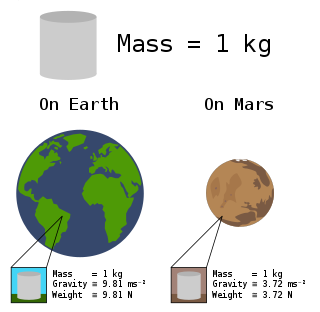
In science and engineering, the weight of an object, is the force acting on the object due to acceleration or gravity.

A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or fulcrum. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage, which is mechanical advantage gained in the system, equal to the ratio of the output force to the input force. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement.

A counterweight is a weight that, by applying an opposite force, provides balance and stability of a mechanical system. The purpose of a counterweight is to make lifting the load faster and more efficient, which saves energy and causes less wear and tear on the lifting machine.
The Method of Mechanical Theorems, also referred to as The Method, is one of the major surviving works of the ancient Greek polymath Archimedes. The Method takes the form of a letter from Archimedes to Eratosthenes, the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria, and contains the first attested explicit use of indivisibles. The work was originally thought to be lost, but in 1906 was rediscovered in the celebrated Archimedes Palimpsest. The palimpsest includes Archimedes' account of the "mechanical method", so called because it relies on the center of weights of figures (centroid) and the law of the lever, which were demonstrated by Archimedes in On the Equilibrium of Planes.

A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. Pilot-operated relief valves are a specialized type of pressure safety valve. A leak tight, lower cost, single emergency use option would be a rupture disk.

Apache Groovy is a Java-syntax-compatible object-oriented programming language for the Java platform. It is both a static and dynamic language with features similar to those of Python, Ruby, and Smalltalk. It can be used as both a programming language and a scripting language for the Java Platform, is compiled to Java virtual machine (JVM) bytecode, and interoperates seamlessly with other Java code and libraries. Groovy uses a curly-bracket syntax similar to Java's. Groovy supports closures, multiline strings, and expressions embedded in strings. Much of Groovy's power lies in its AST transformations, triggered through annotations.

A submersible is an underwater vehicle which needs to be transported and supported by a larger watercraft or platform. This distinguishes submersibles from submarines, which are self-supporting and capable of prolonged independent operation at sea.
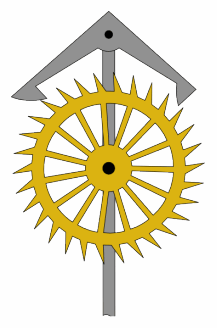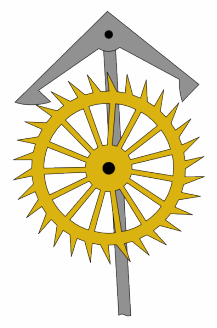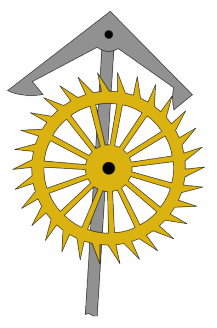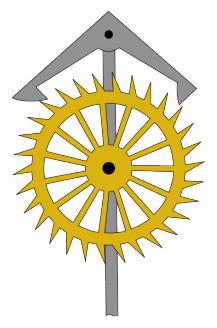
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to the clock's timekeeping element to replace the energy lost to friction during its cycle and keep the timekeeper oscillating. The escapement is driven by force from a coiled spring or a suspended weight, transmitted through the timepiece's gear train. Each swing of the pendulum or balance wheel releases a tooth of the escapement's escape wheel, allowing the clock's gear train to advance or "escape" by a fixed amount. This regular periodic advancement moves the clock's hands forward at a steady rate. At the same time, the tooth gives the timekeeping element a push, before another tooth catches on the escapement's pallet, returning the escapement to its "locked" state. The sudden stopping of the escapement's tooth is what generates the characteristic "ticking" sound heard in operating mechanical clocks and watches.

A scale or balance is a device used to measure weight or mass. These are also known as mass scales, weight scales, mass balances, and weight balances.

An anti-roll bar is an automobile suspension part that helps reduce the body roll of a vehicle during fast cornering or over road irregularities. It links opposite front or rear wheels to a torsion spring using short lever arms for anchors. This increases the suspension's roll stiffness—its resistance to roll in turns.

An analytical balance is a class of balance designed to measure small mass in the sub-milligram range. The measuring pan of an analytical balance is inside a transparent enclosure with doors so that dust does not collect and so any air currents in the room do not affect the balance's operation. This enclosure is often called a draft shield. The use of a mechanically vented balance safety enclosure, which has uniquely designed acrylic airfoils, allows a smooth turbulence-free airflow that prevents balance fluctuation and the measure of mass down to 1 μg without fluctuations or loss of product. Also, the sample must be at room temperature to prevent natural convection from forming air currents inside the enclosure from causing an error in reading. Single pan mechanical substitution balance is a method of maintaining consistent response throughout the useful capacity of the balance. This is achieved by maintaining a constant load on the balance beam and thus the fulcrum, by subtracting mass on the same side of the beam as which the sample is added.
A spring scale, spring balance or newton meter is a type of mechanical force gauge or weighing scale. It consists of a spring fixed at one end with a hook to attach an object at the other. It works in accordance with Hooke's Law, which states that the force needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance scales linearly with respect to that distance. Therefore, the scale markings on the spring balance are equally spaced.

The Roberval balance is a weighing scale presented to the French Academy of Sciences by the French mathematician Gilles Personne de Roberval in 1669.

A steelyard balance, steelyard, or stilyard is a straight-beam balance with arms of unequal length. It incorporates a counterweight which slides along the longer arm to counterbalance the load and indicate its weight. A steelyard is also known as a Roman steelyard or Roman balance.

A truck scale (US), weighbridge (non-US) or railroad scale is a large set of scales, usually mounted permanently on a concrete foundation, that is used to weigh entire rail or road vehicles and their contents. By weighing the vehicle both empty and when loaded, the load carried by the vehicle can be calculated.
The center of gravity (CG) of an aircraft is the point over which the aircraft would balance. Its position is calculated after supporting the aircraft on at least two sets of weighing scales or load cells and noting the weight shown on each set of scales or load cells. The center of gravity affects the stability of the aircraft. To ensure the aircraft is safe to fly, the center of gravity must fall within specified limits established by the aircraft manufacturer.

In common usage, the mass of an object is often referred to as its weight, though these are in fact different concepts and quantities. Nevertheless, one object will always weigh more than another with less mass if both are subject to the same gravity.

SEROPI is a wheel based humanoid robot developed by KITECH.

The compound lever is a simple machine operating on the premise that the resistance from one lever in a system of levers acts as effort for the next, and thus the applied force is transferred from one lever to the next. Almost all scales use some sort of compound lever to work. Other examples include nail clippers and piano keys.

A double-beam drawbridge, seesaw or folding bridge is a movable bridge. It opens by rotation about a horizontal axis parallel to the water. Historically, the double-beam drawbridge has emerged from the drawbridge. Unlike a drawbridge, a double-beam drawbridge has counterweights, so that opening requires much less energy.

















