Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 14th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: Regular Freemasonry, which insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member professes belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics do not take place within the lodge; and Continental Freemasonry, which consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions.

The Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite of Freemasonry is a full-fledged Rite within the broader context of Freemasonry. It is the most widely practiced Rite in the world, spanning from the Blue Lodge level, and is sometimes designated as a concordant body due to its relationship with the degrees of Symbolic (Craft) Freemasonry. In contrast to being an appendant body, the Scottish Rite operates as a complete Rite in itself. Its structure includes the first three degrees, administered by various Masonic organizations or bodies. Each such body is governed by its own central authority. In the Scottish Rite, the central authority consists of a Grand Lodge overseeing the 1st to 3rd degrees, and a Supreme Council overseeing the 4th to 33rd degrees. The Droit Humain is an exception, as it maintains a consistent central authority from the 1st to the 33rd degree.
The York Rite, sometimes referred to as the American Rite, is one of several Rites of Freemasonry. It is named for, but not practiced in, York, Yorkshire, England. A Rite is a series of progressive degrees that are conferred by various Masonic organizations or bodies, each of which operates under the control of its own central authority. The York Rite specifically is a collection of separate Masonic Bodies and associated Degrees that would otherwise operate independently. The three primary bodies in the York Rite are the Chapter of Royal Arch Masons, Council of Royal & Select Masters or Council of Cryptic Masons, and the Commandery of Knights Templar, each of which are governed independently but are all considered to be a part of the York Rite. There are also other organizations that are considered to be directly associated with the York Rite, or require York Rite membership to join such as the York Rite Sovereign College but in general the York Rite is considered to be made up of the aforementioned three. The Rite's name is derived from the city of York, where, according to one Masonic legend, the first meetings of Masons in England took place.
The Swedish Rite is a variation or Rite of Freemasonry that is common in Scandinavian countries and to a limited extent in Germany. It is different from other branches of Freemasonry in that, rather than having the three self-contained foundation degrees and seemingly-endless side degrees and appendant bodies, it has an integrated system with ten degrees. It is also different in that, rather than moving through the offices or 'chairs', progress in the Swedish Rite is based on moving through the ten degrees. A fundamental difference is the Swedish Rite's position on religious affiliation: Anglo/American 'Regular' Masonry requires a belief in any theistic religion and Continental 'Liberal' Masonry does not require belief in any religion, whereas Swedish Masonry is specifically Christian, and requires a Christian trinitarian belief in all its members. Nonetheless, the main Swedish Rite constitutions are all recognised as regular by the United Grand Lodge of England, and stand in full amity.

The Order of Mark Master Masons is an appendant order of Freemasonry that exists in some Masonic jurisdictions, and confers the degrees of Mark Mason and Mark Master.
The Royal Order of Scotland is an appendant order within the structures of Freemasonry. Membership is an honour extended to Freemasons by invitation. The Grand Lodge of the Royal Order of Scotland is headquartered in Edinburgh, with a total of 88 subordinate Provincial Grand Lodges; of these, the greatest concentration is in the British Isles, with the rest located in countries around the world.

The Knights Templar, full name The United Religious, Military and Masonic Orders of the Temple and of St John of Jerusalem, Palestine, Rhodes and Malta, is a fraternal order affiliated with Freemasonry. Unlike the initial degrees conferred in a regular Masonic Lodge, which only require a belief in a Supreme Being regardless of religious affiliation, the Knights Templar is one of several additional Masonic Orders in which membership is open only to Freemasons who profess a belief in Christianity. One of the obligations entrants to the order are required to declare is to protect and defend the Christian faith. The word "United" in its full title indicates that more than one historical tradition and more than one actual order are jointly controlled within this system. The individual orders 'united' within this system are principally the Knights of the Temple, the Knights of Malta, the Knights of St Paul, and only within the York Rite, the Knights of the Red Cross.
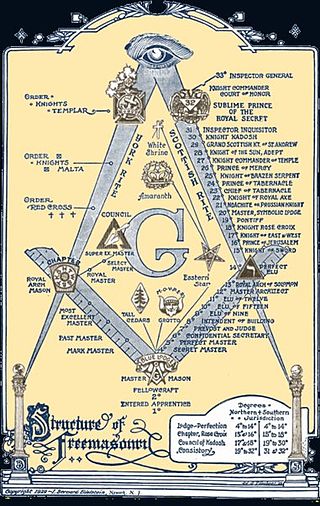
There are many organisations and orders which form part of the widespread fraternity of Freemasonry, each having its own structure and terminology. Collectively these may be referred to as Masonic bodies, Masonic orders, Concordant bodies or appendant bodies of Freemasonry.
Born in New Hampton, New Hampshire, on February 19, 1792, Simon Wiggin Robinson was the son of Captain Noah Robinson, who served honorably in the American Revolution. Young Robinson served his country, also, in the War of 1812 when he was stationed at Portsmouth, New Hampshire, as an Adjutant.
Freemasonry in Denmark was first established in 1743 and is today represented by a number of Grand Lodges. The oldest and biggest Masonic Grand Lodge in Denmark is the Danish Order of Freemasons, in English also known as the Grand Lodge of Denmark.
Robert Macoy was born in Armagh, Ulster County, Ireland. He moved to the United States at the age of 4 months. He was a prominent Freemason, and was instrumental in the founding of the Order of the Eastern Star and the Order of the Amaranth. He also founded what may be the largest Masonic publishing, regalia, and supply house currently active, Macoy Publishing & Masonic Supply Company.

The Royal Arch is a degree of Freemasonry. The Royal Arch is present in all main masonic systems, though in some it is worked as part of Craft ('mainstream') Freemasonry, and in others in an appendant ('additional') order. Royal Arch Masons meet as a Chapter; in the Supreme Order of the Royal Arch as practised in the British Isles, much of Europe and the Commonwealth, Chapters confer the single degree of Royal Arch Mason.
The Allied Masonic Degrees (AMD) are a series of Masonic degrees conferred by Councils of the Allied Masonic Degrees. The Allied Masonic Degrees form an appendant order of Freemasonry that exists in some Masonic jurisdictions; its degrees are conferred only by invitation. Councils of the Allied Masonic Degrees exist in Great Britain, the United States, Canada, France, Australia and Congo, and their members also educate one another by presenting research papers on Freemasonry.

Royal Arch Masonry is the first part of the American York Rite system of Masonic degrees. Royal Arch Masons meet as a Chapter, and the Royal Arch Chapter confers four degrees: Mark Master Mason, Past Master, Most Excellent Master, and Royal Arch Mason.
The history of Freemasonry in Mexico can be traced to at least 1806 when the first Masonic lodge was formally established in the nation.

The Order of Knight Masons is a chivalric Masonic order, open to all Master Masons who are also members of a Mark Lodge and a Royal Arch Chapter Members of the order meet in Councils of Knight Masons which are governed by the Grand Council of Knight Masons based in Dublin, Ireland. A member of the group is a Knight Mason.
The Order of Royal and Select Masters is an appendant order of Freemasonry and frequently referred to as 'Cryptic Degrees'. In England and Wales, the degrees are practiced as a stand-alone organisation of Freemasonry while in some other Masonic Constitutions, they form part of the York Rite.
The Supreme Council, Scottish Rite, Northern Jurisdiction oversees the Scottish Rite of Freemasonry in fifteen states: Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Jersey, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Wisconsin and Vermont.

In Freemasonry, the first three Masonic degrees constitute the fundamental degrees in all Rites they are called Blue Lodge of Craft degree.












