The Japanese numerals are the number names used in Japanese. In writing, they are the same as the Chinese numerals, and large numbers follow the Chinese style of grouping by 10,000. Two pronunciations are used: the Sino-Japanese (on'yomi) readings of the Chinese characters and the Japanese yamato kotoba.

The V sign is a hand gesture in which the index and middle fingers are raised and parted to make a V shape while the other fingers are clenched. It has various meanings, depending on the circumstances and how it is presented.

The two-finger salute is a salute given using only the middle and index fingers, while bending the other fingers at the second knuckle, and with the palm facing the signer. This salute is used by the Polish Armed Forces, other uniformed services in Poland, and, in some countries, the Cub Scouts.

A mudra is a symbolic or ritual gesture or pose in Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism. While some mudras involve the entire body, most are performed with the hands and fingers.
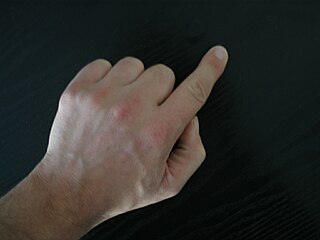
The index finger is the second digit of a human hand. It is located between the thumb and the middle finger. It is usually the most dextrous and sensitive digit of the hand, though not the longest. It is shorter than the middle finger, and may be shorter or longer than the ring finger.
The American Manual Alphabet (AMA) is a manual alphabet that augments the vocabulary of American Sign Language.
Several manual alphabets in use around the world employ two hands to represent some or all of the letters of an alphabet, usually as a part of a deaf sign language. Two-handed alphabets are less widespread than one-handed manual alphabets. They may be used to represent the Latin alphabet or the Cyrillic alphabet.

The OK gesture or OK sign or ring gesture is performed by joining the thumb and index finger in a circle, and holding the other fingers straight or relaxed away from the palm. Commonly used by scuba divers, it signifies "I am OK" or "Are you OK?" when underwater. In most English-speaking countries it denotes approval, agreement, and that all is well or "okay". In other contexts or cultures, similar gestures may have different meanings including those that are negative, offensive, financial, numerical, devotional, political, or purely linguistic.

The sign of the horns is a hand gesture with a variety of meanings and uses in various cultures. It is formed by extending the index and little fingers while holding the middle and ring fingers down with the thumb.

Finger binary is a system for counting and displaying binary numbers on the fingers of either or both hands. Each finger represents one binary digit or bit. This allows counting from zero to 31 using the fingers of one hand, or 1023 using both: that is, up to 25−1 or 210−1 respectively.

A thumb signal, usually described as a thumbs-up or thumbs-down, is a common hand gesture achieved by a closed fist held with the thumb extended upward or downward, respectively. The thumbs-up gesture is associated with positivity, approval, achievement, satisfaction and solidarity, while the thumbs-down gesture is associated with concern, disapproval, dissatisfaction, rejection and failure.
American Sign Language (ASL), the sign language used by the deaf community throughout most of North America, has a rich vocabulary of terms, which include profanity. Within deaf culture, there is a distinction drawn between signs used to curse versus signs that are used to describe sexual acts. In usage, signs to describe detailed sexual behavior are highly taboo due to their graphic nature. As for the signs themselves, some signs do overlap, but they may also vary according to usage. For example, the sign for "shit" when used to curse is different from the sign for "shit" when used to describe the bodily function or the fecal matter.

Hand signaling, also known as arb or arbing, is a system of hand signals used on financial trading floors to communicate buy and sell information in an open outcry trading environment. The system is used at financial exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the American Stock Exchange (AMEX). The AMEX is the only U.S. stock market to permit the transmission of buy and sell orders through hand signals.

Finger-counting, also known as dactylonomy, is the act of counting using one's fingers. There are multiple different systems used across time and between cultures, though many of these have seen a decline in use because of the spread of Arabic numerals.

A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking.
The Hamburg Sign Language Notation System, or HamNoSys, is a transcription system for all sign languages, with a direct correspondence between symbols and gesture aspects, such as hand location, shape and movement. It was developed in 1985 at the University of Hamburg, Germany. As of 2020, it is in its fourth revision.
An obscene gesture is a movement or position of the body, especially of the hands or arms, that is considered exceedingly offensive or vulgar in some particular cultures. Such gestures are often sexually suggestive.

The Schwurhand is a heraldic charge depicting the hand gesture that is used in Germanic Europe and neighbouring countries, when swearing an oath in court, in office, or in swearing-in. The right hand is raised, with the index finger and middle finger extended upwards; the last two digits are curled downwards against the palm. The thumb is shown slightly curled or raised.

An Esperanto manual alphabet is included as part of the Signuno project for manually coded Esperanto. Signuno is based on the signs of International Sign, but adapted to the grammatical system of Esperanto.






























