
A sundial is a horological device that tells the time of day when direct sunlight shines by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word, it consists of a flat plate and a gnomon, which casts a shadow onto the dial. As the Sun appears to move through the sky, the shadow aligns with different hour-lines, which are marked on the dial to indicate the time of day. The style is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, though a single point or nodus may be used. The gnomon casts a broad shadow; the shadow of the style shows the time. The gnomon may be a rod, wire, or elaborately decorated metal casting. The style must be parallel to the axis of the Earth's rotation for the sundial to be accurate throughout the year. The style's angle from horizontal is equal to the sundial's geographical latitude.
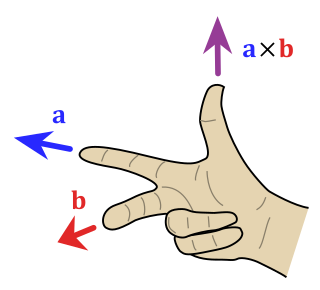
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a convention and a mnemonic for deciding the orientation of axes in three-dimensional space. It is a convenient method for determining the direction of the cross product of two vectors.

A clock face is the part of an analog clock that displays time through the use of a flat dial with reference marks, and revolving pointers turning on concentric shafts at the center, called hands. In its most basic, globally recognized form, the periphery of the dial is numbered 1 through 12 indicating the hours in a 12-hour cycle, and a short hour hand makes two revolutions in a day. A long minute hand makes one revolution every hour. The face may also include a second hand, which makes one revolution per minute. The term is less commonly used for the time display on digital clocks and watches.

Widdershins is a term meaning to go counter-clockwise, anti-clockwise, or lefthandwise, or to walk around an object by always keeping it on the left. Literally, it means to take a course opposite the apparent motion of the sun viewed from the Northern Hemisphere. The earliest recorded use of the word, as cited by the Oxford English Dictionary, is in a 1513 translation of the Aeneid, where it is found in the phrase "Abaisit I wolx, and widdersyns start my hair." In this sense, "widdershins start my hair" means "my hair stood on end".

A bolted joint is one of the most common elements in construction and machine design. It consists of a male threaded fastener that captures and joins other parts, secured with a matching female screw thread. There are two main types of bolted joint designs: tension joints and shear joints.

A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener.

A cheater bar, snipe, or cheater pipe is an improvised breaker bar made from a length of pipe and a wrench (spanner).

A lug wrench, also colloquially known as a tire iron, is the name for a type of socket wrench used to loosen and tighten lug nuts on automobile wheels. In the United Kingdom and Australia, it is commonly known as a wheel brace.

A brace is a hand tool used with a bit to drill holes, usually in wood. Pressure is applied to the top while the handle is rotated. If the bit's lead and cutting spurs are both in good working order, the user should not have to apply any pressure other than for balance: the lead will pull the bit through the wood. Bits used to come in a variety of types but the more commonly used Ridgeway and Irwin-pattern bits also rely on a tip called a snail, which is a tapered threaded screw that pulls the bit forward.

A lug nut or wheel nut is a fastener, specifically a nut, used to secure a wheel on a vehicle. Typically, lug nuts are found on automobiles, trucks (lorries), and other large vehicles using rubber tires.

An impact driver is a tool that delivers a strong, sudden rotational force and forward thrust. The force can be delivered either by striking with a hammer in the case of manual impact drivers, or mechanically in the case of powered impact drivers.

A screw is a mechanism that converts rotational motion to linear motion, and a torque to a linear force. It is one of the six classical simple machines. The most common form consists of a cylindrical shaft with helical grooves or ridges called threads around the outside. The screw passes through a hole in another object or medium, with threads on the inside of the hole that mesh with the screw's threads. When the shaft of the screw is rotated relative to the stationary threads, the screw moves along its axis relative to the medium surrounding it; for example rotating a wood screw forces it into wood. In screw mechanisms, either the screw shaft can rotate through a threaded hole in a stationary object, or a threaded collar such as a nut can rotate around a stationary screw shaft. Geometrically, a screw can be viewed as a narrow inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder.

Wheel studs are the threaded fasteners that hold on the wheels of many automobiles. They are semi-permanently mounted directly to the vehicle hub, usually through the brake drum or brake disk. Lug nuts are fastened onto the wheel stud to secure the wheel. When a wheel is removed for tire changes etc., the stud remains in the hub.

Precession is the process of a round part in a round hole, rotating with respect to each other, wherein the inner part begins rolling around the circumference of the outer bore, in a direction opposite of rotation. This is caused by too much clearance between them and a radial force on the part that constantly changes direction. The direction of rotation of the inner part is opposite to the direction of rotation of the radial force.

The Spinning Dancer, also known as the Silhouette Illusion, is a kinetic, bistable, animated optical illusion originally distributed as a GIF animation showing a silhouette of a pirouetting female dancer. The illusion, created in 2003 by Japanese web designer Nobuyuki Kayahara, involves the apparent direction of motion of the figure. Some observers initially see the figure as spinning clockwise and some counterclockwise. Additionally, some may see the figure suddenly spin in the opposite direction.

A jam nut is a low profile type of nut, typically half as tall as a standard nut. It is commonly used as a type of locknut, where it is "jammed" up against a standard nut to lock the two in place. It is also used in situations where a standard nut would not fit.

A screw and a bolt are similar types of fastener typically made of metal and characterized by a helical ridge, called a male thread.

A nut is a type of fastener with a threaded hole. Nuts are almost always used in conjunction with a mating bolt to fasten multiple parts together. The two partners are kept together by a combination of their threads' friction, a slight stretching of the bolt, and compression of the parts to be held together.
A centerlock wheel is a type of automobile wheel in which the wheel is fastened to the axle using a single, central nut, instead of the more common ring of 4 or 5 lug nuts or bolts.























