
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more in miniature form are found embedded in integrated circuits. Because transistors are the key active components in practically all modern electronics, many people consider them one of the 20th century's greatest inventions.

The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The term metal–insulator–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another near-synonym is insulated-gate field-effect transistor (IGFET).
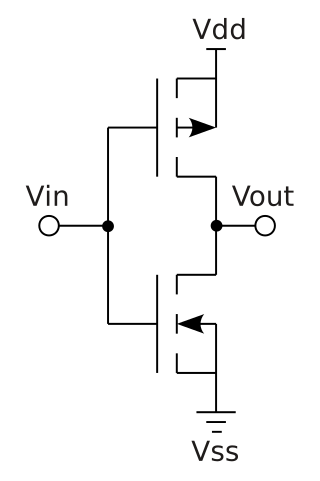
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, RF circuits, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.

An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily forming an electronic switch. It was developed to combine high efficiency with fast switching. It consists of four alternating layers (P–N–P–N) that are controlled by a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) gate structure.
SPICE is a general-purpose, open-source analog electronic circuit simulator. It is a program used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.
SiGe, or silicon–germanium, is an alloy with any molar ratio of silicon and germanium, i.e. with a molecular formula of the form Si1−xGex. It is commonly used as a semiconductor material in integrated circuits (ICs) for heterojunction bipolar transistors or as a strain-inducing layer for CMOS transistors. IBM introduced the technology into mainstream manufacturing in 1989. This relatively new technology offers opportunities in mixed-signal circuit and analog circuit IC design and manufacture. SiGe is also used as a thermoelectric material for high-temperature applications (>700 K).
In electronics, rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) is a digital electronic device that uses superconducting devices, namely Josephson junctions, to process digital signals. In RSFQ logic, information is stored in the form of magnetic flux quanta and transferred in the form of Single Flux Quantum (SFQ) voltage pulses. RSFQ is one family of superconducting or SFQ logic. Others include Reciprocal Quantum Logic (RQL), ERSFQ – energy-efficient RSFQ version that does not use bias resistors, etc. Josephson junctions are the active elements for RSFQ electronics, just as transistors are the active elements for semiconductor electronics. RSFQ is a classical digital, not quantum computing, technology.
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics. Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC.
Transistors are simple devices with complicated behavior. In order to ensure the reliable operation of circuits employing transistors, it is necessary to scientifically model the physical phenomena observed in their operation using transistor models. There exists a variety of different models that range in complexity and in purpose. Transistor models divide into two major groups: models for device design and models for circuit design.

Ngspice is an open-source mixed-level/mixed-signal electronic circuit simulator. It is a successor of the latest stable release of Berkeley SPICE, version 3f.5, which was released in 1993. A small group of maintainers and the user community contribute to the ngspice project by providing new features, enhancements and bug fixes.

Quite Universal Circuit Simulator (Qucs) is a free-software electronics circuit simulator software application released under GPL. It offers the ability to set up a circuit with a graphical user interface and simulate the large-signal, small-signal and noise behaviour of the circuit. Pure digital simulations are also supported using VHDL and/or Verilog. Only a small set of digital devices like flip flops and logic gates can be used with analog circuits. Qucs uses its own SPICE-incompatible backend simulator Qucsator, however the Qucs-S fork supports some SPICE backends.

Technology computer-aided design is a branch of electronic design automation that models semiconductor fabrication and semiconductor device operation. The modeling of the fabrication is termed Process TCAD, while the modeling of the device operation is termed Device TCAD. Included are the modelling of process steps, and modelling of the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. TCAD may also include the creation of compact models, which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally derive them from the underlying physics. SPICE simulator itself is usually considered as part of ECAD rather than TCAD.

Semiconductor device modeling creates models for the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. It may also include the creation of compact models, which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally derive them from the underlying physics. Normally it starts from the output of a semiconductor process simulation.

CircuitLogix is a software electronic circuit simulator which uses PSpice to simulate thousands of electronic devices, models, and circuits. CircuitLogix supports analog, digital, and mixed-signal circuits, and its SPICE simulation gives accurate real-world results. The graphic user interface allows students to quickly and easily draw, modify and combine analog and digital circuit diagrams. CircuitLogix was first launched in 2005, and its popularity has grown quickly since that time. In 2012, it reached the milestone of 250,000 licensed users, and became the first electronics simulation product to have a global installed base of a quarter-million customers in over 100 countries.

Electronic circuit simulation uses mathematical models to replicate the behavior of an actual electronic device or circuit. Simulation software allows for modeling of circuit operation and is an invaluable analysis tool. Due to its highly accurate modeling capability, many colleges and universities use this type of software for the teaching of electronics technician and electronics engineering programs. Electronics simulation software engages its users by integrating them into the learning experience. These kinds of interactions actively engage learners to analyze, synthesize, organize, and evaluate content and result in learners constructing their own knowledge.
The Compact Model Coalition is a working group in the Electronic Design Automation industry formed to choose, maintain and promote the use of standard semiconductor device models. Commercial and industrial analog simulators need to add device models as technology advances and earlier models become inaccurate. Before this group was formed, new transistor models were largely proprietary, which severely limited the choice of simulators that could be used.
In semiconductor manufacturing, a process corner is an example of a design-of-experiments (DoE) technique that refers to a variation of fabrication parameters used in applying an integrated circuit design to a semiconductor wafer. Process corners represent the extremes of these parameter variations within which a circuit that has been etched onto the wafer must function correctly. A circuit running on devices fabricated at these process corners may run slower or faster than specified and at lower or higher temperatures and voltages, but if the circuit does not function at all at any of these process extremes the design is considered to have inadequate design margin.

PSIM is an Electronic circuit simulation software package, designed specifically for use in power electronics and motor drive simulations but can be used to simulate any electronic circuit. Developed by Powersim, PSIM uses nodal analysis and the trapezoidal rule integration as the basis of its simulation algorithm. PSIM provides a schematic capture interface and a waveform viewer Simview. PSIM has several modules that extend its functionality into specific areas of circuit simulation and design including: control theory, electric motors, photovoltaics and wind turbines PSIM is used by industry for research and product development and it is used by educational institutions for research and teaching and was acquired by Altair Engineering in March 2022.
Advanced Linear Devices Incorporated, also known as ALD, is a semiconductor device design and manufacturing company based in Sunnyvale, California. The company develops and manufactures precision analog CMOS linear integrated circuits for industrial controls, instrumentation, computers, medical devices, automotive, and telecommunications products. t is best known for its redesign of the 555 timer IC as a low-voltage CMOS device.








