Related Research Articles

The Government of Barbados (GoB), is a unitary parliamentary republic, where the President of Barbados is the head of state and the Prime Minister of Barbados is the head of government.

Democracy is a system of government in which state power is vested in the people or the general population of a state. According to the United Nations, democracy "provides an environment that respects human rights and fundamental freedoms, and in which the freely expressed will of people is exercised."
The politics of Hungary takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic. The prime minister is the head of government of a pluriform multi-party system, while the president is the head of state and holds a largely ceremonial position.

The politics of Indonesia take place in the framework of a presidential representative democratic republic whereby the President of Indonesia is both head of state and head of government and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the bicameral People's Consultative Assembly. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.
The Republic of South Africa is a unitary parliamentary democratic republic. The President of South Africa serves both as head of state and as head of government. The President is elected by the National Assembly and must retain the confidence of the Assembly in order to remain in office. South Africans also elect provincial legislatures which govern each of the country's nine provinces.
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with others. The typical division into three branches of government, sometimes called the trias politica model, includes a legislature, an executive, and a judiciary. It can be contrasted with the fusion of powers in monarchies, but also parliamentary and semi-presidential systems where there can be overlap in membership and functions between different branches, especially the executive and legislative.
Judicial independence is the concept that the judiciary should be independent from the other branches of government. That is, courts should not be subject to improper influence from the other branches of government or from private or partisan interests. Judicial independence is important for the idea of separation of powers.
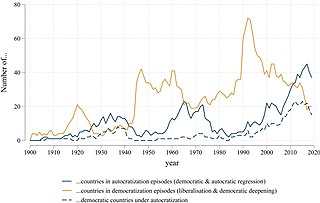
Democratization, or democratisation, is the democratic transition to a more democratic political regime, including substantive political changes moving in a democratic direction.
Liberalism in the Netherlands started as an anti-monarchical effort spearheaded by the Dutch statesman Thorbecke, who almost single-handedly wrote the 1848 Constitution of the Netherlands that turned the country into a constitutional monarchy.

A democracy is a political system, or a system of decision-making within an institution, organization, or state, in which all members have an equal share of power. Modern democracies are characterized by two capabilities of their citizens that differentiate them fundamentally from earlier forms of government: to intervene in society and have their sovereign held accountable to the international laws of other governments of their kind. Democratic government is commonly juxtaposed with oligarchic and monarchic systems, which are ruled by a minority and a sole monarch respectively.

Radicalism was a political movement representing the leftward flank of liberalism during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and a precursor to social liberalism, social democracy, civil libertarianism, and modern progressivism. This ideology is commonly referred to as "radicalism" but is sometimes referred to as radical liberalism, or classical radicalism, to distinguish it from radical politics. Its earliest beginnings are to be found during the English Civil War with the Levellers and later the Radical Whigs.

Liberal democracy, substantive democracy, or western democracy is a form of government that combines the structure of a representative democracy with the principles of liberal political philosophy. It is characterized by elections between or among multiple distinct political parties, a separation of powers into different branches of government, the rule of law in everyday life as part of an open society, a market economy with private property, universal suffrage, and the equal protection of human rights, civil rights, civil liberties, and political freedoms for all people. To define the system in practice, liberal democracies often draw upon a constitution, either codified or uncodified, to delineate the powers of government and enshrine the social contract. The purpose of a constitution is often seen as a limit on the authority of the government.
Politics is the process by which groups of people make decisions. Although the term is generally applied to behavior within civil governments, politics is observed in all human group interactions, including corporate, academic, and religious institutions. Politics consists of "social relations involving authority or power. The definition of "politics" from "The Free Dictionary" is the study of political behavior and examines the acquisition and application of power. Politics study include political philosophy, which seeks a rationale for politics and an ethic of public behavior, and public administration, which examines the practices of governance.
Civil liberties in the United Kingdom are part of UK constitutional law and have a long and formative history. This is usually considered to have begun with Magna Carta of 1215, a landmark document in British constitutional history. Development of civil liberties advanced in common law and statute law in the 17th and 18th centuries, notably with the Bill of Rights 1689. During the 19th century, working-class people struggled to win the right to vote and join trade unions. Parliament responded with new legislation beginning with the Reform Act 1832. Attitudes towards suffrage and liberties progressed further in the aftermath of the first and second world wars. Since then, the United Kingdom's relationship to civil liberties has been mediated through its membership of the European Convention on Human Rights. The United Kingdom, through Sir David Maxwell-Fyfe, led the drafting of the Convention, which expresses a traditional civil libertarian theory. It became directly applicable in UK law with the enactment of the Human Rights Act 1998.

The Constitution of Ghana is the supreme law of the Republic of Ghana. It was approved on 28 April 1992 through a national referendum after 92% support. It defines the fundamental political principles, establishing the structure, procedures, powers and duties of the government, structure of the judiciary and legislature, and spells out the fundamental rights and duties of citizens. It is made up of 26 chapters, not including the preamble.

The constitution of the United Kingdom is the set of laws and conventions that make up the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland as a political body. Unlike in most countries, the constitution is not codifed, but is written into thousands of statutes and court cases, and found in unwritten political conventions and social consensus. The UK Supreme Court recognises principles, that guide the constitution, including parliamentary sovereignty, the rule of law, democracy, and upholding international law. It also recognises that some Acts of Parliament have special constitutional status. These include Magna Carta, which in 1215 required the King to call a "common counsel" to represent people, to hold courts in a fixed place, to guarantee fair trials, to guarantee free movement of people, to free the church from the state, and to guarantee rights of "common" people to use the land. After the Glorious Revolution, the Bill of Rights 1689 and the Claim of Right Act 1689 cemented Parliament's position as the supreme law-making body, and said that the "election of members of Parliament ought to be free". The Treaty of Union in 1706 and the Acts of Union 1707 Kingdoms of England, Wales and Scotland, the Acts of Union 1800 joined Ireland, but the Irish Free State separated after the Anglo-Irish Treaty in 1922, leaving Northern Ireland within the UK. After struggles for universal suffrage, the UK guaranteed every adult citizen over 21 years the equal right to vote in the Representation of the People Act 1928. After World War II, the UK became a founding member of the Council of Europe to uphold human rights, and the United Nations to guarantee international peace and security. The UK was a member of the European Union, joining its predecessor in 1973, but left in 2020. The UK is also a founding member of the International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization to participate in regulating the global economy.
Types of democracy refers to pluralism of governing structures such as governments and other constructs like workplaces, families, community associations, and so forth. Types of democracy can cluster around values. Some such types promote equal and direct participation in political acts. Others favor more indirect or procedural approaches to collective self-governance. Types of democracy can be found across time, space, and language. The foregoing examples are just a few of the thousands of refinements of, and variations on, the central notion of "democracy."
Anocracy, or semi-democracy, is a form of government that is loosely defined as part democracy and part dictatorship, or as a "regime that mixes democratic with autocratic features". Another definition classifies anocracy as "a regime that permits some means of participation through opposition group behavior but that has incomplete development of mechanisms to redress grievances." The term "semi-democratic" is reserved for stable regimes that combine democratic and authoritarian elements. Scholars distinguish anocracies from autocracies and democracies in their capability to maintain authority, political dynamics, and policy agendas. Similarly, the regimes have democratic institutions that allow for nominal amounts of competition. Such regimes are particularly susceptible to outbreaks of armed conflict and unexpected or adverse changes in leadership.

Embedded democracy is a form of government in which democratic governance is secured by democratic partial regimes. The term "embedded democracy" was coined by political scientists Wolfgang Merkel, Hans-Jürgen Puhle, and Aurel Croissant, who identified "five interdependent partial regimes" necessary for an embedded democracy: electoral regime, political participation, civil rights, horizontal accountability, and the power of the elected representatives to govern. The five internal regimes work together to check the power of the government, while external regimes also help to secure and stabilize embedded democracies. Together, all the regimes ensure that an embedded democracy is guided by the three fundamental principles of freedom, equality, and control.

Herrenvolk democracy is a system of government in which only a specific ethnic group participates in government, while other groups are disenfranchised. Ethnocracy, in which one group dominates the state, is a related concept. The German term Herrenvolk, meaning "master race", was used in 19th century discourse that justified colonialism with the supposed racial superiority of Europeans.
References
- ↑ Oser, Jennifer; Hooghe, Marc (August 2018). "Democratic ideals and levels of political participation: The role of political and social conceptualisations of democracy". The British Journal of Politics and International Relations. 20 (3): 711–730. doi:10.1177/1369148118768140. S2CID 149607518.
- ↑ Maginnis, Robert L. (September 12, 1999). "The Foundations Of Human Rights". Thought You Should Know.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help)[ verification needed ] - ↑ Powell, Colin L. (May 17, 2004). "New Report Shows U.S. Work for Human Rights, Powell Says". Archived from the original on November 19, 2004. Retrieved July 3, 2016.
- ↑ Cummings, Briana (May 2004). "A Tame Revolution? Explaining Soldiers' Restraint Toward Civilians in the American War of Independence". Harvard Graduate School of Education. Archived from the original on July 9, 2004. Retrieved July 3, 2016.[ self-published source? ]
- ↑ Amar, Akhil Reed (1991). "The Bill of Rights as a Constitution". The Yale Law Journal. 100 (5): 1131–1210. doi:10.2307/796690. JSTOR 796690.
- ↑ Burger, Warren E. (1991). "America's Bill of Rights at 200 Years". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 21 (3): 453–457. JSTOR 27550765.
- ↑ Warren, Mark E. (2002). "What Can Democratic Participation Mean Today?". Political Theory. 30 (5): 677–701. doi:10.1177/0090591702030005003. JSTOR 3072498. S2CID 145107871.
- ↑ "Political Systems & Structure of the U.S. vs. Great Britain". study.com. Retrieved 2023-05-20.