
The German Shepherd, also known in Britain as an Alsatian, is a German breed of working dog of medium to large size. The breed was developed by Max von Stephanitz using various traditional German herding dogs from 1899.

The Flat-coated Retriever is a gundog breed originating from England. It was developed as a retriever both on land and in the water.

In dogs, hip dysplasia is an abnormal formation of the hip socket that, in its more severe form, can eventually cause lameness and arthritis of the joints. It is a genetic (polygenic) trait that is affected by environmental factors. It is common in many dog breeds, particularly the larger breeds, and is the most common single cause of arthritis of the hips.

A therapy dog is a dog that is trained to provide affection, comfort and support to people, often in settings such as hospitals, retirement homes, nursing homes, schools, libraries, hospices, or disaster areas. In contrast to assistance dogs, which are trained to assist specific patients with their day-to-day physical needs, therapy dogs are trained to interact with all kinds of people, not just their handlers.
Laryngeal paralysis in animals is a condition in which the nerves and muscles that control the movements of one or both arytenoid cartilages of the larynx cease to function, and instead of opening during aspiration and closing during swallowing, the arytenoids remain stationary in a somewhat neutral position. Specifically, the muscle that causes abduction of the arytenoid cartilage, the cricoarytenoideus dorsalis muscle, ceases to function. This leads to inadequate ventilation during exercise and during thermoregulatory panting as well as incomplete protection of the airway during swallowing.

The health of dogs is a well studied area in veterinary medicine.

The Boykin Spaniel is a medium-sized breed of dog, a Spaniel bred for hunting wild turkeys and ducks in the Wateree River Swamp of South Carolina, in the United States. It is the state dog of South Carolina, where it was discovered and further developed by hunters in the 1900s. 1 September, 1984 is Boykin Spaniel Day in South Carolina.
Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is a group of genetic diseases seen in certain breeds of dogs and, more rarely, cats. Similar to retinitis pigmentosa in humans, it is characterized by the bilateral degeneration of the retina, causing progressive vision loss culminating in blindness. The condition in nearly all breeds is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, with the exception of the Siberian Husky (inherited as an X chromosome linked trait) and the Bullmastiff (inherited as an autosomal dominant trait). There is no treatment.
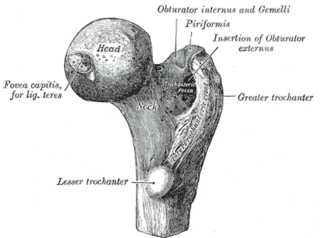
A femoral head ostectomy is a surgical operation to remove the head and neck from the femur. It is performed to alleviate pain, and is a salvage procedure, reserved for condition where pain can not be alleviated in any other way. It is common in veterinary surgery. Other names are excision arthroplasty of the femoral head and neck, Girdlestone's operation, Girdlestone procedure, and femoral head and neck ostectomy.

TPLO, or tibial-plateau-leveling osteotomy, is a surgery performed on dogs to stabilize the stifle joint after ruptures of the cranial cruciate ligament.

Animal-assisted therapy (AAT) is an alternative or complementary type of therapy that includes the use of animals in a treatment. The goal of this animal-assisted intervention is to improve a patient's social, emotional, or cognitive functioning. Studies have documented some positive effects of the therapy on subjective self-rating scales and on objective physiological measures such as blood pressure and hormone levels.

Canine degenerative myelopathy, also known as chronic degenerative radiculomyelopathy, is an incurable, progressive disease of the canine spinal cord that is similar in many ways to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Onset is typically after the age of 7 years and it is seen most frequently in the German shepherd dog, Pembroke Welsh corgi, and boxer dog, though the disorder is strongly associated with a gene mutation in SOD1 that has been found in 43 breeds as of 2008, including the wire fox terrier, Chesapeake Bay retriever, Rhodesian ridgeback, and Cardigan Welsh corgi. Progressive weakness and incoordination of the rear limbs are often the first signs seen in affected dogs, with progression over time to complete paralysis. Myelin is an insulating sheath around neurons in the spinal cord. One proposed cause of degenerative myelopathy is that the immune system attacks this sheath, breaking it down. This results in a loss of communication between nerves in lower body of the animal and the brain.

Cancer is the leading cause of death in dogs. It is estimated that 1 in 3 domestic dogs will develop cancer, which is the same incidence of cancer among humans. Dogs can develop a variety of cancers and most are very similar to those found in humans. Dogs can develop carcinomas of epithelial cells and organs, sarcomas of connective tissues and bones, and lymphomas or leukemias of the circulatory system. Selective breeding of dogs has led certain pure-bred breeds to be at high-risk for specific kinds of cancer.
Aquatic therapy refers to treatments and exercises performed in water for relaxation, fitness, physical rehabilitation, and other therapeutic benefit. Typically a qualified aquatic therapist gives constant attendance to a person receiving treatment in a heated therapy pool. Aquatic therapy techniques include Ai Chi, Aqua Running, Bad Ragaz Ring Method, Burdenko Method, Halliwick, Watsu, and other aquatic bodywork forms. Therapeutic applications include neurological disorders, spine pain, musculoskeletal pain, postoperative orthopedic rehabilitation, pediatric disabilities, and pressure ulcers.

Veterinary chiropractic, also known as animal chiropractic, is chiropractic for animals – a type of spinal manipulation. Veterinary chiropractors typically treat horses, racing greyhounds, and pets. Veterinary chiropractic is a controversial method due to a lack of evidence as to the efficacy of chiropractic methods. Contrary to traditional medicine, chiropractic therapies are alternative medicine. There is some degree of risk associated with even skilled manipulation in animals as the potential for injury exists with any technique used. The founder of chiropractic, Daniel David Palmer, used the method on animals, partly to challenge claims that the placebo effect was responsible for favorable results in humans. Chiropractic treatment of large animals dates back to the early 1900s. As of 2019, many states in the US provide statutory or regulatory guidelines for the practice of chiropractic and related treatments on animals, generally requiring some form of veterinary involvement.

Physical therapy for canines adapts human physical therapy techniques to increase function and mobility of joints and muscles in animals. Animal rehabilitation can reduce pain and enhance recovery from injury, surgery, degenerative diseases, age-related diseases, and obesity.
Canine massage is a branch of massage therapy that promotes health in dogs. Specifically, canine massage therapy is a form of alternative therapy the benefits of which may include relaxation, increased oxygenation, relief from pain, improved joint flexibility, as well as miscellaneous benefits to the immune system. It uses touch to maintain or improve both physical and emotional well-being. However, be careful and make sure to consult with your vet before attempting to massage your dog yourself.
The treatment of equine lameness is a complex subject. Lameness in horses has a variety of causes, and treatment must be tailored to the type and degree of injury, as well as the financial capabilities of the owner. Treatment may be applied locally, systemically, or intralesionally, and the strategy for treatment may change as healing progresses. The end goal is to reduce the pain and inflammation associated with injury, to encourage the injured tissue to heal with normal structure and function, and to ultimately return the horse to the highest level of performance possible following recovery.
Simitri Stable in Stride is a three part modular surgical implant used during surgery performed on dogs to stabilize the stifle joint (knee) after rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament (CrCL) which is analogous to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in humans.














