In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
In cellular biology, P-bodies, or processing bodies, are distinct foci formed by phase separation within the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell consisting of many enzymes involved in mRNA turnover. P-bodies are highly conserved structures and have been observed in somatic cells originating from vertebrates and invertebrates, plants and yeast. To date, P-bodies have been demonstrated to play fundamental roles in general mRNA decay, nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, adenylate-uridylate-rich element mediated mRNA decay, and microRNA (miRNA) induced mRNA silencing. Not all mRNAs which enter P-bodies are degraded, as it has been demonstrated that some mRNAs can exit P-bodies and re-initiate translation. Purification and sequencing of the mRNA from purified processing bodies showed that these mRNAs are largely translationally repressed upstream of translation initiation and are protected from 5' mRNA decay.

The exosome complex is a multi-protein intracellular complex capable of degrading various types of RNA molecules. Exosome complexes are found in both eukaryotic cells and archaea, while in bacteria a simpler complex called the degradosome carries out similar functions.

Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 1, also known as protein phosphatase 2C, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDP1 gene. PDPC 1 is an enzyme which serves to reverse the effects of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase upon pyruvate dehydrogenase, activating pyruvate dehydrogenase.

The 5' cap of eukaryotic messenger RNA is bound at all times by various cap-binding complexes (CBCs).

5′-3′ exoribonuclease 1 (Xrn1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the XRN1 gene. Xrn1 hydrolyses RNA in the 5′ to 3′ direction.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF1 gene.
Poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN), also known as polyadenylate-specific ribonuclease or deadenylating nuclease (DAN), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PARN gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF2 gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 3B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF3B gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase SMG1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMG1 gene. SMG1 belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family.

Exosome component 10, also known as EXOSC10, is a human gene, the protein product of which is part of the exosome complex and is an autoantigen is patients with certain auto immune diseases, most notably scleromyositis.

Exosome component 4, also known as EXOSC4, is a human gene, which is part of the exosome complex.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF3A gene.

Scavenger mRNA-decapping enzyme DcpS is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCPS gene.

mRNA-decapping enzyme 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCP1A gene.

mRNA-decapping enzyme 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCP1B gene.
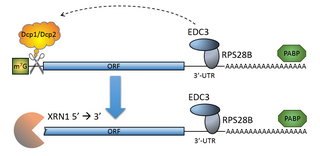
The process of messenger RNA decapping consists of hydrolysis of the 5' cap structure on the RNA exposing a 5' monophosphate. In eukaryotes, this 5' monophosphate is a substrate for the 5' exonuclease Xrn1 and the mRNA is quickly destroyed. There are many situations which may lead to the removal of the cap, some of which are discussed below.

The mRNA decapping complex is a protein complex in eukaryotic cells responsible for removal of the 5' cap. The active enzyme of the decapping complex is the bilobed Nudix family enzyme Dcp2, which hydrolyzes 5' cap and releases 7mGDP and a 5'-monophosphorylated mRNA. This decapped mRNA is inhibited for translation and will be degraded by exonucleases. The core decapping complex is conserved in eukaryotes. Dcp2 is activated by Decapping Protein 1 (Dcp1) and in higher eukaryotes joined by the scaffold protein VCS. Together with many other accessory proteins, the decapping complex assembles in P-bodies in the cytoplasm.
M7GpppN-mRNA hydrolase (EC 3.6.1.62, DCP2, NUDT16, D10 protein, D9 protein, D10 decapping enzyme, decapping enzyme) is an enzyme with systematic name m7GpppN-mRNA m7GDP phosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction