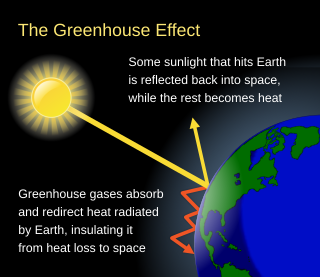
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source as in the case of Jupiter, or from its host star as in the case of the Earth. In the case of Earth, the Sun emits shortwave radiation (sunlight) that passes through greenhouse gases to heat the Earth's surface. In response, the Earth's surface emits longwave radiation (heat) that is mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. That heat absorption reduces the rate at which the Earth can cool off in response to being warmed by the Sun. Adding to greenhouse gases further reduces the rate a planet emits radiation to space, raising its average surface temperature.

Infrared is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with waves that are just longer than those of red light, the longest waves in the visible spectrum, so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to include wavelengths from around 750 nm to 1000 μm. IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon.

Thermal insulation is the reduction of heat transfer between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Thermal insulation can be achieved with specially engineered methods or processes, as well as with suitable object shapes and materials.
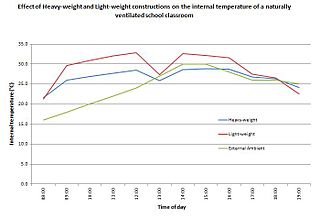
In building design, thermal mass is a property of the mass of a building that enables it to store heat and provide inertia against temperature fluctuations. It is sometimes known as the thermal flywheel effect. The thermal mass of heavy structural elements can be designed to work alongside a construction's lighter thermal resistance components to create energy efficient buildings.

A heat pump is a device that uses work to transfer heat from a cool space to a warm space by transferring thermal energy using a refrigeration cycle, cooling the cool space and warming the warm space. In cold weather, a heat pump can move heat from the cool outdoors to warm a house; the pump may also be designed to move heat from the house to the warmer outdoors in warm weather. As they transfer heat rather than generating heat, they are more energy-efficient than other ways of heating or cooling a home.
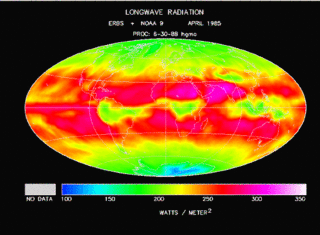
In the study of heat transfer, radiative cooling is the process by which a body loses heat by thermal radiation. As Planck's law describes, every physical body spontaneously and continuously emits electromagnetic radiation.

Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species, either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system.

Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. Thermal radiation transmits as an electromagnetic wave through both matter and vacuum. When matter absorbs thermal radiation its temperature will tend to rise. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electronic, molecular, and lattice oscillations in a material. Kinetic energy is converted to electromagnetism due to charge-acceleration or dipole oscillation. At room temperature, most of the emission is in the infrared (IR) spectrum. Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer, along with conduction and convection.
Thermoelectric cooling uses the Peltier effect to create a heat flux at the junction of two different types of materials. A Peltier cooler, heater, or thermoelectric heat pump is a solid-state active heat pump which transfers heat from one side of the device to the other, with consumption of electrical energy, depending on the direction of the current. Such an instrument is also called a Peltier device, Peltier heat pump, solid state refrigerator, or thermoelectric cooler (TEC) and occasionally a thermoelectric battery. It can be used either for heating or for cooling, although in practice the main application is cooling. It can also be used as a temperature controller that either heats or cools.

An evaporative cooler is a device that cools air through the evaporation of water. Evaporative cooling differs from other air conditioning systems, which use vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycles. Evaporative cooling exploits the fact that water will absorb a relatively large amount of heat in order to evaporate. The temperature of dry air can be dropped significantly through the phase transition of liquid water to water vapor (evaporation). This can cool air using much less energy than refrigeration. In extremely dry climates, evaporative cooling of air has the added benefit of conditioning the air with more moisture for the comfort of building occupants.

Computer cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within permissible operating temperature limits. Components that are susceptible to temporary malfunction or permanent failure if overheated include integrated circuits such as central processing units (CPUs), chipsets, graphics cards, hard disk drives, and solid state drives.

Temperature control is a process in which change of temperature of a space, or of a substance, is measured or otherwise detected, and the passage of heat energy into or out of the space or substance is adjusted to achieve a desired temperature.

Electric heating is a process in which electrical energy is converted directly to heat energy. Common applications include space heating, cooking, water heating and industrial processes. An electric heater is an electrical device that converts an electric current into heat. The heating element inside every electric heater is an electrical resistor, and works on the principle of Joule heating: an electric current passing through a resistor will convert that electrical energy into heat energy. Most modern electric heating devices use nichrome wire as the active element; the heating element, depicted on the right, uses nichrome wire supported by ceramic insulators.

Waste heat is heat that is produced by a machine, or other process that uses energy, as a byproduct of doing work. All such processes give off some waste heat as a fundamental result of the laws of thermodynamics. Waste heat has lower utility than the original energy source. Sources of waste heat include all manner of human activities, natural systems, and all organisms, for example, incandescent light bulbs get hot, a refrigerator warms the room air, a building gets hot during peak hours, an internal combustion engine generates high-temperature exhaust gases, and electronic components get warm when in operation.
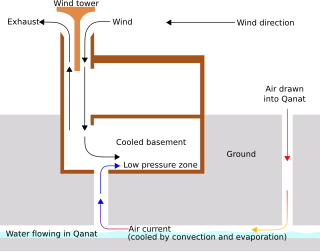
Passive cooling is a building design approach that focuses on heat gain control and heat dissipation in a building in order to improve the indoor thermal comfort with low or no energy consumption. This approach works either by preventing heat from entering the interior or by removing heat from the building.

Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C (US) or air con (UK), is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment and in some cases also strictly controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or by other methods, including passive cooling and ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners, but use a reversing valve to allow them both to heat and to cool an enclosed space.

A waste heat recovery unit (WHRU) is an energy recovery heat exchanger that transfers heat from process outputs at high temperature to another part of the process for some purpose, usually increased efficiency. The WHRU is a tool involved in cogeneration. Waste heat may be extracted from sources such as hot flue gases from a diesel generator, steam from cooling towers, or even waste water from cooling processes such as in steel cooling.
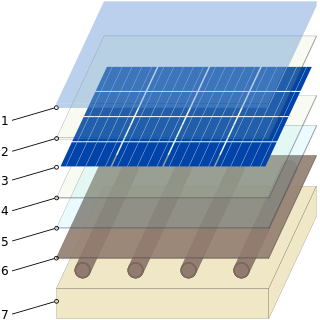
Photovoltaic thermal collectors, typically abbreviated as PVT collectors and also known as hybrid solar collectors, photovoltaic thermal solar collectors, PV/T collectors or solar cogeneration systems, are power generation technologies that convert solar radiation into usable thermal and electrical energy. PVT collectors combine photovoltaic solar cells, which convert sunlight into electricity, with a solar thermal collector, which transfers the otherwise unused waste heat from the PV module to a heat transfer fluid. By combining electricity and heat generation within the same component, these technologies can reach a higher overall efficiency than solar photovoltaic (PV) or solar thermal (T) alone.

The Hygroscopic cycle is a thermodynamic cycle converting thermal energy into mechanical power by the means of a steam turbine. It is similar to the Rankine cycle using water as the motive fluid but with the novelty of introducing salts and their hygroscopic properties for the condensation. The salts are desorbed in the boiler or steam generator, where clean steam is released and superheated in order to be expanded and generate power through the steam turbine. Boiler blowdown with the concentrated hygroscopic compounds is used thermally to pre-heat the steam turbine condensate, and as reflux in the steam-absorber.

Passive daytime radiative cooling (PDRC) is a zero-energy building cooling method proposed as a solution to reduce air conditioning, lower urban heat island effect, cool human body temperatures in extreme heat, move toward carbon neutrality and control global warming by enhancing terrestrial heat flow to outer space through the installation of thermally-emissive surfaces on Earth that require zero energy consumption or pollution. In contrast to compression-based cooling systems that are prevalently used, consume substantial amounts of energy, have a net heating effect, require ready access to electricity and often require coolants that are ozone-depleting or have a strong greenhouse effect, application of PDRCs may also increase the efficiency of systems benefiting from a better cooling, such like photovoltaic systems, dew collection techniques, and thermoelectric generators.





















