An appropriation bill, also known as supply bill or spending bill, is a proposed law that authorizes the expenditure of government funds. It is a bill that sets money aside for specific spending. In most democracies, approval of the legislature is necessary for the government to spend money.
Trespass is an area of criminal law or tort law broadly divided into three groups: trespass to the person, trespass to chattels and trespass to land.
The right of publicity, sometimes referred to as personality rights, is the right of an individual to control the commercial use of one's identity, such as name, image, likeness, or other unequivocal identifiers. It is generally considered a property right as opposed to a personal right, and as such, the validity of the right of publicity can survive the death of the individual.
The United States budget process is the framework used by Congress and the President of the United States to formulate and create the United States federal budget. The process was established by the Budget and Accounting Act of 1921, the Congressional Budget and Impoundment Control Act of 1974, and additional budget legislation.

The United States House Committee on Appropriations is a committee of the United States House of Representatives that is responsible for passing appropriation bills along with its Senate counterpart. The bills passed by the Appropriations Committee regulate expenditures of money by the government of the United States. As such, it is one of the most powerful of the committees, and its members are seen as influential. They make the key decisions about the work of their committees—when their committees meet, which bills they will consider, and for how long.
Prior appropriation water rights is the legal doctrine that the first person to take a quantity of water from a water source for "beneficial use" has the right to continue to use that quantity of water for that purpose.
Trespass to chattels is a tort whereby the infringing party has intentionally interfered with another person's lawful possession of a chattel. The interference can be any physical contact with the chattel in a quantifiable way, or any dispossession of the chattel. As opposed to the greater wrong of conversion, trespass to chattels is argued to be actionable per se.
In law and government, appropriation is the act of setting apart something for its application to a particular usage, to the exclusion of all other uses.
In the United States, a continuing resolution is a type of appropriations legislation. An appropriations bill is a bill that appropriates money to specific federal government departments, agencies, and programs. The money provides funding for operations, personnel, equipment, and activities. Regular appropriations bills are passed annually, with the funding they provide covering one fiscal year. The fiscal year is the accounting period of the federal government, which runs from October 1 to September 30 of the following year. When Congress and the president fail to agree on and pass one or more of the regular appropriations bills, a continuing resolution can be passed instead. A continuing resolution continues the pre-existing appropriations at the same levels as the previous fiscal year for a set amount of time. Continuing resolutions typically provide funding at a rate or formula based on the previous year's funding. The funding extends until a specific date or regular appropriations bills are passed, whichever comes first. There can be some changes to some of the accounts in a continuing resolution. The continuing resolution takes the form of a joint resolution, and may provide bridging funding for existing federal programs at current, reduced, or expanded levels.
Cultural appropriation is the adoption of an element or elements of one culture or identity by members of another culture or identity. This can be controversial when members of a dominant culture appropriate from disadvantaged minority cultures.

In the law of tort, property, and criminal law a trespasser is a person who commits the act of trespassing on a property, that is, without the permission of the owner. Being present on land as a trespasser thereto creates liability in the trespasser, so long as the trespass is intentional. At the same time, the status of a visitor as a trespasser defines the legal rights of the visitor if they are injured due to the negligence of the property owner.

Trespass to land is a common law tort or crime that is committed when an individual or the object of an individual intentionally enters the land of another without a lawful excuse. Trespass to land is actionable per se. Thus, the party whose land is entered upon may sue even if no actual harm is done. In some jurisdictions, this rule may also apply to entry upon public land having restricted access. A court may order payment of damages or an injunction to remedy the tort.
Appropriation is a process by which previously unowned natural resources, particularly land, become the property of a person or group of persons. The term is widely used in economics in this sense. In certain cases, it proceeds under very specifically defined forms, such as driving stakes or other such markers into the land claimed, which form gave rise to the term “staking a claim.” "Squatter’s rights" are another form of appropriation, but are usually asserted against land to which ownership rights of another party have been recognized. In legal regimes recognizing such acquisition of property, the ownership of duly appropriated holdings enjoys such protections as the law provides for ownership of property in general.
The House Subcommittee on Energy and Water Development, and Related Agencies is a standing subcommittee within the House Appropriations Committee. The United States House Committee on Appropriations has joint jurisdiction with the United States Senate Committee on Appropriations over all appropriations bills in the United States Congress. Each committee has 12 matching subcommittees, each of which is tasked with working on one of the twelve annual regular appropriations bills. This subcommittee has jurisdiction over the budget for the United States Department of Energy and Water Development.
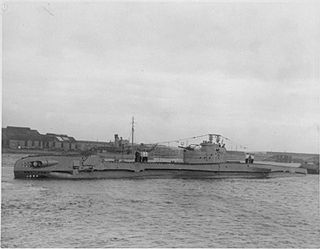
HMS Trespasser was a British submarine of the third group of the T class. She was built as P312 by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow, and launched on 29 May 1942. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Trespasser.
In United States law, littoral rights are rights concerning properties that abut static water like an ocean, bay, delta, sea or lake, rather than a flowing river or stream (riparian). Littoral rights are usually concerned with the use and enjoyment of the shore., but also may include rights to use the water similar to riparian rights.

The Supreme Court of the United States, under Chief Justice Roger B. Taney (1836–1864), issued several important decisions on the status of aboriginal title in the United States, building on the opinions of aboriginal title in the Marshall Court.
Evictionism is a moral theory advanced by Walter Block and Roy Whitehead on a proposed libertarian view of abortion based on property rights. This theory is built upon the earlier work of philosopher Murray Rothbard who wrote that "no being has a right to live, unbidden, as a parasite within or upon some person's body" and that therefore the woman is entitled to eject the baby from her body at any time. Evictionists view a mother's womb as her property and an unwanted fetus as a "trespasser or parasite", even while lacking the will to act. They argue that a mother has the right to evict a fetus from her body since she has no obligation to care for a trespasser. The authors' hope is that bystanders will "homestead" the right to care for evicted babies and reduce the number of human deaths. They argue that life begins at conception and state that the act of abortion must be conceptually separated into the acts of:
- the eviction of the fetus from the womb, and
- the dying of the baby.

In the United States Congress, an appropriations bill is legislation to appropriate federal funds to specific federal government departments, agencies and programs. The money provides funding for operations, personnel, equipment and activities. Regular appropriations bills are passed annually, with the funding they provide covering one fiscal year. The fiscal year is the accounting period of the federal government, which runs from October 1 to September 30 of the following year. Appropriations bills are under the jurisdiction of the United States House Committee on Appropriations and the United States Senate Committee on Appropriations. Both Committees have twelve matching subcommittees, each tasked with working on one of the twelve annual regular appropriations bills.
Departurism is a libertarian approach to the abortion controversy developed by American philosopher Sean Parr which argues, contrary to evictionism, that the lethal removal of an unwanted fetus ought to be legally impermissible.





