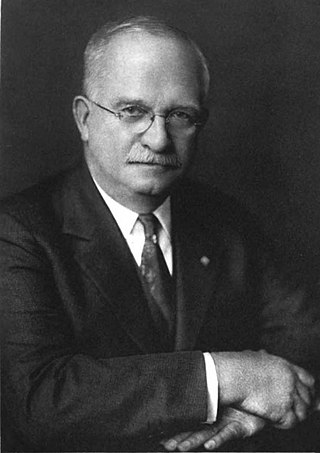Ira Remsen was an American chemist who discovered the artificial sweetener saccharin along with Constantin Fahlberg. He was the second president of Johns Hopkins University.

The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all degree levels and in all fields of chemistry, chemical engineering, and related fields. It is one of the world's largest scientific societies by membership. The ACS is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Its headquarters are located in Washington, D.C., and it has a large concentration of staff in Columbus, Ohio.

The Priestley Medal is the highest honor conferred by the American Chemical Society (ACS) and is awarded for distinguished service in the field of chemistry. Established in 1922, the award is named after Joseph Priestley, the discoverer of oxygen who immigrated to the United States of America in 1794. The ACS formed in 1876, spearheaded by a group of chemists who had met two years previously in Priestley's home.

Richard Neil Zare is the Marguerite Blake Wilbur Professor in Natural Science and a Professor of Chemistry at Stanford University. Throughout his career, Zare has made a considerable impact in physical chemistry and analytical chemistry, particularly through the development of laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) and the study of chemical reactions at the molecular and nanoscale level. LIF is an extremely sensitive technique with applications ranging from analytical chemistry and molecular biology to astrophysics. One of its applications was the sequencing of the human genome.

Mary Lowe Good was an American inorganic chemist who worked academically, in industrial research and in government. Good contributed to the understanding of catalysts such as ruthenium which activate or speed up chemical reactions.
The Irving Langmuir Prize in Chemical Physics is awarded annually, in even years by the American Chemical Society and in odd years by the American Physical Society. The award is meant to recognize and encourage outstanding interdisciplinary research in chemistry and physics, in the spirit of Irving Langmuir. A nominee must have made an outstanding contribution to chemical physics or physical chemistry within the 10 years preceding the year in which the award is made. The award will be granted without restriction, except that the recipient must be a resident of the United States.

JoAnne Stubbe is an American chemist best known for her work on ribonucleotide reductases, for which she was awarded the National Medal of Science in 2009. In 2017, she retired as a Professor of Chemistry and Biology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
William Albert Noyes Jr., commonly known as W. Albert Noyes Jr., was an American chemist known for his contributions to photochemistry. During World War II, he was a leader in U.S. defense research efforts. He chaired the chemistry department at the University of Rochester, edited several important chemistry journals, and throughout his career was a prominent voice for international scientific cooperation. He was the son of the renowned chemist William A. Noyes; they became the first father-son pair to win the Priestley Medal, the highest honor given by the American Chemical Society.
The award, sponsored by The Camille and Henry Dreyfus Foundation, was instituted in 1993 with the intention of recognizing "significant accomplishments by individuals who have stimulated or fostered the interest of women in chemistry, promoting their professional development as chemists or chemical engineers." Recipients receive $5,000, a certificate, up to $1,500 for travel expenses, and a grant of $10,000. The deadline for nomination is 1 November every year.
The Melvin Mooney Distinguished Technology Award is a professional award conferred by the American Chemical Society, Rubber Division. Established in 1983, the award is named after Melvin Mooney, developer of the Mooney viscometer and of the Mooney-Rivlin hyperelastic law. The award consists of an engraved plaque and prize money. The medal honors individuals "who have exhibited exceptional technical competency by making significant and repeated contributions to rubber science and technology".
John Isaiah Brauman is an American chemist.

Zafra M. Lerman is an American chemist, educator, and humanitarian. She is the President of the Malta Conferences Foundation, which aims to promote peace by bringing together scientists from otherwise hostile countries to discuss science and foster international scientific and technical collaboration. From 1986 to 2010, she chaired the American Chemical Society's Subcommittee on Scientific Freedom and Human Rights. She has been successful in preventing executions, releasing prisoners of conscience from jail and bringing dissidents to freedom. She is the recipient of many awards for education and science diplomacy, including the 1999 Presidential Award from U.S. President Clinton, the 2005 Nyholm Prize for Education from the Royal Society of Chemistry (England), the 2015 Science Diplomacy Award from the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the 2016 Andrei Sakharov Award for human rights from the American Physical Society (APS), the 2016 United Nations NOVUS Award for the 16th Sustainable Development Goal: Peace and Justice, and the 2017 International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry Distinguished Women in Chemistry or Chemical Engineering Award.
Allison A. Campbell is an American chemist who is known in the areas of biomineralization, biomimetics and biomaterials for her innovative work on bioactive coatings for medical implants. She is the acting associate laboratory director for the Earth and Biological Sciences Directorate at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) of the Department of Energy. She previously served as director of the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL) at PNNL. She was elected as the 2017 president of the American Chemical Society (ACS).
The William H. Nichols Medal is awarded annually for original research in chemistry. Nominees must have made a "significant and original contribution in any field of chemistry" during the five years preceding the presentation date. The medallist receives a gold medal, a bronze replica and a cash award. The award was established in 1902 by the New York Section of the American Chemical Society (ACS) through a gift from chemist and businessman William H. Nichols. It was the first award to be approved by the ACS. The medal was first awarded in 1903.
The Award for Encouraging Disadvantaged Students into Careers in the Chemical Sciences is an American Chemical Society (ACS) award, sponsored by The Camille and Henry Dreyfus Foundation, was instituted in 1993 with the intention of recognizing "significant accomplishments by individuals in stimulating students, underrepresented in the profession, to elect careers in the chemical sciences and engineering." It is awarded by the American Chemical Society as part of their national awards program. Recipients receive $5,000, a certificate, up to $1,500 for travel expenses, and a grant of $10,000 to their designee of choice. The first recipient was Henry C. McBay.
The Local Section of the American Chemical Society has awarded the Herty Medal since 1933 in honor of Charles Herty. The medallion is solid gold and is inscribed with the words "pro scientia et patria - Herty 1933." The Latin phrase translates roughly as "for science and country".

Charles C. Price was an American chemist and president of the American Chemical Society (1965). He taught at the University of Illinois at Chicago, the University of Notre Dame, and the University of Pennsylvania.
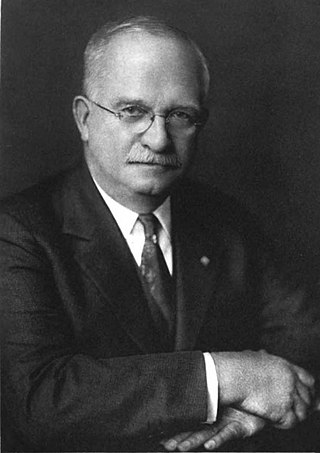
Charles Lathrop Parsons was an American chemist. He was a professor at the University of New Hampshire for twenty years, and then a chemist and mineralogist at the U.S. Bureau of Mines. For nearly forty years, Parsons served as executive secretary of the American Chemical Society, becoming known as "Mr. ACS" and substantially influencing the formation of the association.
Cathleen M. Crudden is a Canadian chemist. She is a Canada Research Chair in Metal Organic Chemistry at Queen's University at Kingston. In February 2021, she took up the role of Editor-in-chief at ACS Catalysis.
Sarah Elizabeth Reisman is a Chemistry Professor at the California Institute of Technology. She received the (2013) Arthur C. Cope Scholar Award and the (2014) Tetrahedron Young Investigator Award for Organic Synthesis. Her research focuses on the total synthesis of complex natural products.