
In computer networking, a thin client is a simple (low-performance) computer that has been optimized for establishing a remote connection with a server-based computing environment. They are sometimes known as network computers, or in their simplest form as zero clients. The server does most of the work, which can include launching software programs, performing calculations, and storing data. This contrasts with a rich client or a conventional personal computer; the former is also intended for working in a client–server model but has significant local processing power, while the latter aims to perform its function mostly locally.

In computing, load balancing is the process of distributing a set of tasks over a set of resources, with the aim of making their overall processing more efficient. Load balancing can optimize the response time and avoid unevenly overloading some compute nodes while other compute nodes are left idle.

A web hosting service is a type of Internet hosting service that hosts websites for clients, i.e. it offers the facilities required for them to create and maintain a site and makes it accessible on the World Wide Web. Companies providing web hosting services are sometimes called web hosts.
NetApp, Inc. is an American data storage and data management solutions company headquartered in San Jose, California. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012 to 2021. Founded in 1992 with an IPO in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.

A diskless node is a workstation or personal computer without disk drives, which employs network booting to load its operating system from a server.
A file-hosting service, also known as cloud-storage service, online file-storage provider, or cyberlocker is an internet hosting service specifically designed to host user files. These services allows users to upload files that can be accessed over the internet after providing a username and password or other authentication. Typically, file hosting services allow HTTP access, and in some cases, FTP access. Other related services include content-displaying hosting services, virtual storage, and remote backup solutions.
A remote, online, or managed backup service, sometimes marketed as cloud backup or backup-as-a-service, is a service that provides users with a system for the backup, storage, and recovery of computer files. Online backup providers are companies that provide this type of service to end users. Such backup services are considered a form of cloud computing.
Content-addressable storage (CAS), also referred to as content-addressed storage or fixed-content storage, is a way to store information so it can be retrieved based on its content, not its name or location. It has been used for high-speed storage and retrieval of fixed content, such as documents stored for compliance with government regulations. Content-addressable storage is similar to content-addressable memory.

Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data. This is expected to improve response times and save bandwidth. Edge computing is an architecture rather than a specific technology, and a topology- and location-sensitive form of distributed computing.
Apache Hadoop is a collection of open-source software utilities that facilitates using a network of many computers to solve problems involving massive amounts of data and computation. It provides a software framework for distributed storage and processing of big data using the MapReduce programming model. Hadoop was originally designed for computer clusters built from commodity hardware, which is still the common use. It has since also found use on clusters of higher-end hardware. All the modules in Hadoop are designed with a fundamental assumption that hardware failures are common occurrences and should be automatically handled by the framework.
Cloud storage is a model of computer data storage in which the digital data is stored in logical pools, said to be on "the cloud". The physical storage spans multiple servers, and the physical environment is typically owned and managed by a hosting company. These cloud storage providers are responsible for keeping the data available and accessible, and the physical environment secured, protected, and running. People and organizations buy or lease storage capacity from the providers to store user, organization, or application data.
In cryptography, a hybrid cryptosystem is one which combines the convenience of a public-key cryptosystem with the efficiency of a symmetric-key cryptosystem. Public-key cryptosystems are convenient in that they do not require the sender and receiver to share a common secret in order to communicate securely. However, they often rely on complicated mathematical computations and are thus generally much more inefficient than comparable symmetric-key cryptosystems. In many applications, the high cost of encrypting long messages in a public-key cryptosystem can be prohibitive. This is addressed by hybrid systems by using a combination of both.

A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software.

The Rackspace Cloud is a set of cloud computing products and services billed on a utility computing basis from the US-based company Rackspace. Offerings include Cloud Storage, virtual private server, load balancers, databases, backup, and monitoring.

Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each of which is a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically uses a pay-as-you-go model, which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for users.

A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
Sector/Sphere is an open source software suite for high-performance distributed data storage and processing. It can be broadly compared to Google's GFS and MapReduce technology. Sector is a distributed file system targeting data storage over a large number of commodity computers. Sphere is the programming architecture framework that supports in-storage parallel data processing for data stored in Sector. Sector/Sphere operates in a wide area network (WAN) setting.
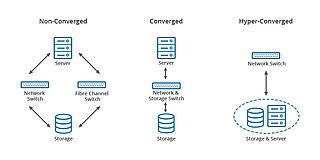
Converged infrastructure is a way of structuring an information technology (IT) system which groups multiple components into a single optimized computing package. Components of a converged infrastructure may include servers, data storage devices, networking equipment and software for IT infrastructure management, automation and orchestration.
A distributed file system for cloud is a file system that allows many clients to have access to data and supports operations on that data. Each data file may be partitioned into several parts called chunks. Each chunk may be stored on different remote machines, facilitating the parallel execution of applications. Typically, data is stored in files in a hierarchical tree, where the nodes represent directories. There are several ways to share files in a distributed architecture: each solution must be suitable for a certain type of application, depending on how complex the application is. Meanwhile, the security of the system must be ensured. Confidentiality, availability and integrity are the main keys for a secure system.

Dell Technologies PowerFlex, is a commercial software-defined storage product from Dell Technologies that creates a server-based storage area network (SAN) from local server storage using x86 servers. It converts this direct-attached storage into shared block storage than runs over an IP-based network.










