Ardrahan and Duhallow. Eugene and Mary Burns first made Ardrahan cheese on their farm in County Cork in 1983 using traditional techniques. Both varieties are made entirely from the milk of the Burnses' cow herd, which is composed of Friesian cows.

The economy of Northern Ireland is the smallest of the four constituents of the United Kingdom and the smaller of the two jurisdictions on the island of Ireland. At the time of the Partition of Ireland in 1922, and for a period afterwards, Northern Ireland had a predominantly industrial economy, most notably in shipbuilding, rope manufacture and textiles, but most heavy industry has since been replaced by services. Northern Ireland's economy has strong links to the economies of the Republic of Ireland and Great Britain.
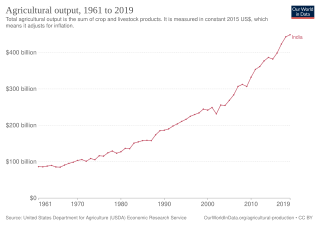
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic period. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2020 -21, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 20.2% to the country's GDP.
The primary natural resources of the Republic of Ireland include natural gas, petroleum, peat, copper, lead, dolomite, barite, limestone, gypsum, silver and zinc. Key industries based on these and other natural resources include fishing, mining, and various forms of agriculture and fish farming. The Department of Communications, Energy and Natural Resources is charged with the legislative protection of Ireland's natural resources.
AHDB Potatoes, previously known as the Potato Council, is a trade organisation that aims to develop and promote the potato industry in Great Britain. Previously an independent non-departmental public body, it has been a division of the Agriculture and Horticulture Development Board since 1 April 2008.

Fáilte Ireland is the operating name of the National Tourism Development Authority of Ireland. This authority was established under the National Tourism Development Authority Act of 2003 to replace and build upon the functions of Bord Fáilte, its predecessor organisation. The organisation was established to support the development and promotion of tourism in Ireland, and it undertakes tourism marketing, training and research activities.
The Meat and Livestock Commission, (MLC), was set up by the UK Government under the Agriculture Act 1967 with government money with the remit to promote the sale of red meat. The MLC was previously an independent non-departmental public body, but from 1 April 2008 it was superseded by the Agriculture and Horticulture Development Board.

Organic farming is practiced around the globe, but the markets for sale are strongest in North America and Europe, while the greatest dedicated area is accounted for by Australia, the greatest number of producers are in India, and the Falkland Islands record the highest share of agricultural land dedicated to organic production.
By 2008 Christmas tree production in Denmark totalled around 9 million trees and Denmark was one of Europe's largest producers of natural Christmas trees. By far the most popular species grown in Denmark is the sought after Nordmann fir. Between 1999 and 2007 Danish tree production jumped from 6-7 million trees annually to 9-12 million trees annually. In 2009 the Danish Christmas Tree Growers Association (DCTGA) was convicted in a price fixing scheme that resulted in fines for the association and its executives.

Greyhound Racing Ireland is an Irish semi-state body charged with regulating and promoting Greyhound racing in Ireland. The organisation has been active in developing the sport in Ireland since its founding on 11 July 1958.

The economy of the Republic of Ireland is a highly developed knowledge economy, focused on services in high-tech, life sciences, financial services and agribusiness, including agrifood. Ireland is an open economy, and ranks first for high-value foreign direct investment (FDI) flows. In the global GDP per capita tables, Ireland ranks 2nd of 192 in the IMF table and 4th of 187 in the World Bank ranking.

Anna Maria Agnes "Agnes" van Ardenne-Van der Hoeven is a retired Dutch politician and diplomat of the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA).
Safefood, stylised safefood, is the public body responsible for raising consumer awareness of issues relating to food safety and healthy eating across the island of Ireland. Founded in 1999, Safefood is one of six North-South implementation bodies established jointly by the British and Irish governments under the terms of the British-Irish Agreement Act.

Agriculture in Ireland began during the neolithic era, when inhabitants of the island began to practice animal husbandry and farming grains. Principal crops grown during the neolithic era included barley and wheat.












