Winnipeg is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. As of 2021, Winnipeg had a city population of 749,607 and a metropolitan population of 834,678, making it Canada's sixth-largest city and eighth-largest metropolitan area.

The Pas is a town in Manitoba, Canada, at the confluence of the Pasquia River and the Saskatchewan River and surrounded by the unorganized Northern Region of the province. It is approximately 520 km (320 mi) northwest of the provincial capital, Winnipeg, and 35 km (22 mi) from the border of Saskatchewan. It is sometimes still called Paskoyac by locals after the first trading post, called Fort Paskoya and constructed during French colonial rule. The Pasquia River begins in the Pasquia Hills in east central Saskatchewan. The French in 1795 knew the river as Basquiau.

The humidex is an index number used by Canadian meteorologists to describe how hot the weather feels to the average person, by combining the effect of heat and humidity. The term humidex was coined in 1965. The humidex is a nominally dimensionless quantity based on the dew point.

Brandon is the second-largest city in the province of Manitoba, Canada. It is located in the southwestern corner of the province on the banks of the Assiniboine River, approximately 214 km (133 mi) west of the provincial capital, Winnipeg, and 120 km (75 mi) east of the Saskatchewan border. Brandon covers an area of 77.41 km2 (29.89 sq mi) with a population of 51,313, and a census metropolitan area population of 54,268. It is the primary hub of trade and commerce for the Westman Region as well as parts of southeastern Saskatchewan and northern North Dakota, an area with a combined population of over 190,000 people.

Flin Flon is a mining city, located on a correction line on the border of the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan, with the majority of the city located within Manitoba. Residents thus travel southwest into Saskatchewan, and northeast into Manitoba. The city is incorporated in and is jointly administered by both provinces.
Lynn Lake is a town in the northwest region of Manitoba, Canada, approximately 1,071 km (665 mi) from Winnipeg. The town is the fourth-largest town in Manitoba in terms of land area. It is centred on the original urban community of Lynn Lake. The town was named after Lynn Smith, chief engineer of Sherritt Gordon Mines Ltd. There are many outfitters in the Lynn Lake area, offering services for most wilderness experiences, including sport fishing and bear and moose hunting.

Dauphin is a city in Manitoba, Canada, with a population of 8,368 as of the 2021 Canadian Census, with an additional 2,136 living in the surrounding Rural Municipality of Dauphin (RM), for a total of 10,504 in the RM and city combined. The city takes its name from Lake Dauphin and Fort Dauphin, which were named by explorer Pierre Gaultier de La Vérendrye in honour of the Dauphin of France, the heir to the French throne. Dauphin is Manitoba's ninth largest community and serves as a hub to the province's Parkland Region. The current mayor of Dauphin is David Bosiak. Conservative Dan Mazier has been the member of Parliament for the Dauphin—Swan River—Neepawa riding since October 2019. Progressive Conservative Brad Michaleski is the current member of the Legislative Assembly of Manitoba.

Deloraine is an unincorporated urban community in the Municipality of Deloraine – Winchester within the Canadian province of Manitoba that held town status prior to January 1, 2015. It is situated near the Turtle Mountains in the southwestern corner of the province. Located in the Westman Region, the community is 100 km (62 mi) south of Brandon. Deloraine originally incorporated as a village in 1904 and then as a town in 1907. Its town status was relinquished in 2015 when it amalgamated with the Rural Municipality of Winchester.

Selkirk is a city in the western Canadian province of Manitoba, located on the Red River about 22 kilometres (14 mi) northeast of Winnipeg, the provincial capital. It has a population of 10,504 as of the 2021 census.

Morden is a city located in the Pembina Valley region of southern Manitoba, Canada near the United States border. It is about 11 km (6.8 mi) west of the neighbouring city of Winkler; together Morden and Winkler are often referred to as Manitoba's Twin Cities. Morden, which is surrounded by the Rural Municipality of Stanley, is the eighth largest and fastest-growing city in Manitoba. According to Statistics Canada, the city had a population of 9,929 in 2021, an increase of 14.5% from 2016, making it Manitoba's fastest growing city.

CBW is the call sign of the CBC Radio One station in Winnipeg, Manitoba. The station broadcasts at 990 kHz. CBW is a Class A Clear-channel station reserved for Canada under the North American Regional Broadcasting Agreement allocations.
Emerson is an unincorporated community recognized as a local urban district in south central Manitoba, Canada, located within the Municipality of Emerson – Franklin. It has a population of 678 as of the 2016 Canada census.

Pinawa is a local government district and small community of 1,331 residents located in southeastern Manitoba, Canada. It is 110 kilometres north-east of Winnipeg. The town is situated on the Canadian Shield within the western boundary of Whiteshell Provincial Park, which lies near the Manitoba-Ontario provincial boundary. Administratively, the town includes the surrounding area, and is officially the Local Government District of Pinawa. Except for a small eastern border with the unorganized area of the Eastman Region, it is surrounded by the Rural Municipalities of Lac du Bonnet to the north and Whitemouth to the south, but is independent of either one. The community lies on the north bank of the Winnipeg River in the southeastern part of the Local Government District.

Beausejour is a town in the Canadian province of Manitoba. It is 46 kilometres northeast of Winnipeg, just west of the Canadian Shield and Whiteshell Provincial Park. The French name Beauséjour [beau + séjour] means "beautiful stay". The town is surrounded by the Rural Municipality of Brokenhead. Originally known as Stony Prairie, Beausejour was named in 1877 by Mrs H.W.D. Armstrong, wife of a government railway surveyor, when a telegraph office was installed there to serve settlers along the nearby Brokenhead River.
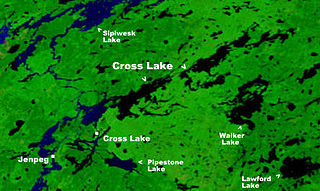
Cross Lake is a community in the Northern Region of the Canadian province of Manitoba, situated on the shores of the Nelson River where the river enters the namesake Cross Lake. An all-weather road, PR 374, connects the communities to PR 373 via the Kichi Sipi Bridge.

Stonewall is a town in the Canadian province of Manitoba with a population of 5,046 as of the 2021 census. The town is situated approximately 25 kilometres (16 mi) north of Winnipeg on PTH 67. It is known for its limestone quarries. The local festival is the Quarry Days which is usually held over three days in August on Main Street. The town is surrounded by the R.M. of Rockwood.

Russell is an unincorporated urban community in the Municipality of Russell – Binscarth, Manitoba.

Oak Lake is an unincorporated urban community in the Rural Municipality of Sifton within the Canadian province of Manitoba that held town status prior to January 1, 2015. It is located 52 km (32 mi) west of Brandon along the Trans-Canada Highway. The lake after which it was named is in the rural municipality's western area.

Ste. Anne, or Sainte-Anne-des-Chênes, is a town in Manitoba, Canada, located about 42 km southeast of Winnipeg. The population was 2,114 in 2016, 1,524 in 2011, and 1,513 in 2011. It is known for being located on the Seine River and at the heart of the Old Dawson Trail. The town is surrounded by the Rural Municipality of Ste. Anne.
Dufferin is a rural municipality in the province of Manitoba in Western Canada. The separately administered town of Carman lies near its centre.