UNICOS is a range of Unix and after it Linux operating system (OS) variants developed by Cray for its supercomputers. UNICOS is the successor of the Cray Operating System (COS). It provides network clustering and source code compatibility layers for some other Unixes. UNICOS was originally introduced in 1985 with the Cray-2 system and later ported to other Cray models. The original UNICOS was based on UNIX System V Release 2, and had many Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) features added to it.
Floating point operations per second is a measure of computer performance in computing, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations.
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world.

Quadrics was a supercomputer company formed in 1996 as a joint venture between Alenia Spazio and the technical team from Meiko Scientific. They produced hardware and software for clustering commodity computer systems into massively parallel systems. Their highpoint was in June 2003 when six out of the ten fastest supercomputers in the world were based on Quadrics' interconnect. They officially closed on June 29, 2009.

ASCI Red was the first computer built under the Accelerated Strategic Computing Initiative (ASCI), the supercomputing initiative of the United States government created to help the maintenance of the United States nuclear arsenal after the 1992 moratorium on nuclear testing.
SUNMOS is an operating system jointly developed by Sandia National Laboratories and the Computer Science Department at the University of New Mexico. The goal of the project, started in 1991, is to develop a highly portable, yet efficient, operating system for massively parallel-distributed memory systems.

The Cray T3E was Cray Research's second-generation massively parallel supercomputer architecture, launched in late November 1995. The first T3E was installed at the Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center in 1996. Like the previous Cray T3D, it was a fully distributed memory machine using a 3D torus topology interconnection network. The T3E initially used the DEC Alpha 21164 (EV5) microprocessor and was designed to scale from 8 to 2,176 Processing Elements (PEs). Each PE had between 64 MB and 2 GB of DRAM and a 6-way interconnect router with a payload bandwidth of 480 MB/s in each direction. Unlike many other MPP systems, including the T3D, the T3E was fully self-hosted and ran the UNICOS/mk distributed operating system with a GigaRing I/O subsystem integrated into the torus for network, disk and tape I/O.
Red Storm was a supercomputer architecture designed for the US Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration Advanced Simulation and Computing Program. Cray, Inc developed it in 2004 based on the contracted architectural specifications provided by Sandia National Laboratories. The architecture was later commercially produced as the Cray XT3.

The Cray XT4 is an updated version of the Cray XT3 supercomputer. It was released on November 18, 2006. It includes an updated version of the SeaStar interconnect router called SeaStar2, processor sockets for Socket AM2 Opteron processors, and 240-pin unbuffered DDR2 memory. The XT4 also includes support for FPGA coprocessors that plug into riser cards in the Service and IO blades. The interconnect, cabinet, system software and programming environment remain unchanged from the Cray XT3. It was superseded in 2007 by the Cray XT5.
HECToR was a British academic national supercomputer service funded by EPSRC, Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and BBSRC for the UK academic community. The HECToR service was run by partners including EPCC, Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) and Numerical Algorithms Group (NAG).

The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non-distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coincides with the International Supercomputing Conference in June, and the second is presented at the ACM/IEEE Supercomputing Conference in November. The project aims to provide a reliable basis for tracking and detecting trends in high-performance computing and bases rankings on HPL benchmarks, a portable implementation of the high-performance LINPACK benchmark written in Fortran for distributed-memory computers.
The Bigben supercomputer was a Cray XT3 MPP system with 2068 nodes located at Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center. It was decommissioned on March 31, 2010. Bigben was a part of the TeraGrid.

The Cray XT5 is an updated version of the Cray XT4 supercomputer, launched on November 6, 2007. It includes a faster version of the XT4's SeaStar2 interconnect router called SeaStar2+, and can be configured either with XT4 compute blades, which have four dual-core AMD Opteron processor sockets, or XT5 blades, with eight sockets supporting dual or quad-core Opterons. The XT5 uses a 3-dimensional torus network topology.
The Cray CX1 is a deskside workstation designed by Cray Inc., based on the x86-64 processor architecture. It was launched on September 16, 2008, and was discontinued in early 2012. It comprises a single chassis blade server design that supports a maximum of eight modular single-width blades, giving up to 96 processor cores. Computational load can be run independently on each blade and/or combined using clustering techniques.
The National Center for Computational Sciences (NCCS) is a United States Department of Energy (DOE) Leadership Computing Facility that houses the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF), a DOE Office of Science User Facility charged with helping researchers solve challenging scientific problems of global interest with a combination of leading high-performance computing (HPC) resources and international expertise in scientific computing.

Jaguar or OLCF-2 was a petascale supercomputer built by Cray at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. The massively parallel Jaguar had a peak performance of just over 1,750 teraFLOPS. It had 224,256 x86-based AMD Opteron processor cores, and operated with a version of Linux called the Cray Linux Environment. Jaguar was a Cray XT5 system, a development from the Cray XT4 supercomputer.
A lightweight kernel (LWK) operating system is one used in a large computer with many processor cores, termed a parallel computer.
The Cray XK6 made by Cray is an enhanced version of the Cray XE6 supercomputer, announced in May 2011. The XK6 uses the same "blade" architecture of the XE6, with each XK6 blade comprising four compute "nodes". Each node consists of a 16-core AMD Opteron 6200 processor with 16 or 32 GB of DDR3 RAM and an Nvidia Tesla X2090 GPGPU with 6 GB of GDDR5 RAM, the two connected via PCI Express 2.0. Two Gemini router ASICs are shared between the nodes on a blade, providing a 3-dimensional torus network topology between nodes. This means that it has 576 GB of Graphics memory and over 1500 CPU cores, several orders of magnitude more powerful than the best publicly available computer on the market.

Catamount is an operating system for supercomputers.
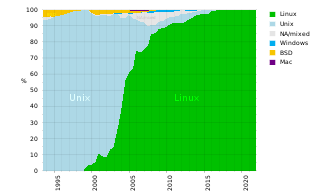
A supercomputer operating system is an operating system intended for supercomputers. Since the end of the 20th century, supercomputer operating systems have undergone major transformations, as fundamental changes have occurred in supercomputer architecture. While early operating systems were custom tailored to each supercomputer to gain speed, the trend has been moving away from in-house operating systems and toward some form of Linux, with it running all the supercomputers on the TOP500 list in November 2017. In 2021, top 10 computers run for instance Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), or some variant of it or other Linux distribution e.g. Ubuntu.









