
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. Two large observatories were built in the United States with the aim of detecting gravitational waves by laser interferometry. These observatories use mirrors spaced four kilometers apart which are capable of detecting a change of less than one ten-thousandth the charge diameter of a proton.

Kip Stephen Thorne is an American theoretical physicist known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. Along with Rainer Weiss and Barry C. Barish, he was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics for his contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves.

Rainer "Rai" Weiss is a German-born American physicist, known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. He is a professor of physics emeritus at MIT and an adjunct professor at LSU. He is best known for inventing the laser interferometric technique which is the basic operation of LIGO. He was Chair of the COBE Science Working Group.

Sir Michael Victor Berry, is a British mathematical physicist at the University of Bristol, England.

The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) is a planned space probe to detect and accurately measure gravitational waves—tiny ripples in the fabric of spacetime—from astronomical sources. LISA will be the first dedicated space-based gravitational-wave observatory. It aims to measure gravitational waves directly by using laser interferometry. The LISA concept has a constellation of three spacecraft arranged in an equilateral triangle with sides 2.5 million kilometres long, flying along an Earth-like heliocentric orbit. The distance between the satellites is precisely monitored to detect a passing gravitational wave.

The Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics is a Max Planck Institute whose research is aimed at investigating Einstein's theory of relativity and beyond: Mathematics, quantum gravity, astrophysical relativity, and gravitational-wave astronomy. The institute was founded in 1995 and is located in the Potsdam Science Park in Golm, Potsdam and in Hannover where it closely collaborates with the Leibniz University Hannover. Both the Potsdam and the Hannover parts of the institute are organized in three research departments and host a number of independent research groups.

Bruce Allen is an American physicist and director of the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Hannover Germany and leader of the Einstein@Home project for the LIGO Scientific Collaboration. He is also a physics professor at the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee and the initiator / project leader of smartmontools hard disk utility.
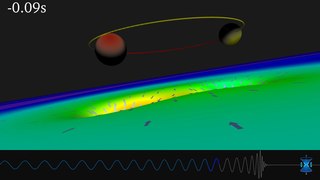
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity that are generated by the accelerated masses of binary stars and other motions of gravitating masses, and propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as the gravitational equivalent of electromagnetic waves. Gravitational waves are sometimes called gravity waves, but gravity waves typically refer to displacement waves in fluids. In 1916 Albert Einstein demonstrated that gravitational waves result from his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime.

A gravitational-wave detector is any device designed to measure tiny distortions of spacetime called gravitational waves. Since the 1960s, various kinds of gravitational-wave detectors have been built and constantly improved. The present-day generation of laser interferometers has reached the necessary sensitivity to detect gravitational waves from astronomical sources, thus forming the primary tool of gravitational-wave astronomy.
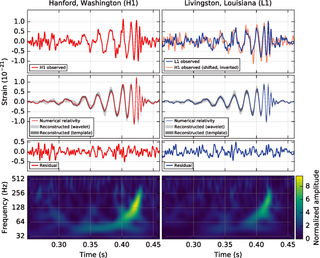
Gravitational-wave astronomy is an emerging field of science, concerning the observations of gravitational waves to collect relatively unique data and make inferences about objects such as neutron stars and black holes, events such as supernovae, and processes including those of the early universe shortly after the Big Bang.
The Australian International Gravitational Observatory (AIGO) is a research facility located near Gingin, north of Perth in Western Australia. It is part of a worldwide effort to directly detect gravitational waves. Note that these are a major prediction of the general theory of relativity and are not to be confused with gravity waves, a phenomenon studied in fluid mechanics.
Bernard F. Schutz FInstP FLSW is an American and naturalised British physicist. He is well known for his research in Einstein's theory of general relativity, especially for his contributions to the detection of gravitational waves, and for his textbooks. Schutz is a Fellow of the Royal Society and a Member of the US National Academy of Sciences. He is a professor of physics and astronomy at Cardiff University, and was a founding director of the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Potsdam, Germany, where he led the Astrophysical Relativity division from 1995 to 2014. Schutz was a founder and principal investigator of the GEO gravitational wave collaboration, which became part of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC). Schutz was also one of the initiators of the proposal for the space-borne gravitational wave detector LISA, and he coordinated the European planning for its data analysis until the mission was adopted by ESA in 2016. Schutz conceived and in 1998 began publishing from the AEI the online open access (OA) review journal Living Reviews in Relativity, which for many years has been the highest-impact OA journal in the world, as measured by Clarivate.

The Gravity Discovery Centre and Observatory is a "hands-on" science education, astronomy, Aboriginal culture and tourist centre, situated on the site of the Gravity Precinct in bushland near Gingin, north of Perth, Western Australia.

Barry Clark Barish is an American experimental physicist and Nobel Laureate. He is a Linde Professor of Physics, emeritus at California Institute of Technology and a leading expert on gravitational waves.

Alexei Alexandrovich Starobinsky was a Soviet and Russian theoretical physicist and cosmologist. He was a pioneer of the theory of cosmic inflation, for which he received the 2014 Kavli Prize in Astrophysics together with Alan Guth and Andrei Linde.
David Ernest McClelland is an Australian physicist, with his research focused on the development of the manipulation and control of optical quantum states, and its implementation into gravitational wave observatories. He is a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Science, the American Physical Society and the Optical Society of America. Since 2001, he has been a professor at the Australian National University (ANU) in the Research School of Physics and Engineering, in Canberra (Australia). He is Director of the ANU's Centre for Gravitational Astrophysics and Deputy Director of OzGrav - the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence in Gravitational Wave Discovery.

Hiranya Vajramani Peiris is a British astrophysicist at the University of Cambridge, where she holds the Professorship of Astrophysics (1909). She is best known for her work on the cosmic microwave background radiation, and interdisciplinary links between cosmology and high-energy physics. She was one of 27 scientists who received the Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics in 2018 for their "detailed maps of the early universe."
Susan Marjorie Scott is an Australian mathematical physicist whose work concerns general relativity, gravitational singularities, and black holes. She is a Professor of Theoretical Physics at the Australian National University (ANU).

Rana X. Adhikari is an American experimental physicist. He is a professor of physics at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and an associate faculty member of the International Centre for Theoretical Sciences of Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (ICTS-TIFR).

C. S. Unnikrishnan is an Indian physicist and professor known for his contributions in multiple areas of experimental and theoretical physics. He has been a professor at the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai and is currently a professor in the School of Quantum Technology at the Defence Institute of Advanced Technology in Pune. He has made significant contributions in foundational issues in gravity and quantum physics and has published over 250 research papers and articles. Unnikrishnan is also a key member of the LIGO-India project and a member of the global LIGO Scientific Collaboration
















