
Aeclanum was an ancient town of Samnium, Southern Italy, about 25 km east-southeast of Beneventum, on the Via Appia. It lies in Passo di Mirabella, near the modern Mirabella Eclano.

Capua is a city and comune in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated 25 km (16 mi) north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.

The Osci were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum before and during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the language of the Samnites was called Oscan, the Samnites were never referred to as Osci, nor were the Osci called Samnites.
Monte Massico is a mountain situated in the Italian Province of Caserta (Campania) between the rivers Volturno and Garigliano.

Grumentum was an ancient Roman city in the centre of Lucania, in what is now the comune of Grumento Nova, c. 50 km (31 mi) south of Potenza by the direct road through Anxia, and 80 km (50 mi) by the Via Herculia, at the point of divergence of a road eastward to Heraclea.

Ferentino is a town and comune in Italy, in the province of Frosinone, Lazio, 65 kilometres (40 mi) southeast of Rome. It is situated on a hill 400 metres above sea level, in the Monti Ernici area.

Velia was the Roman name of an ancient city of Magna Graecia on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea. It was founded by Greeks from Phocaea as Hyele around 538–535 BC. The name later changed to Ele and then Elea before it became known by its current Latin and Italian name during the Roman era. Its ruins are located in the Cilento region near the modern village Velia, which was named after the ancient city. The village is a frazione of the comune Ascea in the Province of Salerno, Campania, Italy.

Teano is a town and comune in the province of Caserta, Campania, southern Italy, 30 kilometres (19 mi) northwest of Caserta on the main line to Rome from Naples. It stands at the southeast foot of an extinct volcano, Rocca Monfina. Its St. Clement's cathedral is the see of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Teano-Calvi, which started as the Diocese of Teano circa AD 300.

Caere is the Latin name given by the Romans to one of the larger cities of southern Etruria, the modern Cerveteri, approximately 50–60 kilometres north-northwest of Rome. To the Etruscans it was known as Cisra, to the Greeks as Agylla and to the Phoenicians as 𐤊𐤉𐤔𐤓𐤉𐤀.

Sessa Aurunca is a town and comune in the province of Caserta, Campania, southern Italy. It is located on the south west slope of the extinct volcano of Roccamonfina, 40 kilometres (25 mi) by rail west north west of Caserta and 30 kilometres (19 mi) east of Formia.
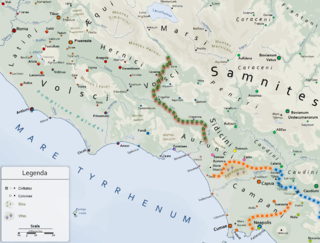
The Aurunci were an Italic tribe that lived in southern Italy from around the 1st millennium BC. They were eventually defeated by Rome and subsumed into the Roman Republic during the second half of the 4th century BC.
Suessula was an ancient city of Campania, southern Italy, situated in the interior of the peninsula, near the frontier with Samnium, between Capua and Nola, and about 7 km northeast of Acerrae, Suessula is now a vanished city and the archeological site belongs to the city of Acerra, and not to San Felice a Cancello as reported in some sources.

Latium adiectum or Latium Novum was a region of Roman Italy between Monte Circeo and the river Garigliano, south of and immediately adjacent to Old Latium, hence its name of attached Latium.
Telese Terme, called simply Telese until 1991, is a city, comune (municipality) and former episcopal seat in the Province of Benevento, in the Campania region of southern Italy. It is located in the valley of the Calore, well known for its sulfuric hot springs.

"Ausones", the original name and the extant Greek form for the Latin "Aurunci", was a name applied by Greek writers to describe various Italic peoples inhabiting the southern and central regions of Italy. The term was used, specifically, to denote the particular tribe which Livy called the Aurunci, but later it was applied to all Italians, and Ausonia became a poetic term, in Greek and Latin, for Italy itself.

Ausonia is a town and comune in southern Lazio, central Italy. It takes its name from the Ausones/Aurunci, whose ancient town Ausona, located nearby, was destroyed by the Romans in 314 BC. In the Middle Ages it was known as Fratte.

Circeii was an ancient Roman city on the site of modern San Felice Circeo and near Mount Circeo, the mountain promontory on the southwest coast of Italy. The area around Circeii and Mount Circeo was thickly populated with Roman villas and other buildings, of which the remains of many can still be seen.

Nola is a town and a municipality in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania, southern Italy. It lies on the plain between Mount Vesuvius and the Apennines. It is traditionally credited as the diocese that introduced bells to Christian worship.
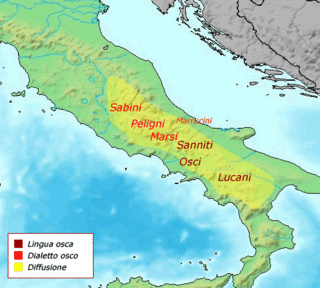
The Campanians were an ancient Italic tribe, part of the Osci nation, speaking an Oscan language.
The Sidicini were one of the Italic peoples of ancient Italy. Their territory extended northward from their capital, Teanum Sidicinum, along the valley of the Liri river up to Fregellae, covering around 3,000 square kilometres in total. They were neighbors of the Samnites and Campanians, and allies of the Ausones and Aurunci. Their language was a part of the Osco-Umbrian linguistic family.



















