Christian eschatology, is a minor branch of study within Christian theology which deals with the doctrine of the "last things", especially the Second Coming of Christ, or Parousia. Eschatology – the word derives from two Greek roots meaning "last" (ἔσχατος) and "study" (-λογία) – involves the study of "end things", whether of the end of an individual life, of the end of the age, of the end of the world, or of the nature of the Kingdom of God. Broadly speaking, Christian eschatology focuses on the ultimate destiny of individual souls and of the entire created order, based primarily upon biblical texts within the Old and New Testaments.

The resurrection of Jesus is the Christian belief that God raised Jesus from the dead on the third day after his crucifixion, starting – or restoring – his exalted life as Christ and Lord. According to the New Testament writing, Jesus was firstborn from the dead, ushering in the Kingdom of God. He appeared to his disciples, calling the apostles to the Great Commission of forgiving sin and baptizing repenters, and ascended to Heaven.
Salvation is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, salvation generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its consequences. The academic study of salvation is called soteriology.

The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord is a concept found across the Abrahamic religions and the Frashokereti of Zoroastrianism.

The Westminster Confession of Faith, or simply the Westminster Confession, is a Reformed confession of faith. Drawn up by the 1646 Westminster Assembly as part of the Westminster Standards to be a confession of the Church of England, it became and remains the "subordinate standard" of doctrine in the Church of Scotland and has been influential within Presbyterian churches worldwide.

Christian mortalism is the Christian belief that the human soul is not naturally immortal and may include the belief that the soul is "sleeping" after death until the Resurrection of the Dead and the Last Judgment, a time known as the intermediate state. "Soul sleep" is often used as a pejorative term, so the more neutral term "mortalism" was also used in the nineteenth century, and "Christian mortalism" since the 1970s. Historically the term psychopannychism was also used, despite problems with the etymology and application. The term thnetopsychism has also been used; for example, Gordon Campbell (2008) identified John Milton as believing in the latter.
John Wroe was a British evangelist who founded the Christian Israelite Church in the 1820s after having what he believed were a series of visions.
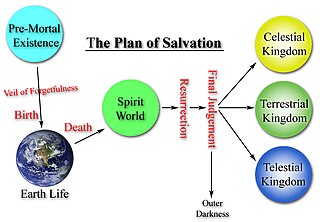
According to the doctrine of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, the largest denomination in the Latter Day Saint movement, the plan of salvation is a plan God created to save, redeem, and exalt humankind, through the atonement of Jesus Christ. The elements of this plan are drawn from various sources, including the Bible, Book of Mormon, Doctrine & Covenants, Pearl of Great Price, and numerous statements made by the leadership of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. The first appearance of the graphical representation of the plan of salvation was provided in the 1952 missionary manual entitled A Systematic Program for Teaching the Gospel.
A spirit body is, according to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, the organization of a spiritual element, made into the spiritual form of man, which was made in the same likeness of God the Father. This likeness apparently gave rise to the phrase and meaning of, "like father like son," which means the son is in the likeness of the father, which provides meaning to the claim that humanity was made in the likeness of God. Generally, people in the world have commonly used the word "soul" to denote this spirit body.
144,000 is a natural number. It has significance in various religious movements and ancient prophetic belief systems.

Mormon cosmology is the description of the history, evolution, and destiny of the physical and metaphysical universe according to Mormonism, which includes the doctrines taught by leaders and theologians of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, Mormon fundamentalism, the Restoration Church of Jesus Christ, and other Brighamite denominations within the Latter Day Saint movement. Mormon cosmology draws from Biblical cosmology, but has many unique elements provided by movement founder Joseph Smith. These views are not generally shared by adherents of other Latter Day Saint movement denominations who do not self-identify as "Mormons", such as the Community of Christ.
Members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and other adherents in the Latter Day Saint movement, believe that there will be a Second Coming of Jesus Christ to the earth sometime in the future. The LDS Church and its leaders do not make predictions of the actual date of the Second Coming.
Catholic theology is the understanding of Catholic doctrine or teachings, and results from the studies of theologians. It is based on canonical scripture, and sacred tradition, as interpreted authoritatively by the magisterium of the Catholic Church. This article serves as an introduction to various topics in Catholic theology, with links to where fuller coverage is found.

The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints focuses its doctrine and teaching on Jesus Christ; that he was the Son of God, born of Mary, lived a perfect life, performed miracles, bled from every pore in the Garden of Gethsemane, died on the cross, rose on the third day, appeared again to his disciples, and now resides, authoritatively, on the right hand side of God. In brief, some beliefs are in common with Catholics, Orthodox and Protestant traditions. However, teachings of the LDS Church differ significantly in other ways and encompass a broad set of doctrines, so that the above-mentioned denominations usually place the LDS Church outside the bounds of orthodox Christian teaching as summarized in the Nicene Creed.
Christian theology is the theology – the systematic study of the divine and religion – of Christianity and Christian belief and practice. It concentrates primarily upon the texts of the Old Testament and of the New Testament, as well as on Christian tradition. Christian theologians use biblical exegesis, rational analysis and argument. Theologians may undertake the study of Christian theology for a variety of reasons, such as in order to:

In Christianity, heaven is traditionally the location of the throne of God and the angels of God, and in most forms of Christianity it is the abode of the righteous dead in the afterlife. In some Christian denominations it is understood as a temporary stage before the resurrection of the dead and the saints' return to the New Earth.
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead by which most or all people who have died would be resurrected. Various forms of this concept can be found in Christian, Islamic, Jewish, Samaritan and Zoroastrian eschatology.
The Pillars of Adventism are landmark doctrines for Seventh-day Adventists. They are Bible doctrines that define who they are as a people of faith; doctrines that are "non-negotiables" in Adventist theology. The Seventh-day Adventist church teaches that these Pillars are needed to prepare the world for the second coming of Jesus Christ, and sees them as a central part of its own mission. Adventists teach that the Seventh-day Adventist Church doctrines were both a continuation of the reformation started in the 16th century and a movement of the end time rising from the Millerites, bringing God's final messages and warnings to the world.

Eternal life traditionally refers to continued life after death, as outlined in Christian eschatology. The Apostles' Creed testifies: "I believe... the resurrection of the body, and life everlasting." In this view, eternal life commences after the second coming of Jesus and the resurrection of the dead, although in the New Testament's Johannine literature there are references to eternal life commencing in the earthly life of the believer, possibly indicating an inaugurated eschatology.
The beliefs of Jehovah's Witnesses are based on the Bible teachings of Charles Taze Russell—founder of the Bible Student movement—and successive presidents of the Watch Tower Society, Joseph Franklin Rutherford, and Nathan Homer Knorr. Since 1976, all doctrinal decisions have been made by the Governing Body of Jehovah's Witnesses, a group of elders at the denomination's headquarters. These teachings are disseminated through The Watchtower magazine and other publications of Jehovah's Witnesses, and at conventions and congregation meetings.








