Related Research Articles

The Dead Sea is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank to the west. It lies in the Jordan Rift Valley, and its main tributary is the Jordan River.

Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply at the tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either generalized, affecting the whole body, or local, affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during hypoventilation training or strenuous physical exercise.

Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, or purple on some people with darker skin, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon.
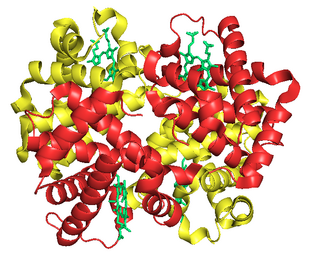
Fetal hemoglobin, or foetal haemoglobin is the main oxygen carrier protein in the human fetus. Hemoglobin F is found in fetal red blood cells, and is involved in transporting oxygen from the mother's bloodstream to organs and tissues in the fetus. It is produced at around 6 weeks of pregnancy and the levels remain high after birth until the baby is roughly 2–4 months old. Hemoglobin F has a different composition from the adult forms of hemoglobin, which allows it to bind oxygen more strongly. This way, the developing fetus is able to retrieve oxygen from the mother's bloodstream, which occurs through the placenta found in the mother's uterus.

Hydroxycarbamide, also known as hydroxyurea, is a medication used in sickle-cell disease, essential thrombocythemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia and cervical cancer. In sickle-cell disease it increases fetal hemoglobin and decreases the number of attacks. It is taken by mouth.
PUVA is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for skin diseases: Eczema, Psoriasis, Graft-versus-host disease, Vitiligo, Mycosis Fungoides, Large Plaque Parapsoriasis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma using the sensitizing effects of the drug Psoralen. The psoralen is applied or taken orally to sensitize the skin, then the skin is exposed to UVA.

Sickle cell trait describes a condition in which a person has one abnormal allele of the hemoglobin beta gene, but does not display the severe symptoms of sickle cell disease that occur in a person who has two copies of that allele. Those who are heterozygous for the sickle cell allele produce both normal and abnormal hemoglobin.
Alefacept is a genetically engineered immunosuppressive drug. It was sold under the brand name Amevive in Canada, the United States, Israel, Switzerland and Australia. In 2011, the manufacturers made a decision to cease promotion, manufacturing, distribution and sales of Amevive during a supply disruption. According to Astellas Pharma US, Inc., the decision to cease Amevive sales was neither the result of any specific safety concern nor the result of any FDA-mandated or voluntary product recall. On the other hand, usage of Amevive was associated with a certain risk of development systemic diseases such as malignancies. This drug was never approved for the European drug market.
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma, so TNF inhibitors may be used in their treatment. The important side effects of TNF inhibitors include lymphomas, infections, congestive heart failure, demyelinating disease, a lupus-like syndrome, induction of auto-antibodies, injection site reactions, and systemic side effects.

Interleukin 17 family is a family of pro-inflammatory cystine knot cytokines. They are produced by a group of T helper cell known as T helper 17 cell in response to their stimulation with IL-23. Originally, Th17 was identified in 1993 by Rouvier et al. who isolated IL17A transcript from a rodent T-cell hybridoma. The protein encoded by IL17A is a founding member of IL-17 family. IL17A protein exhibits a high homology with a viral IL-17-like protein encoded in the genome of T-lymphotropic rhadinovirus Herpesvirus saimiri. In rodents, IL-17A is often referred to as CTLA8.
Medical tourism in Israel is medical tourism in which people travel to Israel for medical treatment, which is emerging as an important destination for medical tourists. In 2006, 15,000 people came to Israel for medical treatment, bringing in $40 million in revenue. In 2010, Israel treated 30,000 medical tourists. The Health Ministry estimates that they inject about NIS 200 million a year into the health system, of which more than NIS 100 million goes to government hospitals. Outside experts put the total much higher, at almost NIS 500 million.

Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia (SCA). It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to a rigid, sickle-like shape under certain circumstances. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain, anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke. Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years.

Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus is a rare disease of the skin that presents as multiple, discrete, red papules that tend to coalesce into linear plaques that follow the Lines of Blaschko. The plaques can be slightly warty (psoriaform) or scaly (eczema-like). ILVEN is caused by somatic mutations that result in genetic mosaicism. There is no cure, but different medical treatments can alleviate the symptoms.
Sickle cell nephropathy is a type of nephropathy associated with sickle cell disease which causes kidney complications as a result of sickling of red blood cells in the small blood vessels. The hypertonic and relatively hypoxic environment of the renal medulla, coupled with the slow blood flow in the vasa recta, favors sickling of red blood cells, with resultant local infarction. Functional tubule defects in patients with sickle cell disease are likely the result of partial ischemic injury to the renal tubules.
Ixekizumab, sold under the brand name Taltz, is an injectable medication for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Chemically, it is a form of a humanized monoclonal antibody. The substance acts by binding interleukin 17A and neutralizing it, reducing inflammation.
Itolizumab is a ‘first in class’ humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody developed by Biocon and the Center of Molecular Immunology (CIM), Havana.
GSK2831781 is a monoclonal antibody being developed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) for autoimmune diseases. The antibody targets the T cell activation marker LAG-3, which is mainly expressed in inflamed tissues. In GSK's March 2015 Product development pipeline document the antibody is listed under 'Immuno-inflammation' candidates. GSK2831781 entered a Phase I clinical trial in psoriasis early in 2015.
Crizanlizumab, sold under the brand name Adakveo & Ryverna both by Novartis, is a monoclonal antibody medication that binds to P-selectin. It is a drug used to reduce the frequency of vaso-occlusive crisis in people aged 16 years and older who have sickle cell anemia. Vaso-occlusive crisis is a common and painful complication of sickle cell disease that occurs when blood circulation is obstructed by sickled red blood cells.
Sampat Tukaram Ramteke was an engineer and social activist from Nagpur, Maharashtra, India. In 2018, he was conferred the Padma Shri civilian honour posthumously, for his contribution in raising awareness about the sickle cell disease.
Sickle cell retinopathy can be defined as retinal changes due to blood vessel damage in the eye of a person with a background of sickle cell disease. It can likely progress to loss of vision in late stages due to vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment. Sickle cell disease is a structural red blood cell disorder leading to consequences in multiple systems. It is characterized by chronic red blood cell destruction, vascular injury, and tissue ischemia causing damage to the brain, eyes, heart, lungs, kidneys, spleen, and musculoskeletal system.
References
- ↑ "Sickle Cell Disease-What Increases Your Risk".
- ↑ Climatotherapy sites Archived 2005-06-12 at archive.today National Psoriasis Foundation
- ↑ Hodak, Emmilia; Alice B. Gottlieb; Tsvi Segal; Yael Politi; Lea Maron; Jaqueline Sulkes; Michael David (2003). "Climatotherapy at the Dead Sea is a remittive therapy for psoriasis: combined effects on epidermal and immunologic activation". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 49 (3): 451–7. doi:10.1067/S0190-9622(03)00916-2. PMID 12963909.