Related Research Articles

A dictatorship is an autocratic form of government which is characterized by a leader, or a group of leaders, who hold governmental powers with few to no limitations. Politics in a dictatorship are controlled by a dictator, and they are facilitated through an inner circle of elites that includes advisers, generals, and other high-ranking officials. The dictator maintains control by influencing and appeasing the inner circle and repressing any opposition, which may include rival political parties, armed resistance, or disloyal members of the dictator's inner circle. Dictatorships can be formed by a military coup that overthrows the previous government through force or they can be formed by a self-coup in which elected leaders make their rule permanent. Dictatorships are authoritarian or totalitarian and they can be classified as military dictatorships, one-party dictatorships, personalist dictatorships, or absolute monarchies.

A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.

Totalitarianism is a form of government and a political system that prohibits all opposition parties, outlaws individual and group opposition to the state and its claims, and exercises an extremely high if not complete degree of control and regulation over public and private life. It is regarded as the most extreme and complete form of authoritarianism. In totalitarian states, political power is often held by autocrats, such as dictators and absolute monarchs, who employ all-encompassing campaigns in which propaganda is broadcast by state-controlled mass media in order to control the citizenry.

A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a governance structure in which only a single political party controls the ruling system. All other parties are either outlawed or only enjoy limited and controlled participation in elections. Sometimes the term "de facto one-party state" is used to describe a dominant-party system that, unlike the one-party state, allows democratic multiparty elections, but the existing practices or balance of political power effectively prevent the opposition from winning power.
In political science, a political system means the type of political organization that can be recognized, observed or otherwise declared by a state.

Law and economics, or economic analysis of law, is the application of microeconomic theory to the analysis of law. The field emerged in the United States during the early 1960s, primarily from the work of scholars from the Chicago school of economics such as Aaron Director, George Stigler, and Ronald Coase. The field uses economics concepts to explain the effects of laws, to assess which legal rules are economically efficient, and to predict which legal rules will be promulgated. There are two major branches of law and economics; one based on the application of the methods and theories of neoclassical economics to the positive and normative analysis of the law, and a second branch which focuses on an institutional analysis of law and legal institutions, with a broader focus on economic, political, and social outcomes, and overlapping with analyses of the institutions of politics and governance.
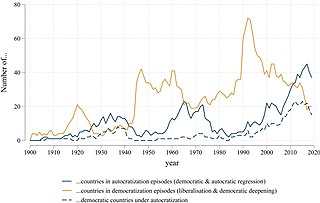
Democratization, or democratisation, is the democratic transition to a more democratic political regime, including substantive political changes moving in a democratic direction.
An illiberal democracy describes a governing system that hides its "nondemocratic practices behind formally democratic institutions and procedures". There is a lack of consensus among experts about the exact definition of illiberal democracy or whether it even exists.

Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture.
Ernst Fraenkel was a German-Jewish lawyer and political scientist. Prior to World War II, Fraenkel served as a criminal defense lawyer for Jews who were targeted by the Nazi regime. After the war, he authored the book The Dual State on the political structure of the Nazi regime and subsequently became one of the founding fathers of German political science.

Richard Sakwa is a British political scientist and a former professor of Russian and European politics at the University of Kent, a senior research fellow at the National Research University-Higher School of Economics in Moscow, and an honorary professor in the Faculty of Political Science at Moscow State University. He has written books about Russian, Central and Eastern European communist and post-communist politics.
Power sharing is a practice in conflict resolution where multiple groups distribute political, military, or economic power among themselves according to agreed rules. It can refer to any formal framework or informal pact that regulates the distribution of power between divided communities. Since the end of the Cold War, power-sharing systems have become increasingly commonplace in negotiating settlements for armed conflict. Two common theoretical approaches to power sharing are consociationalism and centripetalism.
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of democracy and political plurality. It involves the use of strong central power to preserve the political status quo, and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic voting. Political scientists have created many typologies describing variations of authoritarian forms of government. Authoritarian regimes may be either autocratic or oligarchic and may be based upon the rule of a party or the military. States that have a blurred boundary between democracy and authoritarianism have some times been characterized as "hybrid democracies", "hybrid regimes" or "competitive authoritarian" states.

A coup d'état, or simply a coup, is an illegal and overt attempt by a military organisation or other government elites to unseat an incumbent leadership by force. A self-coup is when a leader, having come to power through legal means, tries to stay in power through illegal means.
A hybrid regime is a type of political system often created as a result of an incomplete democratic transition from an authoritarian regime to a democratic one. Hybrid regimes are categorized as having a combination of autocratic features with democratic ones and can simultaneously hold political repressions and regular elections. Hybrid regimes are commonly found in developing countries with abundant natural resources such as petro-states. Although these regimes experience civil unrest, they may be relatively stable and tenacious for decades at a time. There has been a rise in hybrid regimes since the end of the Cold War.

Democratic backsliding, also called autocratization, is a process of regime change towards autocracy that makes the exercise of political power in a democracy more arbitrary and repressive. An autocratization process typically restricts the space for public contestation and political participation in the process of government selection". Democratic decline involves the weakening of democratic institutions, such as the peaceful transition of power or free and fair elections, or the violation of individual rights that underpin democracy, especially freedom of expression.
Jens Meierhenrich is a scholar of international relations at London School of Economics who directs the university's Centre for International Studies.
Hugo Krabbe was a Dutch legal philosopher and writer on public law. Known for his contributions to the theory of sovereignty and the state, he is regarded as a precursor of Hans Kelsen. Also Krabbe identified the state with the law and argued that state law and international law are parts of a single normative system, but contrary to Kelsen he conceived the identity between state and law as the outcome of an evolutionary process. Krabbe maintained that the binding force of the law is founded on the "legal consciousness" of mankind: a normative feeling inherent to human psychology. His work is expressive of the progressive and cosmopolitan ideals of interwar internationalism, and his notion of "sovereignty of law" stirred up much controversy in the legal scholarship of the time.

Law on imposition and enforcement of the death penalty was a German law enacted by the Nazi regime on 29 March 1933, that imposed the death penalty for certain crimes such as arson and high treason, that had formerly meant whole life imprisonment. The name derives from the fact that the law formed the legal basis for the imposition of the death penalty on Marinus van der Lubbe, who had been caught in the arson attack on the Reichstag on 28 February 1933.
An authoritarian enclave is a non-democratic subunit of a democratic system. It may be an administrative division of a state or a ministry.
References
- ↑ Fraenkel 2018, p. 17.
- ↑ Markovits, Inga (2006). "Transitions to Constitutional Democracies: The German Democratic Republic". The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science. 603 (1): 140–154. doi:10.1177/0002716205282408. S2CID 154981020.
- ↑ Suntrup, Jan Christoph (2020). "Between prerogative power and legality – reading Ernst Fraenkel's The Dual State as an analytical tool for present authoritarian rule". Jurisprudence. 11 (3): 335–359. doi:10.1080/20403313.2020.1734337. S2CID 216447975.
- ↑ Schotel, Bas (2021). "Administrative Law as a Dual State. Authoritarian Elements of Administrative Law". Hague Journal on the Rule of Law. 13 (1): 195–222. doi: 10.1007/s40803-021-00156-4 . ISSN 1876-4053. S2CID 234754461.
- ↑ Ben-Natan, Smadar (2021). "The dual penal empire: Emergency powers and military courts in Palestine/Israel and beyond". Punishment & Society. 23 (5): 741–763. doi:10.1177/14624745211040311.
- ↑ Mackert, Jürgen (2021). "Introduction: A 'master-race democracy': Myths and lies of Western liberal civilization". The Condition of Democracy. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-003-15838-7.
- ↑ Dayan, Hilla (2022). "Israel/Palestine: Authoritarian Practices in the Context of a Dual State Crisis". New Authoritarian Practices in the Middle East and North Africa. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 131–151. ISBN 978-1-4744-8943-0.
- ↑ Mehozay, Yoav (2016). Between the Rule of Law and States of Emergency: The Fluid Jurisprudence of the Israeli Regime. State University of New York Press. ISBN 978-1-4384-6340-7.
- ↑ Tushnet, Mark (2022). "The Dual State in the United States: The Case of Lynching and Legal Lynchings". The Law & Ethics of Human Rights. 16 (1): 41–59. doi:10.1515/lehr-2022-2003. ISSN 1938-2545. S2CID 250360161.
- ↑ Saito, Natsu Taylor (2007). From Chinese Exclusion to Guantánamo Bay: Plenary Power and the Prerogative State. University Press of Colorado. ISBN 978-0-87081-851-6.
- ↑ Meierhenrich, Jens (2008). The Legacies of Law: Long-Run Consequences of Legal Development in South Africa, 1652–2000. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-47517-4.
- ↑ Costa, Pietro (2022). "The Fascist Regime between 'Law' and 'Politics': A Case of 'Dual State'?". Giornale di Storia Costituzionale. 43: 93.
- ↑ Pils, Eva (2014). China's Human Rights Lawyers: Advocacy and Resistance. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-45068-8.
- ↑ Fu, Hualing (2022). "Between the Prerogative and the Normative States: The Evolving Power to Detain in China's Political-Legal System". The Law & Ethics of Human Rights. 16 (1): 61–97. doi:10.1515/lehr-2022-2006. ISSN 1938-2545. S2CID 250360175.
- ↑ Sakwa, Richard (2010). "The revenge of the Caucasus: Chechenization and the dual state in Russia". Nationalities Papers. 38 (5): 601–622. doi:10.1080/00905992.2010.498468. S2CID 154320723.
- ↑ Sakwa, Richard (2010). The Crisis of Russian Democracy: The Dual State, Factionalism and the Medvedev Succession. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-76842-9.
- ↑ Sakwa, Richard (2010). "The Dual State in Russia". Post-Soviet Affairs. 26 (3): 185–206. doi:10.2747/1060-586X.26.3.185. S2CID 144025460.