Related Research Articles
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 570 municipalities, of which 418 are governed by the system of usos y costumbres with recognized local forms of self-governance. Its capital city is Oaxaca de Juárez.

The city of Oaxaca de Juárez, or Oaxaca City or simply Oaxaca, is the capital and largest city of the eponymous Mexican state Oaxaca. It is the municipal seat for the surrounding Municipality of Oaxaca. It is in the Centro District in the Central Valleys region of the state, in the foothills of the Sierra Madre at the base of the Cerro del Fortín, extending to the banks of the Atoyac River. Heritage tourism makes up an important part of the city's economy, and it has numerous colonial-era structures as well as significant archeological sites and elements of the continuing native Zapotec and Mixtec cultures. The city, together with the nearby archeological site of Monte Albán, was designated in 1987 as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It is the site of the month-long cultural festival called the "Guelaguetza", which features Oaxacan dance from the seven regions, music, and a beauty pageant for indigenous women.

The Mixtecs, or Mixtecos, are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as the state of Guerrero's Región Montañas, and Región Costa Chica, which covers parts of the Mexican states of Oaxaca, Guerrero and Puebla.

Mitla is the second-most important archeological site in the state of Oaxaca in Mexico, and the most important of the Zapotec culture. The site is located 44 km from the city of Oaxaca, in the upper end of the Tlacolula Valley, one of the three cold, high valleys that form the Central Valleys Region of the state. At an elevation of 4,855 ft, surrounded by the mountains of the Sierra Madre del Sur, the archeological site is within the modern municipality of San Pablo Villa de Mitla. It is 24 mi (38 km) southeast of Oaxaca city. While Monte Albán was the most important politically of the Zapotec centers, Mitla became the main religious one in a later period as the area became dominated by the Mixtec.

The Mixtec languages belong to the Mixtecan group of the Oto-Manguean language family. Mixtec is spoken in Mexico and is closely related to Trique and Cuicatec. The varieties of Mixtec are spoken by over half a million people. Identifying how many Mixtec languages there are in this complex dialect continuum poses challenges at the level of linguistic theory. Depending on the criteria for distinguishing dialects from languages, there may be as few as a dozen or as many as fifty-three Mixtec languages.

In Mixtec mythology, Dzahui or Dzavui was the god of rain. Child sacrifices were performed for Dzahui on the tops of hills during times of drought, sickness, and at harvest time.

Mixtec writing originated as a logographic writing system during the Post-Classic period in Mesoamerican history. Records of genealogy, historic events, and myths are found in the pre-Columbian Mixtec codices. The arrival of Europeans in 1520 AD caused changes in form, style, and the function of the Mixtec writings. Today these codices and other Mixtec writings are used as a source of ethnographic, linguistic, and historical information for scholars, and help to preserve the identity of the Mixtec people as migration and globalization introduce new cultural influences.

Yucuita is an archaeological site located in the Mixtec municipality of San Juan Yucuita in the Mexican state of Oaxaca. It was founded by the Mixtec civilization in the pre-Classic Period as a small village dedicated to agriculture and obsidian.
New Philology generally refers to a branch of Mexican ethnohistory and philology that uses colonial-era native language texts written by Indians to construct history from the indigenous point of view. The name New Philology was coined by James Lockhart to describe work that he and his doctoral students and scholarly collaborators in history, anthropology, and linguistics had pursued since the mid-1970s. Lockhart published a great many essays elaborating on the concept and content of the New Philology and Matthew Restall published a description of it in the Latin American Research Review. The techniques of the New Philology have also been applied in other disciplines such as European medieval studies.

Cuilapan de Guerrero is a town and municipality located in the central valley region of Oaxaca in southern Mexico. It is 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) to the south of the capital city of Oaxaca on the road leading to Villa de Zaachila, and is in the Centro District in the Valles Centrales region.

Ronald M. Spores is an American academic anthropologist, archaeologist and ethnohistorian, whose research career has centered on the pre-Columbian cultures of Mesoamerica. He is Professor Emeritus of anthropology at Vanderbilt University's College of Arts and Science, where he has been a faculty member for over four decades. Spores is most renowned for his scholarship conducted on the cultural history of the Oaxacan region in southwestern Mexico. In particular, he has made many contributions on the Mixtec culture, investigating its archaeological sites, ethnohistorical documents, political economies, and ethnohistory in both the pre-Columbian and Colonial eras. He was Co-Director of the Proyecto Arqueológico de la Ciudad Yucundaa Pueblo Viejo de Teposcolula, Oaxaca, sponsored by the Fundación Alfredo Harp Helu, the National Geographic Society, and INAH (2004–2010), and currently (2017) directs research on the sixteenth century Casa del Cacique de Yanhuitlan, Oaxaca, and related investigation of the surrounding Prehispanic-Colonial city and region. He is also Research Associate at the American Museum of Natural History, New York, and at the University of Oregon and investigator on the Proyecto Geoparque de la Mixteca Alta, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México/UNESCO, centered at Yanhuitlan, Oaxaca (2016-2017). Recent research relates to the colonial Manila Galleon trade between the Philippines and Acapulco.

The Codex Sierra is a colonial Mesoamerican account book from Santa Catalina Texupa, covering the years from 1550 to 1564. It uses both alphabetic and pictorial modes of writing. Though Texupa is a Mixtec and Chocho community, the text is written in Nahuatl, albeit with some Mixtec words. The pictorial portion likewise uses Mixtec conventions, such as the "A-O" year sign.
Yahui is a supernatural figure that takes on various mixtures of animal and human forms within the culture and belief systems of the Mixtec—indigenous Mixtecan-speaking people of La Mixteca in central-southeastern Mexico. It is an important and recurring motif in Mixtec iconography, thought and culture, especially during the pre-Columbian era. As a supernatural figure, the yahui appears in Postclassic Mixtec codices as an entity wearing a serpent or reptilian tail and headdress and the carapace of a turtle.
Lisa Sousa is an American academic historian active in the field of Latin American studies. A specialist in the colonial-era history of Latin America and of Colonial Mexico in particular, Sousa is noted for her research, commentary, and translations of colonial Mesoamerican literature and Nahuatl-language historical texts. She has also published research on historical and contemporary indigenous peoples in Mexico, the roles of women in indigenous societies and cultural definitions of gender. Sousa is a Full Professor in the History Department at Occidental College in Los Angeles, California.

San Juan Achiutla is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in south-western Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 49.76 km2. It is located in a mountain range, between the hills Negro to the East, Yucuquise to the Northwest, Cuate to the North and Totolote to the South. It is crossed by the river Los Sabinos and has a dam called Cahuayande. Its weather is temperate. It is in the Mixteca Alta, one of the three parties that make up the Mixteca region and in the Mixteca Alta is part of what was Achiutla, the significant Prehispanic place.

The Mixteca Region is a region in the state of Oaxaca, Mexico, part of the broader La Mixteca area which covers parts of the states of Puebla, Guerrero and Oaxaca. The region includes the districts of Juxtlahuaca, Silacayoapam, Huajuapan, Coixtlahuaca, Teposcolula, Tlaxiaco and Nochixtlán. The largest cities are Huajuapan and Tlaxiaco. According to the 1990 census the region had 556,256 people over the age of five, of which 227,680 spoke Mixteco.
In the Central Valley region of the Southern Mexican state of Oaxaca archeologists discovered evidence of historic settlements. Aztecs from Tenochtitlan on the volcanic plateau to the North around what today is Mexico City first arrived in this region around 1250 AD establishing military rule in the 15th century until the arrival of the Spanish. After the fall of Tenochtitlan, the Spanish took over Oaxaca which led to the eventual decrease of the Native population and the increase in African slaves. The region was then settled by mostly Spanish immigrants from Europe and the African slaves they brought with them. Oaxaca was considered a department after the Mexican War of Independence, but after the fall of emperor Agustín de Iturbide, it became a state in 1824 with José Murguia as its first governor. During the 19th century, Oaxaca was split between liberal and conservative factions. The political and military struggles between the factions resulted in wars and intrigues. A series of major disasters occurred in the state from the 1920s to the 1940s. In the 1940s and 1950s, new infrastructure projects were begun. From the 1980s to the present, there has been much development of the tourism industry in the state.
Mixteca Alta Formative Project (2003–present) is an archaeological project directed by Andrew Balkansky that focuses on the Mixtec of Oaxaca, Mexico. The project, which is funded by the National Science Foundation, the National Geographic Society, and the H. John Heinz III Fund, seeks to understand Mixtec origins and their transition to urbanism. Excavations are currently taking place at the ancient site of Tayata.

Huamelulpan is an archaeological site of the Mixtec culture, located in the town of San Martín Huamelulpan at an elevation of 2,218 metres (7,277 ft), about 96 kilometres (60 mi) north-west of the city of Oaxaca, the capital of Oaxaca state.
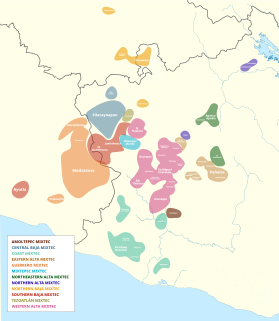
The internal classification of Mixtec is controversial. Many varieties are mutually unintelligible and by that criterion separate languages. In the 16th century, Spanish authorities recognized half a dozen lenguas comprising the Mixtec lengua. It is not clear to what extent these were distinct languages at the time. Regardless, the colonial disintegration of the Mixtec nation and resulting isolation of local communities led to the rapid diversification of local dialects into distinct languages. Below are some attempts at Mixtec classification by various scholars.
References
- Kiracofe, James B. (1995). "Architectural Fusion and Indigenous Ideology in Early Colonial Teposcolula: The Casa de la Cacica: A Building at the Edge of Oblivion" (PDF). Anales de Instituto de Investigaciones Estéticas. 17 (66): 45–84. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-07-10. Retrieved 2008-04-21.
- Terraciano, Kevin (2001). The Mixtecs of Colonial Oaxaca: Ñudzahui History, Sixteenth Through Eighteenth Centuries. Stanford: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-3756-8. OCLC 45861953.