In differential geometry, a subject of mathematics, a symplectic manifold is a smooth manifold, , equipped with a closed nondegenerate differential 2-form , called the symplectic form. The study of symplectic manifolds is called symplectic geometry or symplectic topology. Symplectic manifolds arise naturally in abstract formulations of classical mechanics and analytical mechanics as the cotangent bundles of manifolds. For example, in the Hamiltonian formulation of classical mechanics, which provides one of the major motivations for the field, the set of all possible configurations of a system is modeled as a manifold, and this manifold's cotangent bundle describes the phase space of the system.
The calculus of variations is a field of mathematical analysis that uses variations, which are small changes in functions and functionals, to find maxima and minima of functionals: mappings from a set of functions to the real numbers. Functionals are often expressed as definite integrals involving functions and their derivatives. Functions that maximize or minimize functionals may be found using the Euler–Lagrange equation of the calculus of variations.

In mathematics, the name symplectic group can refer to two different, but closely related, collections of mathematical groups, denoted Sp(2n, F) and Sp(n) for positive integer n and field F (usually C or R). The latter is called the compact symplectic group and is also denoted by . Many authors prefer slightly different notations, usually differing by factors of 2. The notation used here is consistent with the size of the most common matrices which represent the groups. In Cartan's classification of the simple Lie algebras, the Lie algebra of the complex group Sp(2n, C) is denoted Cn, and Sp(n) is the compact real form of Sp(2n, C). Note that when we refer to the (compact) symplectic group it is implied that we are talking about the collection of (compact) symplectic groups, indexed by their dimension n.
In mathematics, the Laplace operator or Laplacian is a differential operator given by the divergence of the gradient of a scalar function on Euclidean space. It is usually denoted by the symbols , (where is the nabla operator), or . In a Cartesian coordinate system, the Laplacian is given by the sum of second partial derivatives of the function with respect to each independent variable. In other coordinate systems, such as cylindrical and spherical coordinates, the Laplacian also has a useful form. Informally, the Laplacian Δf (p) of a function f at a point p measures by how much the average value of f over small spheres or balls centered at p deviates from f (p).
In mathematics, a tangent vector is a vector that is tangent to a curve or surface at a given point. Tangent vectors are described in the differential geometry of curves in the context of curves in Rn. More generally, tangent vectors are elements of a tangent space of a differentiable manifold. Tangent vectors can also be described in terms of germs. Formally, a tangent vector at the point is a linear derivation of the algebra defined by the set of germs at .
In the mathematical field of differential geometry, a metric tensor is an additional structure on a manifold M that allows defining distances and angles, just as the inner product on a Euclidean space allows defining distances and angles there. More precisely, a metric tensor at a point p of M is a bilinear form defined on the tangent space at p, and a metric tensor on M consists of a metric tensor at each point p of M that varies smoothly with p.

Hamiltonian mechanics emerged in 1833 as a reformulation of Lagrangian mechanics. Introduced by Sir William Rowan Hamilton, Hamiltonian mechanics replaces (generalized) velocities used in Lagrangian mechanics with (generalized) momenta. Both theories provide interpretations of classical mechanics and describe the same physical phenomena.
In mathematics, a symplectic vector space is a vector space V over a field F equipped with a symplectic bilinear form.

In mathematics and classical mechanics, the Poisson bracket is an important binary operation in Hamiltonian mechanics, playing a central role in Hamilton's equations of motion, which govern the time evolution of a Hamiltonian dynamical system. The Poisson bracket also distinguishes a certain class of coordinate transformations, called canonical transformations, which map canonical coordinate systems into canonical coordinate systems. A "canonical coordinate system" consists of canonical position and momentum variables that satisfy canonical Poisson bracket relations. The set of possible canonical transformations is always very rich. For instance, it is often possible to choose the Hamiltonian itself as one of the new canonical momentum coordinates.
In mathematics, the Hodge star operator or Hodge star is a linear map defined on the exterior algebra of a finite-dimensional oriented vector space endowed with a nondegenerate symmetric bilinear form. Applying the operator to an element of the algebra produces the Hodge dual of the element. This map was introduced by W. V. D. Hodge.
In mathematics, the Schwarzian derivative is an operator similar to the derivative which is invariant under Möbius transformations. Thus, it occurs in the theory of the complex projective line, and in particular, in the theory of modular forms and hypergeometric functions. It plays an important role in the theory of univalent functions, conformal mapping and Teichmüller spaces. It is named after the German mathematician Hermann Schwarz.

In the differential geometry of curves, the evolute of a curve is the locus of all its centers of curvature. That is to say that when the center of curvature of each point on a curve is drawn, the resultant shape will be the evolute of that curve. The evolute of a circle is therefore a single point at its center. Equivalently, an evolute is the envelope of the normals to a curve.

In geometry, a nephroid is a specific plane curve. It is a type of epicycloid in which the smaller circle's radius differs from the larger one by a factor of one-half.
A first class constraint is a dynamical quantity in a constrained Hamiltonian system whose Poisson bracket with all the other constraints vanishes on the constraint surface in phase space. To calculate the first class constraint, one assumes that there are no second class constraints, or that they have been calculated previously, and their Dirac brackets generated.
In differential geometry, a field in mathematics, a Poisson manifold is a smooth manifold endowed with a Poisson structure. The notion of Poisson manifold generalises that of symplectic manifold, which in turn generalises the phase space from Hamiltonian mechanics.

In nuclear physics, the chiral model, introduced by Feza Gürsey in 1960, is a phenomenological model describing effective interactions of mesons in the chiral limit (where the masses of the quarks go to zero), but without necessarily mentioning quarks at all. It is a nonlinear sigma model with the principal homogeneous space of a Lie group as its target manifold. When the model was originally introduced, this Lie group was the SU(N), where N is the number of quark flavors. The Riemannian metric of the target manifold is given by a positive constant multiplied by the Killing form acting upon the Maurer–Cartan form of SU(N).

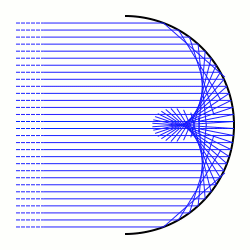
In optics, a caustic or caustic network is the envelope of light rays which have been reflected or refracted by a curved surface or object, or the projection of that envelope of rays on another surface. The caustic is a curve or surface to which each of the light rays is tangent, defining a boundary of an envelope of rays as a curve of concentrated light. Therefore, in the photo to the right, caustics can be seen as patches of light or their bright edges. These shapes often have cusp singularities.
The gradient theorem, also known as the fundamental theorem of calculus for line integrals, says that a line integral through a gradient field can be evaluated by evaluating the original scalar field at the endpoints of the curve. The theorem is a generalization of the second fundamental theorem of calculus to any curve in a plane or space rather than just the real line.
In theoretical physics, Hamiltonian field theory is the field-theoretic analogue to classical Hamiltonian mechanics. It is a formalism in classical field theory alongside Lagrangian field theory. It also has applications in quantum field theory.
In mathematics, and especially symplectic geometry, the Thomas–Yau conjecture asks for the existence of a stability condition, similar to those which appear in algebraic geometry, which guarantees the existence of a solution to the special Lagrangian equation inside a Hamiltonian isotopy class of Lagrangian submanifolds. In particular the conjecture contains two difficulties: first it asks what a suitable stability condition might be, and secondly if one can prove stability of an isotopy class if and only if it contains a special Lagrangian representative.