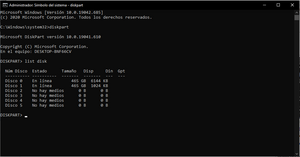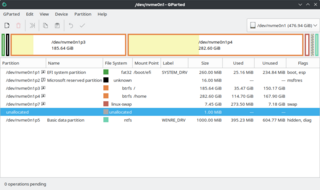
Disk partitioning or disk slicing is the creation of one or more regions on secondary storage, so that each region can be managed separately. These regions are called partitions. It is typically the first step of preparing a newly installed disk, before any file system is created. The disk stores the information about the partitions' locations and sizes in an area known as the partition table that the operating system reads before any other part of the disk. Each partition then appears to the operating system as a distinct "logical" disk that uses part of the actual disk. System administrators use a program called a partition editor to create, resize, delete, and manipulate the partitions. Partitioning allows the use of different filesystems to be installed for different kinds of files. Separating user data from system data can prevent the system partition from becoming full and rendering the system unusable. Partitioning can also make backing up easier. A disadvantage is that it can be difficult to properly size partitions, resulting in having one partition with too much free space and another nearly totally allocated.

In computer data storage, drive letter assignment is the process of assigning alphabetical identifiers to volumes. Unlike the concept of UNIX mount points, where volumes are named and located arbitrarily in a single hierarchical namespace, drive letter assignment allows multiple highest-level namespaces. Drive letter assignment is thus a process of using letters to name the roots of the "forest" representing the file system; each volume holds an independent "tree".

fdisk is a command-line utility for disk partitioning. It has been part of DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and early versions of Microsoft Windows, as well as certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. Windows 2000 and its successors have replaced fdisk with a more advanced tool called diskpart.

Multi-booting is the act of installing multiple operating systems on a single computer, and being able to choose which one to boot. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of specifically two operating systems. Multi-booting may require a custom boot loader.
In computing, data recovery is a process of retrieving deleted, inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged, or formatted data from secondary storage, removable media or files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, magnetic tapes, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being mounted by the host operating system (OS).
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition.

The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of partition tables of a physical computer storage device, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, using universally unique identifiers, which are also known as globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). Forming a part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard, it is nevertheless also used for some BIOSs, because of the limitations of master boot record (MBR) partition tables, which use 32 bits for logical block addressing (LBA) of traditional 512-byte disk sectors.

Windows Preinstallation Environment is a lightweight version of Windows used for the deployment of PCs, workstations, and servers, or troubleshooting an operating system while it is offline. It is intended to replace MS-DOS boot disks and can be booted via USB flash drive, PXE, iPXE, CD, DVD, or hard disk. Traditionally used by large corporations and OEMs, it is now widely available free of charge via Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (WADK).
In computing, SUBST is a command on the DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS operating systems used for substituting paths on physical and logical drives as virtual drives.
The Logical Disk Manager (LDM) is an implementation of a logical volume manager for Microsoft Windows NT, developed by Microsoft and Veritas Software. It was introduced with the Windows 2000 operating system, and is supported in Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 and Windows 11. The MMC-based Disk Management snap-in hosts the Logical Disk Manager. On Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, Microsoft deprecated LDM in favor of Storage Spaces.
In Unix-like operating systems, a loop device, vnd, or lofi is a pseudo-device that makes a computer file accessible as a block device.

The Recovery Console is a feature of the Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 operating systems. It provides the means for administrators to perform a limited range of tasks using a command-line interface.
The NTFS file system defines various ways to redirect files and folders, e.g., to make a file point to another file or its contents without making a copy of it. The object being pointed to is called the target. Such file is called a hard or symbolic link depending on a way it's stored on the filesystem.
NTBackup is the built-in backup application introduced in Windows NT 3.51 and included in Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003. NTBackup comprises a command-line utility and a set of wizard interfaces that provide multiple options to create, customize, and manage backups, and it is integrated with Shadow Copy and Task Scheduler. NTBackup creates backups in a proprietary BKF file format to external sources including floppy disks, hard drives, tape drives, and ZIP drives.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
Windows Deployment Services (WDS) is a deprecated component of the Windows Server operating system that enables centralized, network-based deployment of operating systems to bare-metal computers. It is the successor to Remote Installation Services (RIS). WDS officially supports remote deployment of Windows Vista and later, as well as Windows Server 2008 and later. However, because WDS uses disk imaging, in particular the Windows Imaging Format (WIM), it could deploy virtually any operating system. This is in contrast with its predecessor, RIS, which was a method of automating the installation process.
VHD and its successor VHDX are file formats representing a virtual hard disk drive (HDD). They may contain what is found on a physical HDD, such as disk partitions and a file system, which in turn can contain files and folders. They are typically used as the hard disk of a virtual machine, are built into modern versions of Windows, and are the native file format for Microsoft's hypervisor, Hyper-V.
In some operating systems, vol is a command within the command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe. It is used to display the volume label and volume serial number of a logical drive, such as a hard disk partition or a floppy disk, if they exist.
Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit, formerly Windows Automated Installation Kit, is a collection of tools and technologies produced by Microsoft designed to help deploy Microsoft Windows operating system images to target computers or to a virtual hard disk image in VHD format. It was first introduced with Windows Vista. WAIK is a required component of Microsoft Deployment Toolkit.
In computing, WBAdmin is a command-line utility built into Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 10 and Windows 11 operating systems. The command is used to perform backups and restores of operating systems, drive volumes, computer files, folders, and applications from a command-line interface.