Related Research Articles

A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.

A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspots, such as Hawaii or Iceland, and large igneous provinces such as the Deccan and Siberian Traps. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries.

The lunar maria are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient asteroid impacts on the far side on the Moon that triggered volcanic activity on the opposite (near) side. They were dubbed maria by early astronomers who mistook them for actual seas. They are less reflective than the "highlands" as a result of their iron-rich composition, and hence appear dark to the naked eye. The maria cover about 16% of the lunar surface, mostly on the side visible from Earth. The few maria on the far side are much smaller, residing mostly in very large craters. The traditional nomenclature for the Moon also includes one oceanus (ocean), as well as features with the names lacus ('lake'), palus ('marsh'), and sinus ('bay'). The last three are smaller than maria, but have the same nature and characteristics.

A flood basalt is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reaching the surface of the Earth via a mantle plume. Flood basalt provinces such as the Deccan Traps of India are often called traps, after the Swedish word trappa, due to the characteristic stairstep geomorphology of many associated landscapes.

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive and extrusive, arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems.
Dan Peter McKenzie is a Professor of Geophysics at the University of Cambridge, and one-time head of the Bullard Laboratories of the Cambridge Department of Earth Sciences. He wrote the first paper defining the mathematical principles of plate tectonics on a sphere, and his early work on mantle convection created the modern discussion of planetary interiors.

The Central American Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes which extends parallel to the Pacific coastline of the Central American Isthmus, from Mexico to Panama. This volcanic arc, which has a length of 1,100 kilometers is formed by an active subduction zone, with the Cocos Plate subducting underneath the Caribbean Plate. The region has been volcanically and geologically active for at least the past several million years. Numerous volcanoes are spread throughout various Central American countries; many have been active in the geologic past, some more so than others.

Don Lynn Anderson was an American geophysicist who made significant contributions to the understanding of the origin, evolution, structure, and composition of Earth and other planets. An expert in numerous scientific disciplines, Anderson's work combined seismology, solid state physics, geochemistry and petrology to explain how the Earth works. Anderson was best known for his contributions to the understanding of the Earth's deep interior, and more recently, for the plate theory hypothesis that hotspots are the product of plate tectonics rather than narrow plumes emanating from the deep Earth. Anderson was Professor (Emeritus) of Geophysics in the Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). He received numerous awards from geophysical, geological and astronomical societies. In 1998 he was awarded the Crafoord Prize by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences along with Adam Dziewonski. Later that year, Anderson received the National Medal of Science. He held honorary doctorates from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and the University of Paris (Sorbonne), and served on numerous university advisory committees, including those at Harvard, Princeton, Yale, University of Chicago, Stanford, University of Paris, Purdue University, and Rice University. Anderson's wide-ranging research resulted in hundreds of published papers in the fields of planetary science, seismology, mineral physics, petrology, geochemistry, tectonics and the philosophy of science.

Volcanic gases are gases given off by active volcanoes. These include gases trapped in cavities (vesicles) in volcanic rocks, dissolved or dissociated gases in magma and lava, or gases emanating from lava, from volcanic craters or vents. Volcanic gases can also be emitted through groundwater heated by volcanic action.

The East Australia hotspot is a volcanic province in southeast Australia which includes the Peak Range in central Queensland, the Main Range on the Queensland-New South Wales border, Tweed Volcano in New South Wales, and the Newer Volcanics Province (NVP) in Victoria and South Australia. A number of the volcanoes in the province have erupted since Aboriginal settlement. The most recent eruptions were about 5,600 years ago, and memories of them survive in Aboriginal folklore. These eruptions formed the volcanoes Mount Schank and Mount Gambier in the NVP. There have been no eruptions on the Australian mainland since European settlement.

Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra, and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of eruption during a period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types all in one eruptive series.
The Anahim hotspot is a hypothesized hotspot in the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It has been proposed as the candidate source for volcanism in the Anahim Volcanic Belt, a 300 kilometres long chain of volcanoes and other magmatic features that have undergone erosion. This chain extends from the community of Bella Bella in the west to near the small city of Quesnel in the east. While most volcanoes are created by geological activity at tectonic plate boundaries, the Anahim hotspot is located hundreds of kilometres away from the nearest plate boundary.
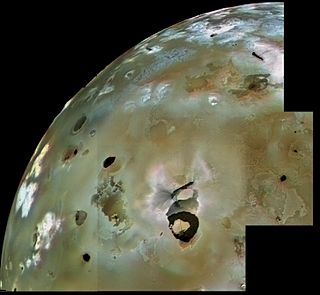
Loki Patera is the largest volcanic depression on Jupiter's moon Io, 202 kilometres (126 mi) in diameter. It contains an active lava lake, with an episodically overturning crust. The level of activity seen is similar to a superfast spreading mid-ocean ridge on Earth. Temperature measurements of thermal emission at Loki Patera taken by Voyager 1's Infrared Interferometer Spectrometer and Radiometer (IRIS) instrument were consistent with sulfur volcanism.

Volcanism on Io, a moon of Jupiter, is represented by the presence of volcanoes, volcanic pits and lava flows on the moon's surface. Its volcanic activity was discovered in 1979 by Voyager 1 imaging scientist Linda Morabito. Observations of Io by passing spacecraft and Earth-based astronomers have revealed more than 150 active volcanoes. Up to 400 such volcanoes are predicted to exist based on these observations. Io's volcanism makes the satellite one of only four known currently volcanically active worlds in the Solar System.
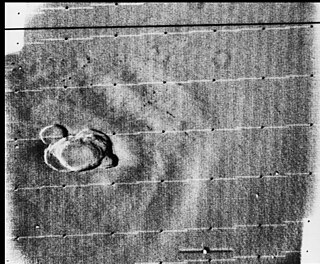
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features include extensive lava flows, vast lava plains, and the largest known volcanoes in the Solar System. Martian volcanic features range in age from Noachian to late Amazonian, indicating that the planet has been volcanically active throughout its history, and some speculate it probably still is so today. Both Earth and Mars are large, differentiated planets built from similar chondritic materials. Many of the same magmatic processes that occur on Earth also occurred on Mars, and both planets are similar enough compositionally that the same names can be applied to their igneous rocks and minerals.
Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.

Earth's internal heat budget is fundamental to the thermal history of the Earth. The flow of heat from Earth's interior to the surface is estimated at 47±2 terawatts (TW) and comes from two main sources in roughly equal amounts: the radiogenic heat produced by the radioactive decay of isotopes in the mantle and crust, and the primordial heat left over from the formation of Earth.

Colin James Ness Wilson FRS FRSNZ is Professor of Volcanology at Victoria University of Wellington in New Zealand.
Intraplate volcanism is volcanism that takes place away from the margins of tectonic plates. Most volcanic activity takes place on plate margins, and there is broad consensus among geologists that this activity is explained well by the theory of plate tectonics. However, the origins of volcanic activity within plates remains controversial.
Catherine Jeanne Annen is a French geologist at the Czech Academy of Sciences. Her research considers igneous bodies, volcanic eruptions. and exploration for geothermal energy. She was awarded the 2022 Geological Society of London Bigsby Medal.
References
- ↑ "Portant nomination du directeur de l'Institut de physique du Globe de Paris". legifrance.gouv.fr (in French). 14 January 2011.
- ↑ "Académie des sciences".
- ↑ "Academia europaea".
- ↑ "De vive voix".
- ↑ Le texte de cette conférence est édité dans le volume 4 Qu'est-ce que l'Univers de la collection « Université de tous les savoirs », sous la direction d'Yves Michaud, aux Éditions Odile Jacob, 2001, p. 414-428
- ↑ "Bibliographie-France culture".