A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region.

A scabbard is a sheath for holding a sword, knife, or other large blade. As well, rifles may be stored in a scabbard by horse riders. Military cavalry and cowboys had scabbards for their saddle ring carbine rifles and lever-action rifles on their horses for storage and protection. Scabbards have been made of many materials over the millennia, including leather, wood, and metals such as brass or steel.

The hilt of a knife, dagger, sword, or bayonet is its handle, consisting of a guard, grip and pommel. The guard may contain a crossguard or quillons. A tassel or sword knot may be attached to the guard or pommel.

The kukri or khukuri is a type of short sword with a distinct recurve in its blade originated in Nepal. It serves multiple purposes as a melee weapon and also as a regular cutting tool throughout most of South Asia. The kukri, khukri, and kukkri spellings are of Indian English origin, with the original Nepalese English spelling being khukuri.

The buckle or clasp is a device used for fastening two loose ends, with one end attached to it and the other held by a catch in a secure but adjustable manner. Often taken for granted, the invention of the buckle was indispensable in securing two ends before the invention of the zipper. The basic buckle frame comes in a variety of shapes and sizes depending on the intended use and fashion of the era. Buckles are as much in use today as they have been in the past: used for much more than just securing ones belt, instead they are one of the most dependable devices in securing a range of items.

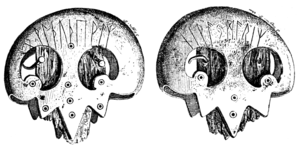
The Elder Futhark, also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Period. Inscriptions are found on artifacts including jewelry, amulets, plateware, tools, and weapons, as well as runestones in Scandinavia, from the 2nd to the 10th centuries.

Celtic art is associated with the peoples known as Celts; those who spoke the Celtic languages in Europe from pre-history through to the modern period, as well as the art of ancient peoples whose language is uncertain, but have cultural and stylistic similarities with speakers of Celtic languages.

The Viking Age sword or Carolingian sword is the type of sword prevalent in Western and Northern Europe during the Early Middle Ages.

Japanese sword mountings are the various housings and associated fittings that hold the blade of a Japanese sword when it is being worn or stored. Koshirae (拵え) refers to the ornate mountings of a Japanese sword used when the sword blade is being worn by its owner, whereas the shirasaya is a plain undecorated wooden mounting composed of a saya and tsuka that the sword blade is stored in when not being used.

A belt buckle is a buckle, a clasp for fastening two ends, such as of straps or a belt, in which a device attached to one of the ends is fitted or coupled to the other. The word enters Middle English via Old French and the Latin buccula or "cheek-strap," as for a helmet. Belt buckles and other fixtures are used on a variety of belts, including cingula, baltea, baldrics and later waist-belts.
A runic inscription is an inscription made in one of the various runic alphabets. They generally contained practical information or memorials instead of magic or mythic stories. The body of runic inscriptions falls into the three categories of Elder Futhark, Anglo-Frisian Futhorc and Younger Futhark.

On a sword, the crossguard, or cross-guard, the individual bars on either side known as quillon, is a bar of metal at right angles to the blade, placed between the blade and the hilt.

The Thorsberg moor near Süderbrarup in Anglia, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, is a peat bog in which the Angles deposited votive offerings for approximately four centuries. It is the location of important Roman Iron Age finds, including early Elder Futhark runic inscriptions such as the Thorsberg chape, a Roman helmet, a shield buckle, and an early example of socks. The finds are of similar importance as the contemporaneous finds from Illerup and Vimose in Denmark.
Swords made of iron appear from the Early Iron Age, but do not become widespread before the 8th century BC.

The St Ninian's Isle Treasure, found on St Ninian's Isle, Scotland in 1958 is the best example of surviving silver metalwork from the Early Medieval period in Scotland. The 28-piece hoard includes various silver metalwork items, including twelve pennanular brooches. The treasure is now in the National Museum of Scotland.

The Sutton Hoo purse-lid is one of the major objects excavated from the Anglo-Saxon royal burial-ground at Sutton Hoo in Suffolk, England. The site contains a collection of burial mounds, of which much the most significant is the undisturbed ship burial in Mound 1 containing very rich grave goods including the purse-lid. The person buried in Mound 1 is usually thought to have been Rædwald, King of East Anglia, who died around 624. The purse-lid is considered to be "one of the most remarkable creations of the early medieval period." About seven and a half inches long, it is decorated with beautiful ornament in gold and garnet cloisonné enamel, and was undoubtedly a symbol of great wealth and status. In 2017 the purse-lid was on display at the British Museum.

The Seax of Beagnoth is a 10th-century Anglo-Saxon seax. It was found in the inland estuary of the Thames in 1857, and is now at the British Museum in London. It is a prestige weapon, decorated with elaborate patterns of inlaid copper, brass and silver wire. On one side of the blade is the only known complete inscription of the twenty-eight letter Anglo-Saxon runic alphabet, as well as the name "Beagnoth" in runic letters. It is thought that the runic alphabet had a magical function, and that the name Beagnoth is that of either the owner of the weapon or the smith who forged it. Although many Anglo-Saxon and Viking swords and knives have inscriptions in the Latin alphabet on their blades, or have runic inscriptions on the hilt or scabbard, the Seax of Beagnoth is one of only a handful of finds with a runic inscription on its blade.

Art in Medieval Scotland includes all forms of artistic production within the modern borders of Scotland, between the fifth century and the adoption of the Renaissance in the early sixteenth century. In the early Middle Ages, there were distinct material cultures evident in the different federations and kingdoms within what is now Scotland. Pictish art was the only uniquely Scottish Medieval style; it can be seen in the extensive survival of carved stones, particularly in the north and east of the country, which hold a variety of recurring images and patterns. It can also be seen in elaborate metal work that largely survives in buried hoards. Irish-Scots art from the kingdom of Dál Riata suggests that it was one of the places, as a crossroads between cultures, where the Insular style developed.

A rain-guard or chappe is a piece of leather fitted to the crossguard of European swords of the later medieval period. The purpose of this leather is not entirely clear, but it seems to have originated as a part of the scabbard, functioning as a lid when the sword was in the scabbard.

Ratings of the Royal Navy have used cutlasses, short, wide bladed swords, since the early 18th century. These were originally of non-uniform design but the 1804 Pattern, the first Navy-issue standard cutlass, was introduced at the start of the 19th century. This was a bluntish weapon that was perhaps intended for cutting away canvas and ropes rather than as a thrusting combat weapon. The 1845 Pattern cutlass introduced a bowl-style hand guard which provided greater protection, with a longer and more curved blade. Its sharper point made it more useful for thrusting attacks, which were now emphasised in the drill manual. The 1845 Pattern was modified several times including shortening and straightening the blades, which weakened them. The 1889 Pattern had a straight, spear-pointed blade with a hilt that curved outwards to catch and redirect an opponent's sword point. The 1900 Pattern, the last navy-issue cutlass, was similar to its predecessor with the introduction of a fuller and a hilt insert that cushioned the user's little finger. The cutlass was withdrawn from service in 1936 but remains in use for ceremonial purposes. It is thought that it was last used in combat in 1900 during the Boxer Rebellion.