
The Hexanchiformes are a primitive order of sharks, that numbering just seven extant species in two families. Fossil sharks that were apparently very similar to modern sevengill species are known from Jurassic specimens.

Elasmobranchii is a subclass of Chondrichthyes or cartilaginous fish, including modern sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish. Members of this subclass are characterised by having five to seven pairs of gill clefts opening individually to the exterior, rigid dorsal fins and small placoid scales on the skin. The teeth are in several series; the upper jaw is not fused to the cranium, and the lower jaw is articulated with the upper. The details of this jaw anatomy vary between species, and help distinguish the different elasmobranch clades. The pelvic fins in males are modified to create claspers for the transfer of sperm. There is no swim bladder; instead, these fish maintain buoyancy with large livers rich in oil.

Cladoselache is an extinct genus of shark-like chondrichthyan from the Late Devonian (Famennian) of North America. It was similar in body shape to modern lamnid sharks, but was not closely related to lamnids or to any other modern (selachian) shark. As an early chondrichthyan, it had yet to evolve traits of modern sharks such as accelerated tooth replacement, a loose jaw suspension, enameloid teeth, and possibly claspers.

Orthacanthus is an extinct genus of fresh-water xenacanthiform elasmobranch, named by Louis Agassiz in 1843, ranging from the Upper Carboniferous into the Lower Permian. Orthacanthus had a nektobenthic life habitat, with a carnivorous diet. Multiple authors have also discovered evidence of cannibalism in the diet of Orthacanthus and of "filial cannibalism" where adult Orthacanthus preyed upon juvenile Orthacanthus. Synonyms of the genus Orthacanthus are Dittodus Owen, 1867, Didymodus Cope, 1883, Diplodus Agassiz, 1843, Chilodus Giebel, 1848.

Stethacanthus is an extinct genus of shark-like holocephalians which lived from the Late Devonian to Late Carboniferous epoch, dying out around 298.9 million years ago. Fossils have been found in Australia, Asia, Europe and North America.

Xenacanthida is an order or superorder of extinct shark-like chondrichthyans known from the Carboniferous to Triassic. They were native to freshwater, marginal marine and shallow marine habitats. Some xenacanths may have grown to lengths of 5 m (16 ft). Most xenacanths died out at the end of the Permian in the End-Permian Mass Extinction, with only a few forms surviving into the Triassic.

Symmoriiformes is an extinct order of stem-group holocephalians. Originally named Symmoriida by Zangerl (1981), it has subsequently been known by several other names. Lund (1986) synonymized the group with Cladodontida, while Maisey (2008) corrected the name to Symmoriiformes in order to prevent it from being mistaken for a family. The symmoriiform fossils record begins during the late Devonian. Most of them died out at the start of the Permian, but Dwykaselachus is known from the Artinskian-Kungurian of South Africa. Teeth described from the Valanginian of France and Austria indicate that members of the family Falcatidae might have survived until the Early Cretaceous; however, these teeth were also argued to be more likely neoselachian teeth.

Falcatus is an extinct genus of falcatid chondrichthyan which lived during the early Carboniferous Period in Bear Gulch bay in what is now Montana.

Glikmanius is an extinct genus of ctenacanth shark which lived in the Carboniferous of North America and Russia. The genus is based on a whole specimen from Nebraska, USA. Glikmanius is named in honour of the Russian palaeontologist, Dr. Leonid Glikman, who studied the genus and was "the first to propose its ctenacanthiform affinity". G. careforum may have reached lengths of 3 metres (9.8 ft), while G. occidentalis may have reached lengths of over 6 metres (20 ft), making it one the largest marine predators of its era.

Falcatidae is a family of Paleozoic holocephalians. Members of this family include Falcatus, a small fish from the Bear Gulch Limestone of Montana. The family first appeared around the start of the Carboniferous, and there is some evidence that they survived well into the early Cretaceous, though its putative Cretaceous members were also argued to be more likely neoselachians.

Hybodontiformes, commonly called hybodonts, are an extinct group of shark-like cartilaginous fish (chondrichthyans) which existed from the late Devonian to the Late Cretaceous. Hybodonts share a close common ancestry with modern sharks and rays (Neoselachii) as part of the clade Euselachii. They are distinguished from other chondrichthyans by their distinctive fin spines and cephalic spines present on the heads of males. An ecologically diverse group, they were abundant in marine and freshwater environments during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic, but were rare in open marine environments by the end of the Jurassic, having been largely replaced by modern sharks, though they were still common in freshwater and marginal marine habitats. They survived until the end of the Cretaceous, before going extinct.
Cladodus is an extinct genus of cartilaginous fishes in the family Ctenacanthidae. As the name implies, they are a type of cladodont, primitive sharks with teeth designed to snag fish and swallow them whole, instead of sawing off chunks to swallow.
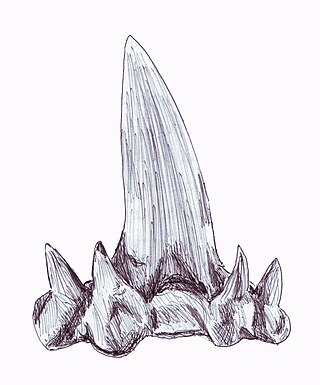
Cladodont is the term for a common category of early Devonian shark known primarily for its "multi-cusped" tooth consisting of one long blade surrounded by many short, fork-like tines, designed to catch food that was swallowed whole, instead of being used to saw off chunks of meat like many modern sharks. The skinny teeth would puncture and grasp the prey, keeping it from wriggling free.

Thrinacodus is an extinct genus of basal elasmobranch, found worldwide from the Late Devonian-Lower Carboniferous. The type species is Thrinacodus nanus. Most species are only known from their tricuspid teeth. T. gracia, originally placed in the separate genus Thrinacoselache from the Serpukhovian-aged Bear Gulch Limestone, of what is now Montana, is known from full body impressions, showing a long, slender eel-like body up to a metre in length, with an elongate rostrum. Stomach contents of T. gracia include remains of crustaceans and small chondrichthyan fish. It is a member of the Phoebodontiformes.

Kaibabvenator swiftae is a very large, extinct ctenacanthiform fish hat lived in marine environments in what is now Arizona, during the Middle Permian Period. K. swiftae is known from large teeth up to 30 millimeters long found in the Kachina Microsite, of the lower Fossil Mountain Member, in the Kaibab Formation near Flagstaff, Arizona, suggesting a total body length of around 5–6 metres (16–20 ft). The specific name honors researcher Sandra Swift for her paleontological contributions to Northern Arizona University.

Squatinactis is a genus of extinct elasmobranch chondrichthyan known from the Carboniferous aged Bear Gulch Limestone in Montana. This fish was discovered in 1974 by Richard Lund. The type specimen, named CMNH 46133, consists of a brain case, poorly preserved jaws and gills, a pectoral fin, and a partial vertebral axis. This creatures most startling feature were its broad pectoral fins which resembled those of stingrays and angel sharks (Squatina). The holotype specimen has about 15 teeth in its jaw. This creature is named after the angel shark. Remains found in the South Urals of Russia and the Eyam Limestone of Derbyshire, England, have been tentatively identified as those belonging to S. caudispinatus.
Saivodus is an extinct genus of ctenacanthiform fish that existed in early Mississippian of the Carboniferous period. Fossils have been found in Ireland, Scotland, England, Belgium, Morocco, and the United States. Teeth assigned to that genus are also known from the Permian (Leonardian) Kaibab Formation.

Phoebodontiformes is an extinct group of elasmobranchs, known from the Devonian and Carboniferous periods. It includes the genera Phoebodus, Diademodus and Thrinacodus. Phoebodus and Thrinacodus have slender, elongate bodies. Their teeth are tricuspate. Some studies have recovered the group as paraphyletic.
Anachronistidae is an extinct family of cartilaginous fish, known from the Carboniferous and Permian periods. They are considered to be the oldest known members of Neoselachii, with a close relationship to modern sharks and rays. They are known from isolated teeth.

















