Related Research Articles
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating systems as a set of processes and services. Initially, Active Directory was used only for centralized domain management. However, Active Directory eventually became an umbrella title for a broad range of directory-based identity-related services.

Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and oriented towards businesses. It was the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0, and was released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999, and was officially released to retail on February 17, 2000. It was Microsoft's business operating system until the introduction of Windows XP in 2001.
Windows Server 2003 is the third version of Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft. It is part of the Windows NT family of operating systems and was released on April 24, 2003. Derived from the Windows XP operating system, Windows Server 2003 is the successor to Windows 2000 Server and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008. An updated version, Windows Server 2003 R2, was released to manufacturing on December 6, 2005.
Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) is a Windows service that enables one Internet-connected computer to share its Internet connection with other computers on a local area network (LAN). The computer that shares its Internet connection serves as a gateway device, meaning that all traffic between other computers and the Internet go through this computer. ICS provides Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and network address translation (NAT) services for the LAN computers.

In computing, netstat is a command-line network utility that displays network connections for Transmission Control Protocol, routing tables, and a number of network interface and network protocol statistics. It is available on Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems including macOS, Linux, Solaris and BSD. It is also available on IBM OS/2 and on Microsoft Windows NT-based operating systems including Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 10.
On Microsoft Servers, a domain controller (DC) is a server computer that responds to security authentication requests within a Windows domain. A domain is a concept introduced in Windows NT whereby a user may be granted access to a number of computer resources with the use of a single username and password combination.
Flexible Single Master Operations, or just single master operation or operations master, is a feature of Microsoft's Active Directory (AD). As of 2005, the term FSMO has been deprecated in favour of operations masters.

Group Policy is a feature of the Microsoft Windows NT family of operating systems that controls the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. Group Policy provides centralized management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and users' settings in an Active Directory environment. A set of Group Policy configurations is called a Group Policy Object (GPO). A version of Group Policy called Local Group Policy allows Group Policy Object management without Active Directory on standalone computers.
Remote administration refers to any method of controlling a computer from a remote location. Software that allows remote administration is becoming increasingly common and is often used when it is difficult or impractical to be physically near a system in order to use it. A remote location may refer to a computer in the next room or one on the other side of the world. It may also refer to both legal and illegal remote administration.

Messenger service is a network-based system notification Windows service by Microsoft that was included in some earlier versions of Microsoft Windows.
My Network Places is the network browser feature in Windows Explorer. It was first introduced in Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0 and was renamed My Network Places in Windows 2000 and later.
As the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000, as well as the successor to Windows Me, Windows XP introduced many new features but it also removed some others.
The Windows NT booting process is the process by which Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 operating systems initialize. In Windows Vista and later, this process has changed significantly; see Windows NT 6 startup process for information about what has changed.
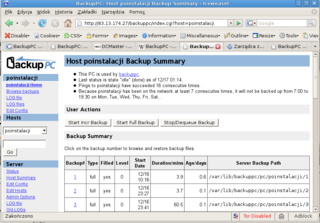
BackupPC is a free disk-to-disk backup software suite with a web-based frontend. The cross-platform server will run on any Linux, Solaris, or UNIX-based server. No client is necessary, as the server is itself a client for several protocols that are handled by other services native to the client OS. In 2007, BackupPC was mentioned as one of the three most well known open-source backup software, even though it is one of the tools that are "so amazing, but unfortunately, if no one ever talks about them, many folks never hear of them".
NTBackup is the built-in backup application introduced in Windows NT 3.51 and included in Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003. NTBackup comprises a command-line utility and a set of wizard interfaces that provide multiple options to create, customize, and manage backups, and it is integrated with Shadow Copy and Task Scheduler. NTBackup creates backups in a proprietary BKF file format to external sources including floppy disks, hard drives, tape drives, and ZIP drives.
Inter-domain routing is data flow control and interaction between Primary Domain Controller (PDC) computers. This type of computer uses various computer protocols and services to operate. It is most commonly used to multicast between internet domains.
The Domain Master Browser is necessary on a routed TCP/IP network, that is, when a Windows domain spans more than one TCP/IP network. When a Windows domain spans multiple subnets each of the subnets has an independent browser called the Master Browser. The Master Browser is responsible for the browse list within its respective subnet and portion of the domain on its subnet. The Domain Master Browser is used to collect information from each of the Master Browsers via the NetServerEnum API call. Once collected the list is merged with the Domain Master Browsers list for its own subnet. This merged list forms the enterprise wide browse list for the domain. This merged list is then distributed to the Master Browsers in each subnet so that the enterprise list can be available to computers requesting services.
A roaming user profile is a file synchronization concept in the Windows NT family of operating systems that allows users with a computer joined to a Windows domain to log on to any computer on the same domain and access their documents and have a consistent desktop experience, such as applications remembering toolbar positions and preferences, or the desktop appearance staying the same, while keeping all related files stored locally, to not continuously depend on a fast and reliable network connection to a file server.
A domain controller (DC) is a server computer that responds to security authentication requests within a computer network domain. It is a network server that is responsible for allowing host access to domain resources. It authenticates users, stores user account information and enforces security policy for a domain. It is most commonly implemented in Microsoft Windows environments, where it is the centerpiece of the Windows Active Directory service. However, non-Windows domain controllers can be established via identity management software such as Samba and Red Hat FreeIPA.
References
- ↑ "The Elder Geek on Windows XP: Computer Browser Service". Archived from the original on 2008-12-18. Retrieved 2009-01-04.
- ↑ Microsoft: What Is Computer Browser Service?
- 1 2 3 Kesharwani, Mukesh (18 March 2011). "Understand the Computer Browser Service" . Retrieved 19 June 2013.