Related Research Articles

British Columbia is the westernmost province of Canada. Situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains. British Columbia borders the province of Alberta to the east, the territories of Yukon and the Northwest Territories to the north, and the US states of Washington, Idaho and Montana to the south and Alaska to the northwest. With an estimated population of over 5.4 million as of 2023, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, while the province's largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver and its suburbs together make up the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada; with the 2021 census recording 2.6 million people in Metro Vancouver.

Vancouver is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. The Greater Vancouver area had a population of 2.6 million in 2021, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Greater Vancouver, along with the Fraser Valley, comprises the Lower Mainland with a regional population of over 3 million. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada, with over 5,700 people per square kilometre, and fourth highest in North America.

Richmond is a city in the coastal Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, Canada. It occupies almost the entirety of Lulu Island, between the two estuarine distributaries of the Fraser River. Encompassing the adjacent Sea Island and several other smaller islands and uninhabited islets to its north and south, it neighbours Vancouver and Burnaby on the Burrard Peninsula to the north, New Westminster and Annacis Island to the east, Delta to the south, and the Strait of Georgia to the west.

Surrey is a city in British Columbia, Canada. It is located south of the Fraser River on the Canada–United States border. It is a member municipality of the Metro Vancouver regional district and metropolitan area. Mainly a suburban city, Surrey is the province's second-largest by population after Vancouver and the third-largest by area after Abbotsford and Prince George. Seven neighbourhoods in Surrey are designated town centres: Cloverdale, Fleetwood, Guildford, Newton, South Surrey, and City Centre encompassed by Whalley.

Burnaby is a city in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, Canada. Located in the centre of the Burrard Peninsula, it neighbours the City of Vancouver to the west, the District of North Vancouver across the confluence of the Burrard Inlet with its Indian Arm to the north, Port Moody and Coquitlam to the east, New Westminster and Surrey across the Fraser River to the southeast, and Richmond on the Lulu Island to the southwest.

Canada has a large domestic and foreign tourism industry. The second largest country in the world, Canada's incredible geographical variety is a significant tourist attractor. Much of the country's tourism is centred in the following regions: Toronto, Montreal, Quebec City, Vancouver/Whistler, Niagara Falls, Vancouver Island, Canadian Rockies, British Columbia's Okanagan Valley, Churchill, Manitoba and the National Capital Region of Ottawa-Gatineau. The large cities are known for their culture, diversity, as well as the many national parks and historic sites.
Hollywood North is a colloquialism used to describe film production industries and/or film locations north of its namesake, Hollywood, California. The term has been applied principally to the film industry in Canada, specifically to the city of Vancouver, British Columbia.

Hope is a district municipality at the confluence of the Fraser and Coquihalla rivers in the province of British Columbia, Canada. Hope is at the eastern end of both the Fraser Valley and the Lower Mainland region, and is at the southern end of the Fraser Canyon. To the east, over the Cascade Mountains, is the Interior region, beginning with the Similkameen Country on the farther side of the Allison Pass in Manning Park. Located 154 kilometres (96 mi) east of Vancouver, Hope is at the southern terminus of the Coquihalla Highway and the western terminus of the Crowsnest Highway, locally known as the Hope-Princeton, where they merge with the Trans-Canada Highway. Hope is at the eastern terminus of Highway 7. As it lies at the eastern end of the Fraser Valley in the windward Cascade foothills, the town gets very high amounts of rain and cloud cover – particularly throughout the autumn and winter.

Greater Vancouver, also known as Metro Vancouver, is the metropolitan area with its major urban centre being the city of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. The term "Greater Vancouver" describes an area that is roughly coterminous with the region governed by the Metro Vancouver Regional District (MVRD), though it predates the 1966 creation of the regional district. It is often used to include areas beyond the boundaries of the regional district but does not generally include wilderness and agricultural areas that are included within the MVRD.

Capilano University (CapU) is a teaching-focused public university based in North Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, located on the slopes of the North Shore Mountains, with programming that also serves the Sea-to-Sky Corridor and the Sunshine Coast. The university is named after Chief Joe Capilano Sa7plek (Sahp-luk) who was the leader of the Squamish people (Sḵwx̱wú7mesh) from 1895 to 1910.

Suzanne Anton, is a Canadian politician and the former Minister of Justice and Attorney General of British Columbia. Elected to the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia in the 2013 provincial election, Anton represented the riding of Vancouver-Fraserview as a member of the British Columbia Liberal Party, following a career at the municipal level. She was appointed British Columbia's Attorney General and Minister of Justice on June 10, 2013.

This is an overview of media in Vancouver, British Columbia.
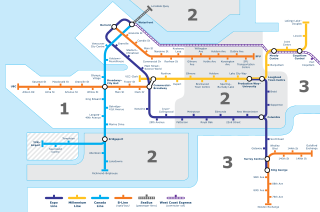
Transportation in Vancouver, British Columbia, has many of the features of modern cities worldwide. Unlike many large metropolises, Vancouver has no freeways into or through the downtown area. A proposed freeway through the downtown was rejected in the 1960s by a coalition of citizens, community leaders and planners. This event "signalled the emergence of a new concept of the urban landscape" and has been a consistent element of the city's planning ever since.

Vancouver's economy is one of the most vibrant in Canada. The British Columbian city is Canada's official gateway to the Pacific Rim, a major port, and the main western terminus of transcontinental highway and rail routes. Vancouver has successfully transitioned from a predominantly resource-based economy to a diverse knowledge-based one, and in recent years has been the fastest growing economy in Canada. According to the Conference Board of Canada, in 2017 Vancouver's GDP was CA$137 billion, with a GDP growth rate of 4.5%, meaning that Vancouver represents approximately 7.5% of Canada's overall economy. Major economic sectors include trade, film and TV, technology, tourism, natural resources, and construction.

Spencer Chandra Herbert is a Canadian politician who serves in the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia in Canada. Representing the British Columbia New Democratic Party, he won an October 2008 by-election in the electoral district of Vancouver-Burrard. He was re-elected to the Legislature, this time in the newly created riding of Vancouver-West End, in the 2009, 2013, and 2017 general elections.

Grouse Mountain is one of the North Shore Mountains of the Pacific Ranges in the District Municipality of North Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. With a maximum elevation of over 1,200m (4,100ft) at its peak, the mountain is the site of an alpine ski area, Grouse Mountain Resort, which overlooks Metro Vancouver and has four chairlifts servicing 33 runs. In the summer, Grouse Mountain Resort features lumberjack shows, the "Birds in Motion" birds of prey demonstration, a scenic chairlift ride, disc golf, mountain biking, zip lining, tandem paragliding, helicopter tours, and guided ecowalks. Year-round operations include a 100-seat mountaintop theatre and a wildlife refuge. The mountain operates two aerial tramways, known officially as the Skyride. The Blue Skyride is used mainly for freight transportation, while public access to the mountain top is provided by the Swiss-built Garaventa Red Skyride, which has a maximum capacity of 101 passengers. Summer access is also provided by the 2.9 kilometre Grouse Grind hiking trail, which is open for hiking from May to October.
Pixar Canada was a short-lived, wholly owned subsidiary of Pixar Animation Studios. It was located in Vancouver, British Columbia. The studio was tasked to produce short films based on Pixar’s feature film characters.
The SkyTrain rapid transit system in Greater Vancouver, Canada, was conceived as a legacy project of Expo 86 and was finished in time to showcase the fair's theme: "Transportation and Communication: World in Motion – World in Touch". Construction was funded by the provincial and federal governments. Vancouver had plans as early as the 1950s to build a monorail system, with modernist architect Wells Coates pencilled in to design it; that project was abandoned. The lack of a rapid transit system was said to be the cause of traffic problems in the 1970s, and the municipal government could not fund the construction of such a system. During the same period, Urban Transportation Development Corporation, then an Ontario crown corporation, was developing a new rapid transit technology known as an "Intermediate Capacity Transit System". In 1980, the need for rapid transit was great, and Ontario needed buyers for its new technology. "Advanced Rapid Transit" was selected to be built in Vancouver to showcase the Ontario project at Expo 86.
Elizabeth Ball is a Canadian politician, actress, and founder of several theatre companies. She served on Vancouver city council 2005 to 2018.

Melanie Joy Mark, also known by her Nisga'a name Hli Haykwhl Ẃii Xsgaak, is a Canadian politician in the province of British Columbia. A member of the New Democratic Party (NDP), she served as the Member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) for Vancouver-Mount Pleasant from 2016 to 2023. From 2017 to 2020, she served as Minister of Advanced Education and Skills Training; from 2020 to 2022, she served as Minister of Tourism, Arts, Culture and Sport. Mark is the first First Nations woman elected to the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia, and the first First Nations woman to serve in the Cabinet of British Columbia. On February 22, 2023, Mark announced her intention to resign as MLA and cabinet minister, her resignation took effect April 14 of the same year.
References
- ↑ "Organization".
- ↑ "B.C. Film Commission budget cut by 23 percent | Vancouver, Canada | Straight.com". Archived from the original on 2012-10-18. Retrieved 2017-08-24.
- ↑ Andrews, Marke. "B.C. Film Commission: A good 30 years". The Vancouver Sun. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ↑ "B.C. Film Commission budget cut by 23 percent | Vancouver, Canada | Straight.com". Archived from the original on 2012-10-18. Retrieved 2017-08-24.
- ↑ "BCFC | Welcome | Industry Contacts". Archived from the original on 2011-01-20. Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ↑ "BC Film Commission 2009 data reveals depleting domestic production levels | Georgia Straight, Vancouver's News & Entertainment Weekly". Archived from the original on 2014-07-28. Retrieved 2017-08-24.
- ↑ "'Hollywood North' to grow again". Archived from the original on 2007-08-24.