
In geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four edges (sides) and four corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words quadri, a variant of four, and latus, meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, derived from Greek "tetra" meaning "four" and "gon" meaning "corner" or "angle", in analogy to other polygons. Since "gon" means "angle", it is analogously called a quadrangle, or 4-angle. A quadrilateral with vertices , , and is sometimes denoted as .

In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal ; or a parallelogram containing a right angle. A rectangle with four sides of equal length is a square. The term "oblong" is used to refer to a non-square rectangle. A rectangle with vertices ABCD would be denoted as ABCD.

In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if their intersection forms right angles at the point of intersection called a foot. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the perpendicular symbol, ⟂. Perpendicular intersections can happen between two lines, between a line and a plane, and between two planes.

In geometry, bisection is the division of something into two equal or congruent parts. Usually it involves a bisecting line, also called a bisector. The most often considered types of bisectors are the segment bisector, a line that passes through the midpoint of a given segment, and the angle bisector, a line that passes through the apex of an angle . In three-dimensional space, bisection is usually done by a bisecting plane, also called the bisector.
In Euclidean geometry, Brahmagupta's formula, named after the 7th century Indian mathematician, is used to find the area of any cyclic quadrilateral given the lengths of the sides. Its generalized version, Bretschneider's formula, can be used with non-cyclic quadrilateral. Heron's formula can be thought as a special case of the Brahmagupta's formula for triangles.

In Euclidean geometry, a cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. This circle is called the circumcircle or circumscribed circle, and the vertices are said to be concyclic. The center of the circle and its radius are called the circumcenter and the circumradius respectively. Other names for these quadrilaterals are concyclic quadrilateral and chordal quadrilateral, the latter since the sides of the quadrilateral are chords of the circumcircle. Usually the quadrilateral is assumed to be convex, but there are also crossed cyclic quadrilaterals. The formulas and properties given below are valid in the convex case.

In geometry, a trapezoid in North American English, or trapezium in British English, is a quadrilateral that has at least one pair of parallel sides.
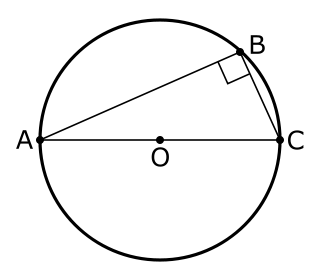
In geometry, Thales's theorem states that if A, B, and C are distinct points on a circle where the line AC is a diameter, the angle ∠ ABC is a right angle. Thales's theorem is a special case of the inscribed angle theorem and is mentioned and proved as part of the 31st proposition in the third book of Euclid's Elements. It is generally attributed to Thales of Miletus, but it is sometimes attributed to Pythagoras.

In geometry, an isosceles triangle is a triangle that has two sides of equal length. Sometimes it is specified as having exactly two sides of equal length, and sometimes as having at least two sides of equal length, the latter version thus including the equilateral triangle as a special case. Examples of isosceles triangles include the isosceles right triangle, the golden triangle, and the faces of bipyramids and certain Catalan solids.
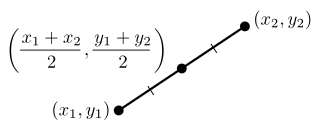
In geometry, the midpoint is the middle point of a line segment. It is equidistant from both endpoints, and it is the centroid both of the segment and of the endpoints. It bisects the segment.

In geometry, a set of points are said to be concyclic if they lie on a common circle. A polygon whose vertices are concyclic is called a cyclic polygon, and the circle is called its circumscribing circle or circumcircle. All concyclic points are equidistant from the center of the circle.
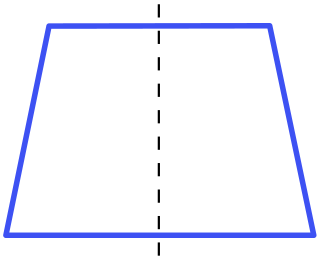
In Euclidean geometry, an isosceles trapezoid is a convex quadrilateral with a line of symmetry bisecting one pair of opposite sides. It is a special case of a trapezoid. Alternatively, it can be defined as a trapezoid in which both legs and both base angles are of equal measure, or as a trapezoid whose diagonals have equal length. Note that a non-rectangular parallelogram is not an isosceles trapezoid because of the second condition, or because it has no line of symmetry. In any isosceles trapezoid, two opposite sides are parallel, and the two other sides are of equal length, and the diagonals have equal length. The base angles of an isosceles trapezoid are equal in measure.
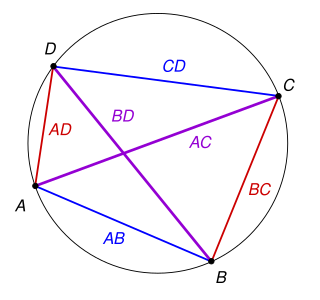
In Euclidean geometry, Ptolemy's theorem is a relation between the four sides and two diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral. The theorem is named after the Greek astronomer and mathematician Ptolemy. Ptolemy used the theorem as an aid to creating his table of chords, a trigonometric table that he applied to astronomy.
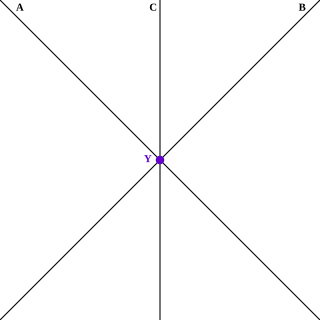
In geometry, lines in a plane or higher-dimensional space are concurrent if they intersect at a single point.

In Euclidean geometry, Varignon's theorem holds that the midpoints of the sides of an arbitrary quadrilateral form a parallelogram, called the Varignon parallelogram. It is named after Pierre Varignon, whose proof was published posthumously in 1731.
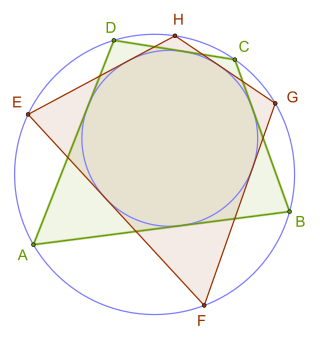
In Euclidean geometry, a bicentric quadrilateral is a convex quadrilateral that has both an incircle and a circumcircle. The radii and centers of these circles are called inradius and circumradius, and incenter and circumcenter respectively. From the definition it follows that bicentric quadrilaterals have all the properties of both tangential quadrilaterals and cyclic quadrilaterals. Other names for these quadrilaterals are chord-tangent quadrilateral and inscribed and circumscribed quadrilateral. It has also rarely been called a double circle quadrilateral and double scribed quadrilateral.
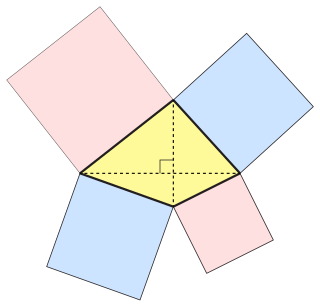
In Euclidean geometry, an orthodiagonal quadrilateral is a quadrilateral in which the diagonals cross at right angles. In other words, it is a four-sided figure in which the line segments between non-adjacent vertices are orthogonal (perpendicular) to each other.
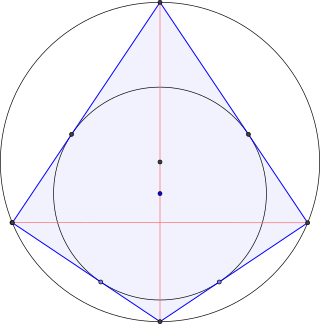
In Euclidean geometry, a right kite is a kite that can be inscribed in a circle. That is, it is a kite with a circumcircle. Thus the right kite is a convex quadrilateral and has two opposite right angles. If there are exactly two right angles, each must be between sides of different lengths. All right kites are bicentric quadrilaterals, since all kites have an incircle. One of the diagonals divides the right kite into two right triangles and is also a diameter of the circumcircle.
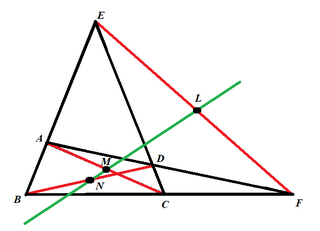
In geometry, the Newton–Gauss line is the line joining the midpoints of the three diagonals of a complete quadrilateral.
In Euclidean geometry, a harmonic quadrilateral, or harmonic quadrangle, is a quadrilateral that can be inscribed in a circle in which the products of the lengths of opposite sides are equal. It has several important properties.
![B
M
-
[?]
A
C
-
,
E
F
-
[?]
B
C
-
{\displaystyle {\overline {BM}}\perp {\overline {AC}},{\overline {EF}}\perp {\overline {BC}}}
=
|
A
F
-
|
=
|
F
D
-
|
{\displaystyle \Rightarrow |{\overline {AF}}|=|{\overline {FD}}|} Brahmaguptra's theorem.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/64/Brahmaguptra%27s_theorem.svg/220px-Brahmaguptra%27s_theorem.svg.png)




















