Amerigo Vespucci was an Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Florence, from whose name the term "America" is derived.

Martin Waldseemüller was a German cartographer and humanist scholar. Sometimes known by the Latinized form of his name, Hylacomylus, his work was influential among contemporary cartographers. His collaborator Matthias Ringmann and he are credited with the first recorded usage of the word America to name a portion of the New World in honour of Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci. Waldseemüller was also the first to map South America as a continent separate from Asia, the first to produce a printed globe, and the first to create a printed wall map of Europe. A set of his maps printed as an appendix to the 1513 edition of Ptolemy's Geography is considered to be the first example of a modern atlas.

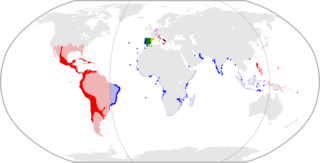
The Spanish colonization of the Americas began in 1493 on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola after the initial 1492 voyage of Genoese mariner Christopher Columbus under license from the Queen Isabella I of Castile. These overseas territories of the Spanish Empire were under the jurisdiction of Crown of Castile until the last territory was lost in 1898. Spaniards saw the dense populations of indigenous peoples as an important economic resource and the territory claimed as potentially producing great wealth for individual Spaniards and the crown. Religion played an important role in the Spanish conquest and incorporation of indigenous peoples, bringing them into the Catholic Church peacefully or by force. The crown created civil and religious structures to administer the vast territory. Spanish colonists settled in greatest numbers where there were dense indigenous populations and the existence of valuable resources for extraction.

New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain, or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish conquest of the Americas and having its capital in Mexico City. Its jurisdiction comprised a large area of the southern and western portions of North America, mainly what is now Mexico and the Southwestern United States, but also California and Florida; Central America, the Caribbean, and northern parts of South America; several Pacific Ocean archipelagos, most notably the Philippines and Guam; and numerous Asian port cities including Nagasaki and Spanish Formosa.

The Casa de Contratación or Casa de la Contratación de las Indias was established by the Crown of Castile, in 1503 in the port of Seville as a crown agency for the Spanish Empire. It functioned until 1790, when it was abolished in a government reorganization.

The term New World is often used to describe the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, including the Americas. The term gained prominence in the early 16th century during Europe's Age of Discovery, shortly after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci concluded that America, now often called the Americas, represented a new continent and subsequently published his findings in Mundus Novus, a Latin language pamphlet. This realization expanded the geographical horizon of classical European geographers, who had thought until then that the world only included Africa, Europe, and Asia, which was collectively referred to as the Old World or Afro-Eurasia. The Americas were then referred to as "the fourth part of the world", or the "New World".
The earliest known world maps date to classical antiquity, the oldest examples of the 6th to 5th centuries BCE still based on the flat Earth paradigm. World maps assuming a spherical Earth first appear in the Hellenistic period. The developments of Greek geography during this time, notably by Eratosthenes and Posidonius culminated in the Roman era, with Ptolemy's world map, which would remain authoritative throughout the Middle Ages. Since Ptolemy, knowledge of the approximate size of the Earth allowed cartographers to estimate the extent of their geographical knowledge, and to indicate parts of the planet known to exist but not yet explored as terra incognita.
The Council of the Indies, officially the Royal and Supreme Council of the Indies, was the most important administrative organ of the Spanish Empire for the Americas and those territories it governed, such as the Spanish East Indies.

The Waldseemüller map or Universalis Cosmographia is a printed wall map of the world by German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, originally published in April 1507. It is known as the first map to use the name "America". The name America is placed on South America on the main map. As explained in Cosmographiae Introductio, the name was bestowed in honor of the Italian Amerigo Vespucci.

Diogo Ribeiro was a Portuguese cartographer and explorer who worked most of his life in Spain where he was known as Diego Ribero. He worked on the official maps of the Padrón Real from 1518 to 1532. He also made navigation instruments, including astrolabes and quadrants.

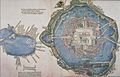
Aztec codices are Mesoamerican manuscripts made by the pre-Columbian Aztec, and their Nahuatl-speaking descendants during the colonial period in Mexico.
The history of cartography refers to the development and consequences of cartography, or mapmaking technology, throughout human history. Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans to explain and navigate their way through the world.

The traditions of indigenous Mesoamerican literature extend back to the oldest-attested forms of early writing in the Mesoamerican region, which date from around the mid-1st millennium BCE. Many of the pre-Columbian cultures of Mesoamerica are known to have been literate societies, who produced a number of Mesoamerican writing systems of varying degrees of complexity and completeness. Mesoamerican writing systems arose independently from other writing systems in the world, and their development represents one of the very few such origins in the history of writing.

The Padrón Real, known after 2 August 1527 as the Padrón General, was the official and secret Spanish master map used as a template for the maps present on all Spanish ships during the 16th century. It was kept in Seville, Spain by the Casa de Contratación. Ship pilots were required to use a copy of the official government chart, or risk the penalty of a 50 doblas fine. The map probably included a large-scale chart that hung on the wall of the old Alcázar of Seville. Well-known official cartographers and pilots who contributed to and used the map included Amerigo Vespucci, Diogo Ribeiro, Sebastian Cabot, Alonzo de Santa Cruz, and Juan Lopez de Velasco.
Quiabelagayo is a Zapotec name associated particularly with the Oaxacan Valley pre-Columbian site of Dainzu. In Zapotec mythology and religion, Quiabelagayo has been interpreted by some researchers such as Alfonso Caso and Ignacio Bernal as a local Oaxacan equivalent of the central Mexican deity Macuilxochitl, or "Five Flower".
Cartographic propaganda is a map created with the goal of achieving a result similar to traditional propaganda. The map can be outright falsified, or created using subjectivity with the goal of persuasion. The idea that maps are subjective is not new; cartographers refer to maps as a human-subjective product and some view cartography as an "industry, which packages and markets spatial knowledge" or as a communicative device distorted by human subjectivity. However, cartographic propaganda is widely successful because maps are often presented as a miniature model of reality, and it is a rare occurrence that a map is referred to as a distorted model, which sometimes can "lie" and contain items that are completely different from reality. Because the word propaganda has become a pejorative, it has been suggested that mapmaking of this kind should be described as "persuasive cartography", defined as maps intended primarily to influence opinions or beliefs – to send a message – rather than to communicate geographic information.

Cartography throughout the 14th-16th centuries played a significant role in the expansion of the kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula for a multitude of reasons. Primarily, the maps developed during this period served as navigational tools for maritime folk such as explorers, sailors and navigators. Mostly the expansion of the Crown of Aragon (which included the Kingdom of Aragon, Kingdom of Valencia and Kingdom of Majorca, together with the Principality of Catalonia, all its territories with seashore on the Mediterranean Sea. The Crown of Aragon controlled the routes across the Mediterranean Sea from the Kingdom of Jerusalem to Europe, as part of the commercial-trade route known as the Silk Road.
Relaciones geográficas were a series of elaborate questionnaires distributed to the lands of King Philip II of Spain in the Viceroyalty of New Spain in North America. They were done so, upon his command, from 1579–1585. This was a direct response to the reforms imposed by the Ordenanzas, ordinances, of 1573.

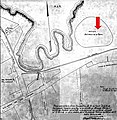
The Salviati Planisphere is a world map showing the Spanish view of the Earth's surface at the time of its creation c. 1525, and includes the eastern coasts of North and South America and the Straits of Magellan. Rather than include imagined material in unexplored areas—as was customary—it is content to leave them blank, inviting future exploration.
Howard F. Cline was an American government official and historian, specialising in Latin America. Cline served as Director of the Hispanic Foundation at the Library of Congress from 1952 until his death in June 1971. He was one of the founders of the Latin American Studies Association. He was also active in the Conference on Latin American History (CLAH), the professional organization of Latin American historians, which he chaired in 1964. He is still highly regarded as a scholar "devoted to and effective in the promotion of Latin American studies in the United States."