
A gluon is an elementary particle that acts as the exchange particle for the strong force between quarks. It is analogous to the exchange of photons in the electromagnetic force between two charged particles. Gluons bind quarks together, forming hadrons such as protons and neutrons.
A quark is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks, down quarks and electrons. Owing to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never found in isolation; they can be found only within hadrons, which include baryons and mesons, or in quark–gluon plasmas. For this reason, much of what is known about quarks has been drawn from observations of hadrons.

In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the theory of the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons. Quarks are fundamental particles that make up composite hadrons such as the proton, neutron and pion. QCD is a type of quantum field theory called a non-abelian gauge theory, with symmetry group SU(3). The QCD analog of electric charge is a property called color. Gluons are the force carriers of the theory, just as photons are for the electromagnetic force in quantum electrodynamics. The theory is an important part of the Standard Model of particle physics. A large body of experimental evidence for QCD has been gathered over the years.

The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles. It was developed in stages throughout the latter half of the 20th century, through the work of many scientists worldwide, with the current formulation being finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, proof of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and the Higgs boson (2012) have added further credence to the Standard Model. In addition, the Standard Model has predicted various properties of weak neutral currents and the W and Z bosons with great accuracy.
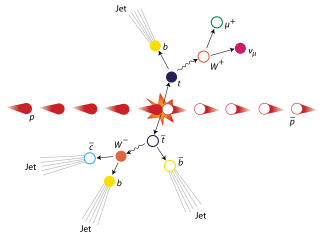
The top quark, sometimes also referred to as the truth quark, is the most massive of all observed elementary particles. It derives its mass from its coupling to the Higgs Boson. This coupling is very close to unity; in the Standard Model of particle physics, it is the largest (strongest) coupling at the scale of the weak interactions and above. The top quark was discovered in 1995 by the CDF and DØ experiments at Fermilab.

Technicolor theories are models of physics beyond the Standard Model that address electroweak gauge symmetry breaking, the mechanism through which W and Z bosons acquire masses. Early technicolor theories were modelled on quantum chromodynamics (QCD), the "color" theory of the strong nuclear force, which inspired their name.

Lattice QCD is a well-established non-perturbative approach to solving the quantum chromodynamics (QCD) theory of quarks and gluons. It is a lattice gauge theory formulated on a grid or lattice of points in space and time. When the size of the lattice is taken infinitely large and its sites infinitesimally close to each other, the continuum QCD is recovered.
Hadronization is the process of the formation of hadrons out of quarks and gluons. There are two main branches of hadronization: quark-gluon plasma (QGP) transformation and colour string decay into hadrons. The transformation of quark-gluon plasma into hadrons is studied in lattice QCD numerical simulations, which are explored in relativistic heavy-ion experiments. Quark-gluon plasma hadronization occurred shortly after the Big Bang when the quark–gluon plasma cooled down to the Hagedorn temperature when free quarks and gluons cannot exist. In string breaking new hadrons are forming out of quarks, antiquarks and sometimes gluons, spontaneously created from the vacuum.
The QCD vacuum is the quantum vacuum state of quantum chromodynamics (QCD). It is an example of a non-perturbative vacuum state, characterized by non-vanishing condensates such as the gluon condensate and the quark condensate in the complete theory which includes quarks. The presence of these condensates characterizes the confined phase of quark matter.

In particle physics, a three-jet event is an event with many particles in final state that appear to be clustered in three jets. A single jet consists of particles that fly off in roughly the same direction. One can draw three cones from the interaction point, corresponding to the jets, and most particles created in the reaction will appear to belong to one of these cones. These events are currently the most direct available evidence for the existence of gluons, and were first observed by the TASSO experiment at the PETRA accelerator at the DESY laboratory.
In particle physics, chiral symmetry breaking is the spontaneous symmetry breaking of a chiral symmetry – usually by a gauge theory such as quantum chromodynamics, the quantum field theory of the strong interaction. Yoichiro Nambu was awarded the 2008 Nobel prize in physics for describing this phenomenon.
Topcolor is a model in theoretical physics, of dynamical electroweak symmetry breaking in which the top quark and anti-top quark form a composite Higgs boson by a new force arising from massive "top gluons". The solution to composite Higgs models was actually anticipated in 1981, and found to be the Infrared fixed point for the top quark mass.

Quark–gluon plasma is an interacting localized assembly of quarks and gluons at thermal and chemical (abundance) equilibrium. The word plasma signals that free color charges are allowed. In a 1987 summary, Léon van Hove pointed out the equivalence of the three terms: quark gluon plasma, quark matter and a new state of matter. Since the temperature is above the Hagedorn temperature—and thus above the scale of light u,d-quark mass—the pressure exhibits the relativistic Stefan-Boltzmann format governed by temperature to the fourth power and many practically massless quark and gluon constituents. It can be said that QGP emerges to be the new phase of strongly interacting matter which manifests its physical properties in terms of nearly free dynamics of practically massless gluons and quarks. Both quarks and gluons must be present in conditions near chemical (yield) equilibrium with their colour charge open for a new state of matter to be referred to as QGP.
Thomas Carlos Mehen is an American physicist. His research has consisted of primarily Quantum chromodynamics (QCD) and the application of effective field theory to problems in hadronic physics. He has also worked on effective field theory for non-relativistic particles whose short range interactions are characterized by a large scattering length, as well as novel field theories which arise from unusual limits of string theory.
In particle physics, W′ and Z′ bosons refer to hypothetical gauge bosons that arise from extensions of the electroweak symmetry of the Standard Model. They are named in analogy with the Standard Model W and Z bosons.
The proton spin crisis is a theoretical crisis precipitated by a 1987 experiment by the European Muon Collaboration (EMC), which tried to determine the distribution of spin within the proton.

In theoretical particle physics, the gluon field strength tensor is a second order tensor field characterizing the gluon interaction between quarks.

In theoretical particle physics, the gluon field is a four-vector field characterizing the propagation of gluons in the strong interaction between quarks. It plays the same role in quantum chromodynamics as the electromagnetic four-potential in quantum electrodynamics – the gluon field constructs the gluon field strength tensor.

Stephan Narison is a Malagasy theoretical high-energy physicist specialized in quantum chromodynamics (QCD), the gauge theory of strong interactions. He is the founder of the Series of International Conferences in Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD-Montpellier) and of the Series of International Conferences in High-Energy Physics (HEPMAD-Madagascar).
Kenneth Alan Johnson was an American theoretical physicist. He was Professor of Physics at MIT, a leader in the study of quantum field theories and the quark substructure of matter. Johnson contributed to the understanding of symmetry and anomalies in quantum field theories and to models of quark confinement and dynamics in quantum chromodynamics.







