
Cooking, also known as cookery or professionally as the culinary arts, is the art, science and craft of using heat to make food more palatable, digestible, nutritious, or safe. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from grilling food over an open fire to using electric stoves, to baking in various types of ovens, reflecting local conditions.

Human evolution is the evolutionary process within the history of primates that led to the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominid family, which includes all the great apes. This process involved the gradual development of traits such as human bipedalism, dexterity and complex language, as well as interbreeding with other hominins, indicating that human evolution was not linear but weblike. The study of human evolution involves several scientific disciplines, including physical and evolutionary anthropology, paleontology, and genetics.

Homininae, also called "African hominids" or "African apes", is a subfamily of Hominidae. It includes two tribes, with their extant as well as extinct species: 1) the tribe Hominini ―and 2) the tribe Gorillini (gorillas). Alternatively, the genus Pan is sometimes considered to belong to its own third tribe, Panini. Homininae comprises all hominids that arose after orangutans split from the line of great apes. The Homininae cladogram has three main branches, which lead to gorillas, and to humans and chimpanzees via the tribe Hominini and subtribes Hominina and Panina. There are two living species of Panina and two living species of gorillas, but only one extant human species. Traces of extinct Homo species, including Homo floresiensis have been found with dates as recent as 40,000 years ago. Organisms in this subfamily are described as hominine or hominines.

The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic, also called the Old Stone Age, is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehistoric technology. It extends from the earliest known use of stone tools by hominins, c. 3.3 million years ago, to the end of the Pleistocene, c. 11,650 cal BP.

Homo ergaster is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether H. ergaster constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into H. erectus is an ongoing and unresolved dispute within palaeoanthropology. Proponents of synonymisation typically designate H. ergaster as "African Homo erectus" or "Homo erectus ergaster". The name Homo ergaster roughly translates to "working man", a reference to the more advanced tools used by the species in comparison to those of their ancestors. The fossil range of H. ergaster mainly covers the period of 1.7 to 1.4 million years ago, though a broader time range is possible. Though fossils are known from across East and Southern Africa, most H. ergaster fossils have been found along the shores of Lake Turkana in Kenya. There are later African fossils, some younger than 1 million years ago, that indicate long-term anatomical continuity, though it is unclear if they can be formally regarded as H. ergaster specimens. As a chronospecies, H. ergaster may have persisted to as late as 600,000 years ago, when new lineages of Homo arose in Africa.
The Middle Paleolithic is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleolithic in African archeology. The Middle Paleolithic broadly spanned from 300,000 to 30,000 years ago. There are considerable dating differences between regions. The Middle Paleolithic was succeeded by the Upper Paleolithic subdivision which first began between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. Pettit and White date the Early Middle Paleolithic in Great Britain to about 325,000 to 180,000 years ago, and the Late Middle Paleolithic as about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago. The Middle Paleolithic was in the geological Chibanian and Late Pleistocene ages.
The evolution of human intelligence is closely tied to the evolution of the human brain and to the origin of language. The timeline of human evolution spans approximately seven million years, from the separation of the genus Pan until the emergence of behavioral modernity by 50,000 years ago. The first three million years of this timeline concern Sahelanthropus, the following two million concern Australopithecus and the final two million span the history of the genus Homo in the Paleolithic era.

Culinary arts are the cuisine arts of food preparation, cooking, and presentation of food, usually in the form of meals. People working in this field – especially in establishments such as restaurants – are commonly called chefs or cooks, although, at its most general, the terms culinary artist and culinarian are also used. Table manners are sometimes referred to as a culinary art.

Richard Walter Wrangham is an English anthropologist and primatologist; he is Professor of Biological Anthropology at Harvard University. His research and writing have involved ape behavior, human evolution, violence, and cooking.
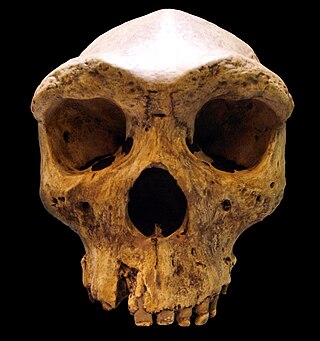
A number of varieties of Homo are grouped into the broad category of archaic humans in the period that precedes and is contemporary to the emergence of the earliest early modern humans around 300 ka. Among the earliest remains of H. sapiens are Omo-Kibish I from southern Ethiopia, the remains from Jebel Irhoud in Morocco and Florisbad in South Africa (259 ka). The term typically includes H. antecessor, H. bodoensis, Denisovans (H. denisova), H. heidelbergensis (600–200 ka), Neanderthals, and H. rhodesiensis (300–125 ka).
Dual inheritance theory (DIT), also known as gene–culture coevolution or biocultural evolution, was developed in the 1960s through early 1980s to explain how human behavior is a product of two different and interacting evolutionary processes: genetic evolution and cultural evolution. Genes and culture continually interact in a feedback loop: changes in genes can lead to changes in culture which can then influence genetic selection, and vice versa. One of the theory's central claims is that culture evolves partly through a Darwinian selection process, which dual inheritance theorists often describe by analogy to genetic evolution.
The control of fire by early humans was a critical technology enabling the evolution of humans. Fire provided a source of warmth and lighting, protection from predators, a way to create more advanced hunting tools, and a method for cooking food. These cultural advances allowed human geographic dispersal, cultural innovations, and changes to diet and behavior. Additionally, creating fire allowed human activity to continue into the dark and colder hours of the evening.

Self-domestication is a scientific hypothesis that suggests that, similar to domesticated animals, there has been a process of artificial selection among members of the human species conducted by humans themselves. In this way, during the process of hominization, a preference for individuals with collaborative and social behaviors would have been shown to optimize the benefit of the entire group: docility, language, and emotional intelligence would have been enhanced during this process of artificial selection. The hypothesis is raised that this is what differentiated Homo sapiens from Homo neanderthalensis and Homo erectus.

Homo erectus is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Its specimens are among the first recognizable members of the genus Homo.

The Hominidae, whose members are known as the great apes or hominids, are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: Pongo ; Gorilla ; Pan ; and Homo, of which only modern humans remain.
The sexual division of labour (SDL) is the delegation of different tasks between male and female animals. Among human foragers, males and females targeted different types of foods and shared them with each other for a mutual or familial benefit. In some species, males and females eat slightly different foods, while in other species, males and females will routinely share food; but only in humans are these two attributes combined. The few remaining hunter-gatherer populations in the world serve as evolutionary models that can help explain the origin of the sexual division of labor. Many studies on the sexual division of labor have been conducted on hunter-gatherer populations, such as the Hadza, a hunter-gatherer population of Tanzania. In modern day society sex differences in occupation is seen across cultures, with the tendency that men do technical work and women tend to do work related to care.
Prehistoric technology is technology that predates recorded history. History is the study of the past using written records. Anything prior to the first written accounts of history is prehistoric, including earlier technologies. About 2.5 million years before writing was developed, technology began with the earliest hominids who used stone tools, which they first used to hunt food, and later to cook.
Leslie Crum Aiello is an American paleoanthropologist and professor emeritus of University College London. She was the president of Axel Lennart Wenner-Gren donated Wenner-Gren Foundation for Anthropological Research from 2005 to 2017. In 2014, Aiello was elected to the American Philosophical Society. She is currently president of the American Association of Physical Anthropologists.
In evolutionary anthropology and evolutionary linguistics, the mimetic theory of speech origins is an analysis of the factors leading to the evolution of language in human ancestors, typically during the Homo erectus era.
The diet of known human ancestors varies dramatically over time. Strictly speaking, according to evolutionary anthropologists and archaeologists, there is not a single hominin Paleolithic diet. The Paleolithic covers roughly 2.8 million years, concurrent with the Pleistocene, and includes multiple human ancestors with their own evolutionary and technological adaptations living in a wide variety of environments. This fact with the difficulty of finding conclusive of evidence often makes broad generalizations of the earlier human diets very difficult. Our pre-hominin primate ancestors were broadly herbivorous, relying on either foliage or fruits and nuts and the shift in dietary breadth during the Paleolithic is often considered a critical point in hominin evolution. A generalization between Paleolithic diets of the various human ancestors that many anthropologists do make is that they are all to one degree or another omnivorous and are inextricably linked with tool use and new technologies. Nonetheless, according to the California Academy of Sciences, "Prior to about 3.5 million years ago, early humans dined almost exclusively on leaves and fruits from trees, shrubs, and herbs—similar to modern-day gorillas and chimpanzees."











