Minivan is a car classification for vehicles designed to transport passengers in the rear seating row(s), with reconfigurable seats in two or three rows. The equivalent classification in Europe is MPV or M-segment.

A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some variation in the scope of the word across the different English-speaking countries. The smallest vans, microvans, are used for transporting either goods or people in tiny quantities. Mini MPVs, compact MPVs, and MPVs are all small vans usually used for transporting people in small quantities. Larger vans with passenger seats are used for institutional purposes, such as transporting students. Larger vans with only front seats are often used for business purposes, to carry goods and equipment. Specially equipped vans are used by television stations as mobile studios. Postal services and courier companies use large step vans to deliver packages.

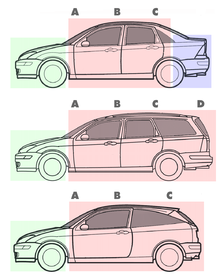
A station wagon or estate car, is an automotive body-style variant of a sedan with its roof extended rearward over a shared passenger/cargo volume with access at the back via a third or fifth door, instead of a trunk/boot lid. The body style transforms a standard three-box design into a two-box design—to include an A, B, and C-pillar, as well as a D-pillar. Station wagons can flexibly reconfigure their interior volume via fold-down rear seats to prioritize either passenger or cargo volume.

A hatchback is a car body configuration with a rear door that swings upward to provide access to the main interior of the car as a cargo area rather than just to a separated trunk. Hatchbacks may feature fold-down second-row seating, where the interior can be reconfigured to prioritize passenger or cargo volume.

The Volkswagen Polo is a supermini car (B-segment) produced by the German car manufacturer Volkswagen since 1975. It is sold in Europe and other markets worldwide in hatchback, saloon, and estate variants throughout its production run.

A sedan or saloon is a passenger car in a three-box configuration with separate compartments for an engine, passengers, and cargo. The first recorded use of sedan in reference to an automobile body occurred in 1912. The name derives from the 17th-century litter known as a sedan chair, a one-person enclosed box with windows and carried by porters. Variations of the sedan style include the close-coupled sedan, club sedan, convertible sedan, fastback sedan, hardtop sedan, notchback sedan, and sedanet.
Governments and private organizations have developed car classification schemes that are used for various purposes including regulation, description, and categorization of cars.
There are many types of car body styles. They vary depending on intended use, market position, location, and the era they were made.

The Volkswagen Type 3 is a compact car manufactured and marketed by Volkswagen from 1961 to 1973. Introduced at the 1961 Frankfurt International Motor Show, the IAA, the Type 3 was marketed as the Volkswagen 1500 and later as the Volkswagen 1600, in two-door Notchback, Fastback, and Variant body styles, the latter marketed as the 'Squareback' in the United States.

A notchback is a car design with the rear section distinct from the passenger compartment and where the back of the passenger compartment is at an angle to the top of what is typically the rear baggage compartment. Notchback cars have "a trunk whose lid forms a distinct deck." In profile view, the body has a step down from the roof with a downward inclined passenger compartment's rear window to meet an almost horizontal trunk lid extending to the rear of the car.

The Chevrolet Lumina APV is a minivan that was produced by the Chevrolet division of General Motors. The first front-wheel drive minivan sold by Chevrolet, the Lumina APV was sold in a single generation from the 1990 to 1996 model years. Marketed alongside the Pontiac Trans Sport and Oldsmobile Silhouette, the Lumina APV competed against the Dodge Grand Caravan/Plymouth Grand Voyager, the extended-length Ford Aerostar, and the Mazda MPV.

The C-segment is the 3rd category of the European segments for passenger cars and is described as "medium cars". It is equivalent to the Euro NCAP "small family car" size class, and the compact car category in the United States.
1995 in motoring includes developments in the automotive industry that occurred throughout the year 1995 by various automobile manufacturers, grouped by country. The automotive industry designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and sells motor vehicles.
1998 in motoring includes developments in the automotive industry that occurred throughout the year 1998 by various automobile manufacturers, grouped by country. The automotive industry designs, develops, manufactures, markets, and sells motor vehicles.
2002 in motoring deals with developments in the automotive industry that occurred throughout the year 2002 by various automobile manufacturers, grouped by country.

A sliding door is a type of door that is mounted on or suspended from a track for the door to slide, usually horizontally and outside. It is a feature predominantly found in minibuses, buses, and vans, so as to allow a large unobstructed access to the interior for loading and unloading of passengers or cargo without the doors interfering with adjacent space.
France was a pioneer in the automotive industry and is the 11th-largest automobile manufacturer in the world by 2015 unit production and the third-largest in Europe. It had consistently been the 4th-largest from the end of World War II up to 2000. It is 16% of sales of French manufactured products.
The VAM Lerma is an automobile that was designed and manufactured by Vehiculos Automotores Mexicanos from 1981 to 1983. The Lerma shared parts with other vehicles by VAM's license partner American Motors (AMC) to reduce manufacturing costs. It was VAM's top-of-the-line flagship model after the discontinuation of the Classic (Matador) line in 1976. The VAM Lerma was unusual in offering a hatchback design focused at the top-end luxury market. The model was an indirect replacement of the VAM Classic and to some extent the VAM Pacer lines.

The Volkswagen Jetta A1 is the first generation of the Volkswagen Jetta compact car, produced by Volkswagen. Although the Golf reached considerable success in the North American markets, Volkswagen observed the hatchback body style lacked some of the appeal to those who preferred the traditional three-box configuration. The styling of the 1970 AMC Gremlin was controversial for truncating the Hornet sedan, but Volkswagen stylists reversed the process by essentially grafting a new trunk onto the tail of the Golf to produce a larger Jetta saloon. The Jetta became the best-selling European car in the United States, Canada and Mexico. Sales were slower in Europe, but were strong enough for Volkswagen to develop future generations of the Jetta.