Related Research Articles
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.
In software development, a lead programmer is responsible for providing technical guidance and mentorship to a team of software developers. Alternative titles include development lead, technical lead, lead programmer, or lead application developer. When primarily contributing a low-level enterprise software design with focus on the structure of the app, e.g. design patterns, the role would be a software architect
Management by objectives (MBO), also known as management by planning (MBP), was first popularized by Peter Drucker in his 1954 book The Practice of Management. Management by objectives is the process of defining specific objectives within an organization that management can convey to organization members, then deciding how to achieve each objective in sequence. This process allows managers to take work that needs to be done one step at a time to allow for a calm, yet productive work environment. In this system of management, individual goals are synchronized with the goals of the organization.
Agile software development is the mindset for developing software that derives from values agreed upon by The Agile Alliance, a group of 17 software practitioners in 2001. As documented in their Manifesto for Agile Software Development the practitioners value:
The Project Management Institute is a U.S.-based not-for-profit professional organization for project management.
In agile principles, timeboxing allocates a maximum unit of time to an activity, called a timebox, within which a planned activity takes place. It is used by agile principles-based project management approaches and for personal time management.
Lean software development is a translation of lean manufacturing principles and practices to the software development domain. Adapted from the Toyota Production System, it is emerging with the support of a pro-lean subculture within the agile community. Lean offers a solid conceptual framework, values and principles, as well as good practices, derived from experience, that support agile organizations.
A product manager (PM) is a professional role that is responsible for the development of products for an organization, known as the practice of product management. Product managers own the product strategy behind a product, specify its functional requirements, and manage feature releases. Product managers coordinate work done by many other functions, and are ultimately responsible for product outcomes.
Operational excellence is a mindset that embraces certain principles and tools to create a culture of excellence within an organization. Operational excellence means every employee can see, deliver, and improve the flow of value to a customer.

Scrum is an agile team collaboration framework commonly used in software development and other industries.

Agile Project Management: Creating Innovative Products by Jim Highsmith discusses the management of projects using the agile software development methodology. The book has been recommended by different reviewers.

Jeff Sutherland is one of the creators of Scrum, a framework for product management. Together with Ken Schwaber, he presented Scrum at OOPSLA'95. Sutherland contributed to the creation of the Agile Manifesto in 2001. Along with Ken Schwaber, he wrote and maintains The Scrum Guide, which contains the official definition of the framework.
Strategic planning software is a category of software that covers a wide range of strategic topics, methodologies, modeling and reporting.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to business management:
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
Alexander Laufer is the Director of the Consortium for Project Leadership at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He is best known for developing a practice-based theory of project management, utilizing the tacit knowledge of competent practitioners from successful organizations.
Lean project management is the application of lean concepts such as lean construction, lean manufacturing and lean thinking to project management.
Extreme project management (XPM) refers to a method of managing very complex and very uncertain projects.
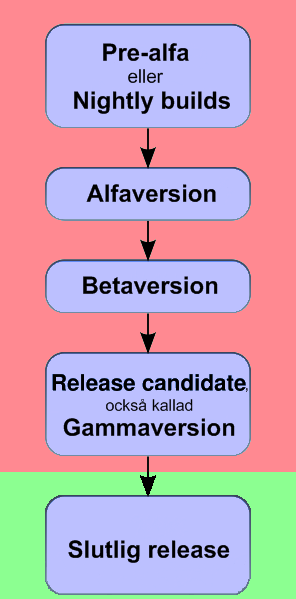
Release management is the process of managing, planning, scheduling and controlling a software build through different stages and environments; it includes testing and deploying software releases.
The scaled agile framework (SAFe) is a set of organization and workflow patterns intended to guide enterprises in scaling lean and agile practices. Along with disciplined agile delivery (DAD) and S@S (Scrum@Scale), SAFe is one of a growing number of frameworks that seek to address the problems encountered when scaling beyond a single team.
References
- ↑ "8 Best Agile Courses for 2024: Sprint, Adapt, Succeed". classcentral.com. 5 March 2024. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Agile Project Management Academy -About Chuck Cobb". managedagile.com. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "Agile Project Management Training". Managed Agile. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "Agile Project Management Academy - Chuck Cobb". udemy.com. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "The Project Manager's Guide to Mastering Agile - Principles and Practices for an Adaptive Approach". High Impact Project Management, Inc. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "The Project Manager's Guide to Mastering Agile: Principles and Practices for an Adaptive Approach, 2nd Edition". wiley.com. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "Best Project Management Books". readthistwice.com. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "Agile Project Management Articles and Useful Information". Managed Agile. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "Making Sense of Agile - A Project Management Perspective". High Impact Project Management, Inc. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "Managed Agile Development - Making Agile Work for Your Business (Superseded)". High Impact Project Management, Inc. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "The Project Manager's Guide to Mastering Agile - Principles and Practices for an Adaptive Approach (First Edition)". High Impact Project Management, Inc. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ Cobb, Charles G. (2011). Making Sense of Agile Project Management: Balancing Control and Agility. doi:10.1002/9781118085950. ISBN 978-0-470-94336-6 . Retrieved 3 May 2024.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ↑ "Making Sense of Agile Project Management: Balancing Control and Agility". everand.com. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "From Quality to Business Excellence: A Systems Approach to Management". High Impact Project Management, Inc. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ↑ "Enterprise Process Mapping: Integrating Systems For Compliance And Business Excellence". High Impact Project Management, Inc. Retrieved 3 May 2024.