Related Research Articles

The Spanish Navy or officially, the Armada, is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, the most famous being the discovery of America and the first global circumnavigation by Elcano. For several centuries, it played a crucial logistical role in the expansion and consolidation of the Spanish Empire, and defended a vast trade network across the Atlantic Ocean between the Americas and Europe, and the Manila Galleon across the Pacific Ocean between the Philippines and the Americas.

The Spanish Republic, historiographically referred to as the First Spanish Republic, was the political regime that existed in Spain from 11 February 1873 to 29 December 1874.

Mazarrón is a municipality in the autonomous community and province of Murcia, southeastern Spain. The municipality has an area of 318.7 square kilometres (123.1 sq mi), and a population of 31,562 inhabitants in 2019. A military fort built between 1930 and 1936 during the reign of Alfonso XIII of Spain and the Second Spanish Republic exists as a tourist attraction on the old road between Mazarrón and Cartagena, and although it is accessible from the Bay of Mazarrón it is not in the municipality itself.

The Region of Murcia, is an autonomous community of Spain located in the southeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Mediterranean coast. The region is 11,313 km2 (4,368 sq mi) in area and had a population of 1,511,251 as at the start of 2020. About one-third of its population lives in the capital, Murcia. At 2,014 m (6,608 ft), the region's highest point is Los Obispos Peak in the Massif of Revolcadores.

The action of 15 July 1798 was a minor naval battle of the French Revolutionary Wars, fought off the Spanish Mediterranean coast by the Royal Navy ship of the line HMS Lion under Captain Manley Dixon and a squadron of four Spanish Navy frigates under Commodore Don Felix O'Neil. Lion was one of several ships sent into the Western Mediterranean by Vice-Admiral Earl St Vincent, commander of the British Mediterranean Fleet based at the Tagus in Portugal during the late spring of 1798. The Spanish squadron was a raiding force that had sailed from Cartagena in Murcia seven days earlier, and was intercepted while returning to its base after an unsuccessful cruise. Although together the Spanish vessels outweighed the British ship, individually they were weaker and Commodore O'Neil failed to ensure that his manoeuvres were co-ordinated. As a result, one of the frigates, Santa Dorotea, fell out of the line of battle and was attacked by Lion.

The invasion of Algiers was a massive and disastrous amphibious attempt in July 1775 by a combined Spanish and Tuscan force to capture the city of Algiers, the capital of The Deylik of Algeria. The amphibious assault was led by Spanish general Alexander O'Reilly and Tuscan admiral Sir John Acton, commanding a total of 20,000 men along with 74 warships of various sizes and 230 transport ships carrying the troops for the invasion. The defending Algerian forces were led by Baba Mohammed ben-Osman. The assault was ordered by the King of Spain, Charles III, who was attempting to demonstrate to the Barbary States the power of the revitalized Spanish military after the disastrous Spanish experience in the Seven Years' War. The assault was also meant to demonstrate that Spain would defend its North African exclaves against any Ottoman or Moroccan encroachment, and reduce the influence that the Barbary states held in the Mediterranean.
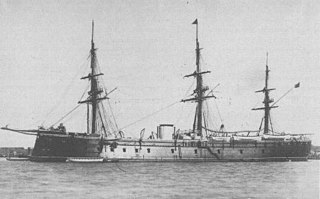
The Spanish ironclad Numancia was an armored frigate bought from France during the 1860s for service with the Royal Spanish Navy. The name was derived from the Siege of Numantia, in which Roman expansion in the Iberian Peninsula was resisted. She was the first ironclad to circumnavigate the Earth. She saw service in the Chincha Islands War and Cantonal Revolution.

The Spanish ironclad Tetuán was an armored frigate built in the royal dockyard at Ferrol during the 1860s for the Spanish Navy. She was captured by rebels during the Cantonal Revolution in 1873 and participated in the Battle off Cartagena. While under repair after the battle, the ship was destroyed by fire and broken up in 1874.

The Spanish ironclad Vitoria was an iron-hulled armored frigate purchased from England during the 1860s. The ship participated on both sides during the Cantonal rebellion of 1873–1874, first on the rebel side and then after her crew surrendered to neutral warships, on the government side. She played a major role in the Battle off Cartagena for the government. Vitoria bombarded rebel towns from 1874 to 1876 during the Third Carlist War. The ship was reconstructed in the late 1890s and reclassified as a coast-defense ship, although she served as a training ship until she was scrapped in 1912.

The Spanish ironclad Méndez Núñez was a wooden-hulled armored corvette converted from the 38-gun, steam-powered frigate Resolución during the 1860s after the ship was badly damaged during the Chincha Islands War of 1864–1866. She was captured by rebels during the Cantonal Revolution in 1873 and participated in the Battle off Cartagena before she was returned to government control after Cartagena surrendered in early 1874. The ship was stricken from the Navy List in 1886 and broken up ten years later.

SMS Friedrich Carl was an ironclad warship built for the Prussian Navy in the mid-1860s. The ship was constructed in the French Societé Nouvelles des Forges et Chantiers shipyard in Toulon; her hull was laid in 1866 and launched in January 1867. The ship was commissioned into the Prussian Navy in October 1867. The ship was the third ironclad ordered by the Prussian Navy, after Arminius and Prinz Adalbert, though the fourth ship to be acquired, Kronprinz, was ordered after but commissioned before Friedrich Carl.
Reinhold von Werner was a Prussian and later Imperial German naval officer in the 19th century, eventually reaching the rank of vice admiral. He commanded warships during the three wars of German Unification, the Second Schleswig War, the Austro-Prussian War, and the Franco-Prussian War in 1864, 1866, and 1870–1871, respectively, and during a naval intervention during a revolution in Spain in 1873. His actions off Spain, considered extreme by Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, resulted in his court-martial. He was promoted two years after the intervention in Spain, but was forced into retirement after a major feud with Albrecht von Stosch three years later. Werner wrote numerous books during and after his naval career, and also founded a periodical on maritime topics. He was ennobled in 1901 and died in February 1909.

The Cantonal rebellion was a cantonalist insurrection that took place during the First Spanish Republic between July 1873 and January 1874. Its protagonists were the "intransigent" federal Republicans, who wanted to establish immediately the Federal Republic from the bottom-up without waiting for the Constituent Cortes to draft and approve the new Federal Constitution, as defended by the president of the Executive Power of the Republic Francisco Pi y Margall, a Proudhonian Mutualist supported by the "centrist" and "moderate" sectors of the Federal Democratic Republican Party.
The Capture of the galleon San Joaquin or the Battle of Cartagena was a naval engagement that took place off the coast near Cartagena. It involved five British ships of the line against the Spanish galleon San Joaquin and a smaller ship. After an action lasting barely an hour the Spanish ship surrendered. The galleon had fought in the previous encounter during Wager's Action nearly three years earlier but had just barely escaped capture.
The Croisière de Bruix was the principal naval campaign of the year 1799 during the French Revolutionary Wars. The expedition began in April 1799 when the bulk of the French Atlantic Fleet under Vice-Admiral Étienne Eustache Bruix departed the base at Brest, evading the British Channel Fleet which was blockading the port and tricking the commander Admiral Lord Bridport into believing their true destination was Ireland. Passing southwards, the French fleet narrowly missed joining with an allied Spanish Navy squadron at Ferrol and was prevented by an easterly gale from uniting with the main Spanish fleet at Cádiz before entering the Mediterranean Sea. The Mediterranean was under British control following the destruction of the French Mediterranean Fleet at the Battle of the Nile in August 1798, and a British fleet nominally under Admiral Earl St Vincent was stationed there. Due however to St. Vincent's ill-health, operational control rested with Vice-Admiral Lord Keith. As Keith sought to chase down the French, the Spanish fleet followed Bruix into the Mediterranean before being badly damaged in a gale and sheltering in Cartagena.
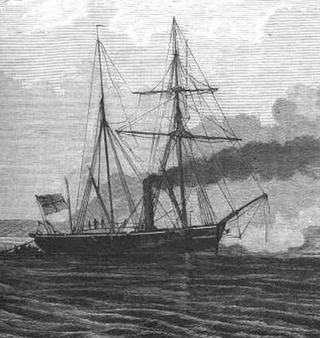
SMS Delphin was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1860. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Delphin served during the Second Schleswig War of 1864 and the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, part of the conflicts that unified Germany. The ship was present at, but was only lightly engaged in the Battle of Jasmund during the Second Schleswig War. The ship spent much of the rest of her career in the Mediterranean Sea, going on three lengthy deployments there in 1865–1866, 1867–1870, and 1871–1873. During the last tour, she took part in operations off the coast of Spain with an Anglo-German squadron during the Third Carlist War, where she helped to suppress forces rebelling against the Spanish government. For the rest of the 1870s, she served as a survey vessel in the North and Baltic Seas before being decommissioned in August 1881, stricken from the naval register the following month, and subsequently broken up for scrap.

The Spanish-Algerian war (1775–1785) was a conflict between the Spanish Empire and the Deylik of Algiers.

The Canton of Cartagena, also known as the Canton of Murcia, was a period of Cartagena, Spain's history when it was governed by a radical cantonalist junta for six months between 1873 and 1874. The city rose up in armed insurrection on July 12, 1873 establishing the Canton's de facto independence from the First Spanish Republic and beginning a wave of cantonal rebellions across southern Spain. Loosely inspired by the more well-known Paris Commune two years earlier, the Canton of Cartagena existed during a turbulent revolutionary period of Spanish history known as the Sexenio Democrático.

Salvador Ardil Navarro, better known as Chiky Ardil, is a Spanish beach soccer player who plays as a forward. He has appeared at two editions of the FIFA Beach Soccer World Cup representing the Spanish national team; at the European qualifying tournament for the latter, he won the MVP award. His younger brother, David, also plays for Spain.
Manuel Cárceles Sabater was a Spanish writer, doctor, politician and one of the protagonists of the Cantonal rebellion of 1873 in Cartagena.
References
- 1 2 Barón Fernández, José. (1998). El movimiento cantonal de 1873 : 1a. República (in Spanish). Sada, A Coruña [Spain]: Ediciós do Castro. pp. 184–187. ISBN 84-7492-896-6. OCLC 41431860.
- ↑ "La revuelta cantonal de 1873, la rebelión por una España federal". historia.nationalgeographic.com.es (in Spanish). 2021-01-31. Retrieved 2022-09-29.